manual
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Scope
- Design Considerations—Connectivity at the Branch Office
- Branch-Office Connectivity over IPsec VPN
- Design Recommendations
- Routing Information Protocol
- Traffic Load Balancing for Type B and Type C Branch Deployments
- Using Border Gateway Protocol for Large Networks
- Using OSPF for Small Number of Branch Offices
- Using Auto Connect VPN to Create Branch-to-Branch IPsec Tunnels
- High Availability for the Branch Office
- High Availability Requirement Levels (Link, Device, Device, and Link Levels)
- High Availability Functionalities
- High Availability for Branch Office Type A
- VPN Security Zone Configuration for Type A
- High Availability for Branch Office Type B
- Using Secure Services Gateway for Type B
- High Availabilty for Branch Office Type C
- Connectivity at the Data Center
- Implementing a High Availability Enterprise Network at the Data Center
- Quality of Service Design Requirements
- WX Design Requirements
- Summary
- Appendix A Related Documents
- Appendix B Naming Conventions
- Appendix C Products
- About Juniper Networks
- Figure 1: Connecting branch offices, campus locations, and data centers over a single converged network
- Figure 2: Branch office reference architecture
- Figure 3: Multi-tiered/layered network architecture
- Figure 4: Two-tier network design for data centers
- Figure 5: Branch with dual internet connections (load balancing using ECMP)
- Figure 6: BGP routing design
- Figure 7: Star topology – connecting branches to central hub
- Figure 8: AC VPN provisioned tunnels between branches in the same region
- Figure 9: Multi-tier topology
- Figure 10: HA configuration for Type A
