64-bit Intel Xeon Processor with 2MB L2 Cache Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
Processor Thermal Management Logic and Thermal Monitor Features
70 64-bit Intel® Xeon™ Processor with 2MB L2 Cache Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
temperature. By comparing this current with the reference current, the processor temperature can
be determined. The reference current source corresponds to the diode current when at the
maximum permissible processor operating temperature. Processors are calibrated during
manufacturing on a small sample set. Once configured, the processor temperature at which the
PROCHOT# signal is asserted (trip point) is not re-configurable.
The PROCHOT# signal is available internally to the processor as well as externally. External
indication of the processor temperature status is provided through the bus signal PROCHOT#.
When the processor temperature reaches the trip point, PROCHOT# is asserted. When the
processor temperature is below the trip point, PROCHOT# is de-asserted. Assertion of the
PROCHOT# signal is independent of any register settings within the processor. It is asserted any
time the processor die temperature reaches the trip point. The point where the TCC activates is set
to the same temperature at which the processor is tested and at which PROCHOT# asserts.
The TCC portion of the Thermal Monitor must be enabled for the processor to operate within
specifications. The Thermal Monitor’s TCC, when active, lowers the processor temperature by
reducing the power consumed by the processor. This is done by changing the duty cycle of the
internal processor clocks, resulting in a lower effective frequency. When active, the TCC turns the
processor clocks off and then back on with a predetermined duty cycle. The duty cycle is processor
specific, and is fixed for a particular processor. The maximum time period the clocks are disabled
is ~3 µs, and is frequency dependent. Higher frequency processors will disable the internal clocks
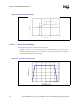
for a shorter time period. Figure E-2 illustrates the relationship between the internal processor
clocks and PROCHOT#.
Performance counter registers, status bits in model specific registers (MSRs), and the PROCHOT#
output pin are available to monitor and control the Thermal Monitor behavior. Details regarding the
use of these registers will be described in the
IA-32 Intel
®
Architecture Software Developer's
Manual Volume 3: System Programming Guide.
Figure E-1. Thermal Sensor Circuit