User manual
Table Of Contents
6 ALT-A02/PLT-A01-BA-e-1310
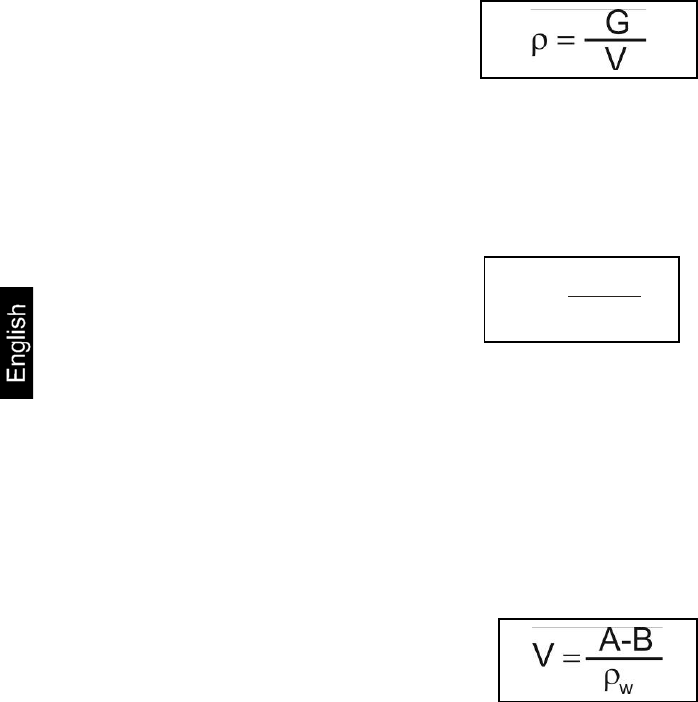
ρ =
V
A-B
Determining density of liquids
The density of a liquid is determined with the help of a sinker providing a known
volume [ V ]. The sinker is weighed in air [ A ] as well as in the test liquid [ B ].
According to the Archimedes’ Principle a body immersed in a liquid experiences a
force of buoyancy [ G ]. This force equals the weight force of the liquid displaced by
the volume of the body.
The volume [ V ] of the immersed body equals the volume of the displaced liquid.
G = buoyancy of sinker
Buoyancy of sinker =
Weight of the sinker in air [ A ] - weight of sinker in test liquid [ B ]
From this follows:
ρ = density of sample liquid
A = weight of sinker in air
B = weight of the sinkers in test liquid
V = volume of sinker*
* If the volume of the sinker is unknown, this can be determined by a solid body
density measurement e.g. in water and be calculated as follows.
V = volume of sinker
A = weight of sinker in air
B = weight of sinker in water
ρ
W
= density of water
2.1 Influencing magnitudes and error sources
Air pressure
Temperature
Volume deviation of the sinker
Surface tension of the liquid
Air bubbles
Immersion depth of the sample dish or of the sinker
Porosity of the solid