- Figure 11: VPN security zone configuration for Type A
- Figure 12: Type B optimized – HA configuration
- Figure 13: Type B – security zones
- Figure 14: Type C – HA configuration
- Figure 15: Intra-branch using OSPF
- Figure 16: Branch Type C – security zones
- Figure 17: Enterprise network for the data center
- Figure 18: M Series Multiservice Edge Routers
- Figure 19: Internet firewalls
- Figure 20: VPN firewalls
- Figure 21: VPN firewall IPS policy
- Figure 2: Branch office reference architecture
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc. 21
APPLICATION NOTE - Branch Office Connectivity Guide
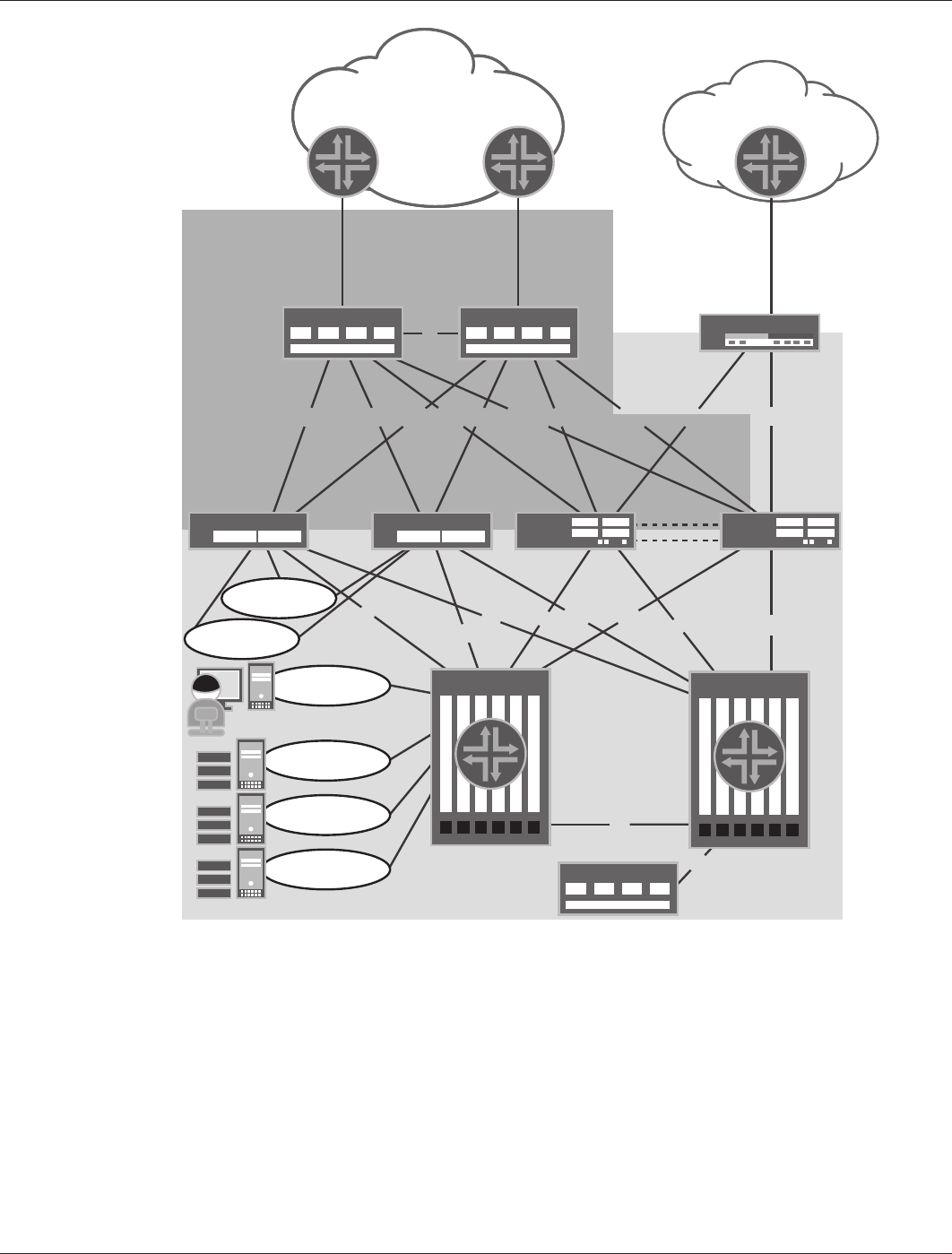
Figure 17: Enterprise network for the data center
Internet Connectivity
The Internet connectivity design (Figure 18 and Figure 19) consists of the following major components:
• Internet Connections
• BGP/EBGP
• Edge Routers
ISP C ISP B
J Series (A)
Io0.0
172.18.8.160
M Series (B)
Io0.0
172.18.8.41
M Series (A)
Io0.0
172.18.8.40
INTERNET
PROVIDER WAN
SSG
Series (B)
loopback.1
172.18.8.43
SSG Series (A)
loopback.1
172.18.8.42
ISG
Series (E)
loopback.10
172.18.8.161
ISG Series (F)
loopback.10
172.18.8.163
AREA 1
AREA 0
DATA CENTER A
1
Shared
Services
Switch (B)
Shared
Services
Switch (A)
M Series (E)
1
5
5 500 10 5 1000 500 10 1000 5000 5000
500
10
5
1000
500
10
1000
ethernet4/1-HA
ethernet4/2-HA
600
VRF 40
Router-ID
172.16.255.251
VRF 40
Router-ID
172.16.255.252
1.253.0.1/30 1.254.0.1/30
172.18.32.1/30
NOC-OBM
e2/0:1-192.168.3.135/24
OSPF-Passive
NOC-OBM
e2/0:1-192.168.4.1/24
OSPF-Passive
Client VLAN2000
IXIA J-IMIX
HSRP-172.18.10.1/24
Servers VLAN2002
Reflector
HSRP-172.18.12.1/24
Server VLAN2001
IXIA J-eMIX
HSRP-172.18.11.1/24
Servers VLAN2003
Real Servers
HSRP-172.18.13.1/24










