User Manual
Deviation User Manual for Jumper T8SG, Release 5.0
88 Chapter 11. Advanced Topics
11.4 Swash Mixing
A swash-plate is used to control flight on an RC helicopter. The swash-plate controls the plane of rotation
of the main-rotor as well as the blade pitch. A swash plate is normally connected to 3 servos known as
Elevator, Aileron, and Collective, but due to its design, there is not a 1-to-1 correspondence between stick-
movement and the servo movement. Instead some mixing is necessary between the throttle, elevator and
aileron sticks and the swash-plate servos. This mixing is known as cyclic Collective Pitch Mixing (CCMP).
Traditionally, RC helicopters have used a flybar above or below the main rotor attached to a series of
linkages to maintain stability. In these setups, the transmitter will normally do all of the mixing, and directly
drive each of the 3 swash-plate servos. This configuration is known as manual-CCPM (mCCPM).
Alternatively, an electronic mixer can be included on the helicopter either as part of the receiver, or
between the receiver and servos, that can implement the proper mixing. This configuration is known as
electronic CCPM (eCCPM) and in this case, the transmitter directly supplies aileron, elevator, and collective
inputs, and the electronic mixer will convert the signals into appropriate swash-plate servo motion.
Recently, flybarless (FBL) helicopters have become more common, especially in the micro size range. These
helicopters use an eCCPM system along with an electronic gyroscope to continuously adjust the
swashplate to maintain stability without the need for a physical flybar. This setup tends to be less expensive
to manufacture, and also provides better stability and more precise control.
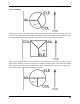
Deviation provides control for several swash-plate layouts, these include: 120°, 120° Alternate, 140°, 90°,
and None. Each of these options are illustrated below:
120 (3 Servo): Servos are placed around the swash-plate at 120° intervals. With Aileron input, the aileron
and pitch servos tilt the swash-plate left and right; with Elevator input, the three servos tilt the swash-
plate fore and aft; with Pitch input, all three servos raise the swash-plate up and down. Servos working in
unison dramatically increases the torque available as well as the precision and centering.