User Guide
18 Kaspersky Anti-Spam 2.0 Enterprise Edition / ISP Edition
Irrespective of the peculiarities of a particular client module, the interaction
between the client and the main module of Kaspersky Anti-Spam, filtering server,
is implemented the same way, using internal data exchange protocol via a
network or a local socket.
The filtering server responses to the clients' requests, receives messages
subject to processing from them and returns results back to the clients.
If the standard installation procedure has been selected, the mail system with the
integrated client module and filtering server will be installed on the same
computer.
However, it is possible to install Kaspersky Anti-Spam filtering server on a
separate server: in this case clients running on a different computer (server), will
exchange data with the filtering server via the local area network using TCP
protocol.
If the filtering server is running on a dedicated computer, it is capable of servicing
several mail servers at the same time provided that this computer has sufficient
power to process the combined mail traffic.
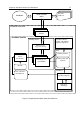
The structure of the filtering server includes:
• the filtering service that checks messages;
• licensing service that checks the availability and the validity of the key
file and works with the list of licensed mail addresses;
• automatic filtering database download and compile script;
• WebConfigurator;
• auxiliary applications and scripts.
The operation of the filtering service is controlled by the master process (ap-
process-server), that:
• keeps track of requests for connection to the filtering process received
from the clients;
• if there are no free processes available, it starts new processes;
• keeps track of the statuses of the running processes (free/busy);
• once a signal (e.g. SIGHUP) is received, it transfers such signal to a
child process.
When the mail traffic is extensive, the number of running filtering processes may
reach several dozens. When the load on the mail system decreases, free filtering
processes will be stopped. The minimum and the maximum number of filtering
processes running at the same time are determined by the settings specified in
the master process configuration file (see para A.1.2, page 94).