User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Labeling of the End Product
- Integration Note
- Using This Guide
- Introduction
- Configuration Using DeviceInstaller
- Server Configuration
- WLAN Configuration
- Host List Configuration
- OEM Pin Configuration
- Channel 1 and Channel 2 Configuration
- Email Configuration
- Accessing WiPort using Web-Manager
- Host List Configuration
- Channel 1 and Channel 2 Configuration
- Email Configuration
- WLAN Configuration
- OEM Pin Configuration
- Updating Settings
- Configuration via Serial Mode or Telnet Port
- Configurable Pins
- Monitor Mode
- Updating Firmware
- Troubleshooting
Configuration using Web-Manager
26 WiPort™ User Guide
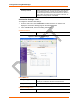
Figure 4-5. Channel Serial Settings
2. In the available fields, enter the following information:
Channel 1
Disable Serial Port Available on Channel 1 settings only. When selected,
disables communication through the serial port.
Port Settings
Protocol Select the protocol type from the pull down menu for the
selected channel. RS-422/485 4-wire and RS-485 2-wire
options are available on the WiPort-485 only.
Flow Control Flow control manages data flow between devices in a network
to ensure it is processed efficiently. Too much data arriving
before a device is prepared to manage it causes lost or
retransmitted data.
Baud Rate The unit and attached serial device, such as a modem, must
agree on a speed or baud rate to use for the serial connection.
Valid baud rates are 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600
(default), 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400, 460800, or
921600.
Data Bits
Indicates the number of bits in a transmitted data package.
Parity Checks for the parity bit. The default is None.
Stop Bits The stop bit follows the data and parity bits in serial
communication. It indicates the end of transmission.