Intel Xeon processor LV Thermal Design Guide
Dual-Core Intel
®
Xeon
®
processor LV and ULV
August 2006 Thermal Design Guide
311374-002 21
Thermal Solution Requirements
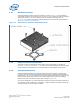
Ψ
SA
is a measure of the thermal characterization parameter from the bottom of the
heatsink to the local ambient air. Ψ
SA
is dependent on the heatsink material, thermal
conductivity, and geometry. It is also strongly dependent on the air velocity through
the fins of the heatsink. Figure 11 illustrates the combination of the different thermal
characterization parameters.
Example 1. Calculating the Required Thermal Performance for Dual-Core Intel
®
Xeon
®
processor LV
The cooling performance, Ψ
JA,
is defined using the thermal characterization parameter:
• Define a target component temperature T
JUNCTION
and corresponding TDP.
• Define a target local ambient temperature, T
LA
.
The following provides an example of how you might determine the appropriate
performance targets.
Assume:
•TDP = 31 W and T
JUNCTION
= 100 °C
• Local processor ambient temperature, T
LA
= 40 °C.
Then the following could be calculated using Equation 1 for the given processor
frequency:
To determine the required heatsink performance, a heatsink solution provider would
need to determine Ψ
JS
performance for the selected TIM and mechanical load
configuration. If the heatsink solution were designed to work with a TIM material
performing at Ψ
TIM
≤ 1.0 °C/W, solving from Equation 2, the performance needed from
the heatsink is:
Figure 11. Processor Thermal Characterization Parameter Relationships
T
S
T
J
T
A
Ψ
SA
Ψ
Ψ
TIM
Device
T
S
T
A
Ψ
SA
Ψ
TIM
Ψ
JA
HEATSINK
W
C
TDP
TT
LAJ
JA
o
94.1
31
40100
=
−
=
−
=Ψ
W
C
TIMJASA
o
94.000.194.1 =−=Ψ−Ψ=Ψ