User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 1.1 Features
- 1.2 Installation Guide
- 1.3 Accessories
- 2. Installation
- 2.1 Unpacking
- 2.2 Driver Installation
- 2.3 Hardware Installation
- 2.4 Device Setup & Configuration
- 2.5 Device Testing
- 3. Signal Connections
- 3.1 Overview
- 3.2 I/O Connector
- 3.3 Analog Input Connections
- 3.4 Analog Output Connections
- 3.5 Field Wiring Considerations
- 4. Software Overview
- 4.1 Programming Choices
- 4.2 DLL Driver Programming Roadmap
- 5. Principles of Operation
- 5.1 Analog Input Features
- 5.2 Analog Output Features
- 5.3 Digital I/O Features
- 5.4 Counter/Timer Features
- 6. Calibration
- 6.1 VR Assignment
- 6.2 A/D Calibration
- 6.3 D/A Calibration
- 6.4 Calibration Utility
- Appendix A. Specification
- Appendix B. Block Diagram
- Appendix C. Screw-terminal Board
- C. 1 Introduction
- C. 2 Features
- C. 3 Board Layout
- C.4 Pin Assignment
- C.5 Single-ended Connections
- C.6 Differential Connections
- Appendix D. Register Structure and Format
- D.1 Overview
- D.2 I/O Port Address Map
- D.3 A/D Single Value Acquisition - Write BASE+0
- D.4 Channel and A/D data - Read BASE + 0
- D.5 A/D Channel Range Setting - Write BASE+2
- D.6 MUX Control - Write BASE+4
- D.7 A/D Control/Status Register - Write/Read BASE+6
- D.8 Clear interrupt and FIFO - Write BASE+8
- D. 9 Interrupt and FIFO status - Read BASE+8
- D.10 D/A control/status register - Write/Read BASE+A
- D.11 D/A Channel 0/1 Data - Write BASE+C/E
- D.12 82C54 Counter Chip 0 - Write/Read BASE+10 to 16
- D.13 82C54 counter chip 1 - Write/Read BASE+18 to 1E
- D.14 Counter gate and clock control/status - Write/ Read BASE+20 to 26
- D.15 Digital I/O registers - Write/Read BASE+28
- D.16 Digital I/O configuration registers - Write/Read BASE+2A
- D.17 Calibration command registers - Write BASE+2C
- D.18 D/A Channel Data for Continuous Output Operation Mode - Write BASE+30
- Figures
- Figure 2-1: The Setup Screen of Advantech Automation Software
- Figure 2-2: Different options for Driver Setup
- Figure 2-3: The device name listed on the Device Manager
- Figure 2-4: The Advantech Device Installation utility program
- Figure 2-5: The I/O Device Installation dialog box
- Figure 2-6: The "Device(s) Found" dialog box
- Figure 2-7: The Device Setting dialog box
- Figure 2-8: The Device Name appearing on the list of devices box
- Figure 2-9: Analog Input tab on the Device Test dialog box
- Figure 2-10: Analog Input tab on the Device Test dialog box
- Figure 2-11: Analog Output tab on the Device Test dialog box
- Figure 2-12: Digital Input tab on the Device Test dialog box
- Figure 2-13: Digital Output tab on the Device Test dialog box
- Figure 2-14: Digital output tab on the Device Test dialog box
- Figure 3-1: I/O connector pin assignments for the PCI-1712/1712L
- Figure 3-2: Single-ended input channel connection
- Figure 3-3: Differential input channel connection - ground reference signal source
- Figure 3-4: Differential input channel connection - floating signal source
- Figure 3-5: Analog output connections
- Figure 5-1: Post-Trigger Acquisition Mode
- Figure 5-2: Delay-Trigger Acquisition Mode
- Figure 5-3: About-Trigger Acquisition Mode
- Figure 5-4: Pre-Trigger Acquisition Mode
- Figure 5-5: PCI-1712/1712L Sample Clock Source
- Figure 5-6: Frequency measurement
- Figure 6-1: PCI-1712/1712L VR1 & TP5
- Figure 6-2: Selecting the device you want to calibrate
- Figure 6-3: Warning message before start calibration
- Figure 6-4: Auto A/D Calibration Dialog Box
- Figure 6-5: A/D Calibration Procedure 1
- Figure 6-6: A/D Calibration Procedure 2
- Figure 6-7: A/D Calibration Procedure 3
- Figure 6-8: A/D Calibration is finished
