Installation Instructions Part 2
19
Chapter 7: Using the WLAN Monitor for Windows 98SE, Me, and 2000
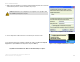
Link Information
Wireless-B USB Network Adapter
Wireless Network Status
Status - The status of the wireless network connection.
SSID - The SSID of the wireless network.
Network Mode - The wireless mode currently in use.
Transfer Rate - The data transfer rate of the current connection.
Channel - The channel to which the wireless network devices are set.
WEP - The status of the WEP encryption security feature.
MAC - The MAC address of the wireless network’s access point.
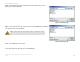
TCP/IP Setting
IP Address - The IP Address of the Adapter.
Subnet Mask - The Subnet Mask of the Adapter.
Default Gateway - The Default Gateway address of the Adapter.
DNS - The DNS address of the Adapter.
DHCP - The status of the DHCP client.
Save to Profile - Click the Save to Profile button to save the current settings in a configuration profile. Then the
Create connection profile screen will appear. Enter a name for the new profile, and click the OK button.
Click the Back button to return to the initial
Link Information screen.
Click the X (Close) button in the upper right corner to exit the WLAN Monitor.
dhcp: a networking protocol that allows administrators to
assign temporary IP addresses to network computers by
"leasing" an IP address to a user for a limited amount of
time, instead of assigning permanent IP addresses.
default gateway: a device that forwards
Internet traffic from your local area network.
Figure 7-3: More Link Information
dns: the IP address of your ISP's server, which
translates the names of websites into IP addresses.
ip address: the address used to identify a
computer or device on a network.
subnet mask: an address code that
determines the size of the network.