Operating Manual Owner manual
Table Of Contents
- Operating overview
- 1 Brief description
- 2 Identifying the device version
- 3 Mounting
- 4 Electrical connection
- 5 Startup of the device
- 5.1 Display and control elements
- 5.2 Setting the display after device is switched on
- 5.3 Selecting and editing parameters (plausibility requirement for input values)
- 5.4 Canceling edit
- 5.5 Acknowledging alarms using the reset key (for temperature limiter STB only)
- 5.6 Acknowledgement of alarms using the binary input (for temperature limiter STB only)
- 5.7 Functional test
- 5.8 Seal device
- 6 Safety Manual
- 6.1 Brief description
- 6.2 Safety temperature monitor (STW)
- 6.3 Safety temperature limiter (STB)
- 6.6 Connection possibilities of the sensors (SIL)
- 6.7 Standards and definitions
- 6.8 Safety-related parameters related to the temperature monitoring unit
- 6.9 Determining the Safety Integrity Level (SIL)
- 6.10 Determining the achieved Performance Level (PL)
- 6.12 Performance Level
- 6.13 Relationship between the Performance Level (PL) and the Safety Integrity Level (SIL)
- 6.14 Other applicable device documentation
- 6.15 Behavior during operation and in the event of a fault
- 6.16 Regular tests
- 6.17 Intrinsic safety according to DIN EN 60079-11
- 6.18 Monitoring of potential ignition sources according to DIN EN 50495 and DIN EN 13463- 6
- 6.19 Certificates
- 7 ATEX
- 7.1 Intended use
- 7.2 Identification markings according to ATEX directive 94/9/EC:
- 7.3 Meaning of the letter X in the type test certificate
- 7.4 Associated intrinsically safe electrical apparatus according to EN 60079-11
- 7.5 Safety device according to EN 50495
- 7.5.1 Temperature monitoring unit based on ignition protection "e" – increased safety according to EN 60079-7
- 7.5.1.1 Function of increased safety
- 7.5.1.2 Application in the 1-sensor variant
- 7.5.1.3 Application in the 2-sensor variant
- 7.5.1.4 Application of temperature transmitters
- 7.5.2 Minimum overpressure monitoring for static pressurized enclosure on the basis of ignition protection "p", pressurized enclosure according to EN 60079-2
- 7.5.2.1 Function of the static pressurized enclosure
- 7.5.2.2 Safety device for static pressurized enclosure
- 7.5.2.3 Application as safety device for static pressurized enclosure
- 7.6 Monitoring of potential ignition sources "b" according to EN 13463-6
- 8 Configuration level
- 9 Technical data
- 9.1 Analog inputs
- 9.2 Analog output
- 9.3 Binary input
- 9.4 Relay outputs
- 9.5 Measuring circuit monitoring
- 9.6 Voltage supply
- 9.7 Test voltages according to EN 60730, Part 1
- 9.8 Electrical safety
- 9.9 Environmental influences
- 9.10 Case
- 9.11 Approvals/approval marks
- 9.12 Important information for the probes in Chapter 9.13 to Chapter 9.15
- 9.13 Probes for the operating medium air
- 9.14 Probes for water and oil
- 9.15 Probes for air, water, and oil
- 10 Setup program
- 11 Alarm messages
- 12 Error messages
- 13 What to do, if ...
- 14 Information for devices with extra code 062 GL
- 15 Behavior of outputs
6 Safety Manual
2013-04-01
34
Important information:
Variants 1 to 4 were evaluated with JUMO probes according to data sheets 901006 and 902006. For variant 5 no sensor sys-
tem was included (only the JUMO safetyM STB/STW Ex). In this case, the plant operator selects the sensor system. For this
reason, the plant operator is responsible for evaluating the achievable SIL.
If the used SIL-capable sensor consists of hardware and software (e.g. transmitter), the maximum SIL that can be achieved –
irrespective of the architecture – is the one according to which the sensor software was developed (so, for example, if the sen-
sor software has SIL2, the max. achievable SIL is 2).
The possibility of connecting passive sensors such as dual thermocouples or Pt100/1000 sensors means that the sensors do
not necessarily require an SIL qualification. In this case, the specification of the failure rates for the passive sensors is sufficient
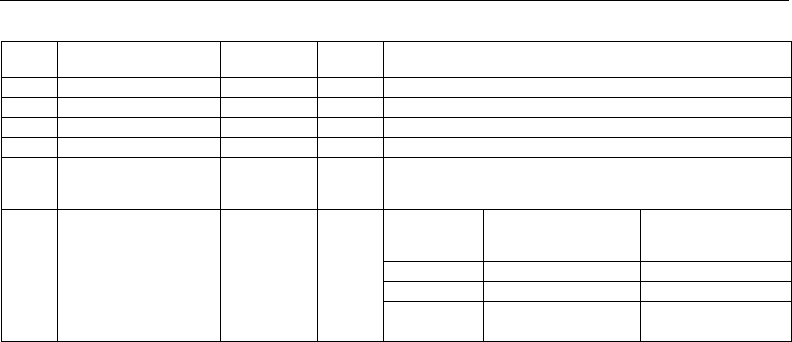
Table 1: Achievable SIL
Variant Connected sensors Sensor system
architecture
Logic ar-
chitecture
Achievable SIL
1 1x Pt100 2-wire circuit 1oo1 1oo2D SIL2
1a 2x Pt100/1000 2-wire circuit 1oo2 1oo2D SIL3
2 2x Pt100/1000 3-wire circuit 1oo2 1oo2D SIL3
3 2x thermocouple 1oo2 1oo2D SIL3
4 1x Pt100/1000 2-wire + 3-
wire circuit
1x thermocouple
1oo2 1oo2D SIL3
5 STB/STW 701155 without
sensor system 1oo2D archi-
tecture
No probe or use of 4 to
20 mA
This means the sensor is not
taken into account in the cal-
culation.
Sensors con-
nected by the
plant operator;
architecture
acc. to connec-
tion 1oo1 or
1oo2
1oo2D SIL of the used
sensor (HW only)
Max. achievable SIL of the
system with 1oo1 sensor
system architecture
Max. achievable SIL of the
system with 1oo2 sensor
system architecture
SIL1 SIL1 SIL2
SIL2 SIL2 SIL3
SIL3 SIL3 SIL3