- Figure 6-9: Range Selection in D/A Calibration
- Figure 6-10: Calibrating D/A Channel 0
- Figure 6-11: Calibrating D/A Channel 1
- Figure 6-12: D/A Calibration is finished
- Figure 6-13: Selecting Input Rage in Manual A/D Calibration panel
- Figure 6-14: Adjusting registers
- Figure 6-15: Selecting D/A Range and
- Figure 6-16: Selecting D/A Range and Choosing Output Voltage
- Figure 6-17: Adjusting registers
- Figure C-1: PCLD-8712 board layout
- Figure C-2: CN2 pin assignments for the PCLD-8712
- Tables
- Table 3-1: I/O Connector Signal Description (Part 1)
- Table 3-1: I/O Connector Signal Description (Part 2)
- Table 3-1: I/O Connector Signal Description (Part 3)
- Table 5-1: Gains and Analog Input Range
- Table 5-2: Analog Input Data Format
- Table 5-3: The corresponding Full Scale values for various Input Voltage Ranges
- Table 5-4: Analog Output Data Format
- Table 5-5: The corresponding Full Scale values for various Output Voltage Ranges
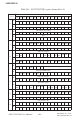
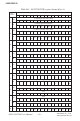
- Table D-1: PCI-1712/1712L register format (Part 1)
- Table D-1: PCI-1712/1712L register format (Part 2)
- Table D-1: PCI-1712/1712L register format (Part 3)
- Table D-2: Register for channel number and A/D data
- Table D-3: Register for A/D channel range setting
- Table D-4: Gain Codes for the PCI-1712/1712L
- Table D-5: Register for multiplexer control
- Table D-6: Register for A/D control/status
- Table D-7: Analog Input Acquisition Mode
- Table D-8: Register for clear interrupt and FIFO
- Table D-9: Register for interrupt and FIFO status
- Table D-10: Register for D/A control
- Table D-11: Analog output operation mode
- Table D-12: Register for D/A channel 0/1 data
- Table D-13: Register for 82C54 counter chip 0
- Table D-14: Register for 82C54 counter chip 1
- Table D-15: Register for counter gate and clock control/status
- Table D-16 : Table of Cn1 to Cn0 register
- Table D-17: Table of Gn1 to Gn0 register
- Table D-18: Table for CLK_SEL1 to CLK_SEL0 register
- Table D-19: Register for Digital I/O
- Table D-20: Register for digital I/O configuration
- Table D-21: Register for digital I/O configuration
- Table D-22: Register for calibration command
- Table D-23: Calibration command
- Table D-24: Register for D/A channel data

– 79 –
APPENDIX D
PCI-1712 User’s Manual
Advantech Co., Ltd.
www.advantech.com
Appendix
D
D. Register Structure and Format
D.1 Overview
The PCI-1712/1712L is delivered with an easy-to-use 32-bit DLL driver
for user programming under Windows 95/98/NT operating system. We
dvise users to program the PCI-1712/1712L using 32-bit DLL driver
provided by Advantech to avoid the complexity of low-level program-
ming by register.
The most important consideration in programming the PCI-1712/1712L
at the register level is to understand the function of the card’s regis-
ters. The information in the following sections is provided for users
who would like to do their own register-level programming.
D.2 I/O Port Address Map
The PCI-1712/1712L requires 50 consecutive addresses in the PC’s I/O
space. The address of each register is specified as an offset from the
card’s base address. For example, BASE+0 is the card’s base address
and BASE+8 is the base address plus eight bytes. The following
sections give the detailed information about register layout, and also
the detailed information about each register or driver and its address
relative to the card’s base address.
Table D-1 shows the function of each register or driver and its address
relative to the card’s base address.
Note
✎ All base address is in hexadecimal in Appendix D.
✎ Users have to use a 16-bit (word) I/O command to read/write each
register.