User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Revision History
- About This Publication
- 1. Product Description
- 2. Programming Models
- 3. Device Handling
- 4. Event Handling
- 5. Error Handling
- 6. Application Development Guidelines
- 7. Call Progress Analysis
- 7.1 Call Progress Analysis Overview
- 7.2 Call Progress and Call Analysis Terminology
- 7.3 Call Progress Analysis Components
- 7.4 Using Call Progress Analysis on DM3 Boards
- 7.5 Call Progress Analysis Tone Detection on DM3 Boards
- 7.6 Media Tone Detection on DM3 Boards
- 7.7 Default Call Progress Analysis Tone Definitions on DM3 Boards
- 7.8 Modifying Default Call Progress Analysis Tone Definitions on DM3 Boards
- 7.9 Call Progress Analysis Errors
- 7.10 Using Call Progress Analysis on Springware Boards
- 7.11 Call Progress Analysis Tone Detection on Springware Boards
- 7.12 Media Tone Detection on Springware Boards
- 7.13 Default Call Progress Analysis Tone Definitions on Springware Boards
- 7.14 Modifying Default Call Progress Analysis Tone Definitions on Springware Boards
- 7.15 SIT Frequency Detection (Springware Only)
- 7.15.1 Tri-Tone SIT Sequences
- 7.15.2 Setting Tri-Tone SIT Frequency Detection Parameters
- 7.15.3 Obtaining Tri-Tone SIT Frequency Information
- 7.15.4 Global Tone Detection Tone Memory Usage
- 7.15.5 Frequency Detection Errors
- 7.15.6 Setting Single Tone Frequency Detection Parameters
- 7.15.7 Obtaining Single Tone Frequency Information
- 7.16 Cadence Detection in Basic Call Progress Analysis (Springware Only)
- 8. Recording and Playback
- 8.1 Overview of Recording and Playback
- 8.2 Digital Recording and Playback
- 8.3 Play and Record Functions
- 8.4 Play and Record Convenience Functions
- 8.5 Voice Encoding Methods
- 8.6 G.726 Voice Coder
- 8.7 Transaction Record
- 8.8 Silence Compressed Record
- 8.9 Recording with the Voice Activity Detector
- 8.10 Streaming to Board
- 8.11 Pause and Resume Play
- 8.12 Echo Cancellation Resource
- 9. Speed and Volume Control
- 10. Send and Receive FSK Data
- 11. Caller ID
- 12. Cached Prompt Management
- 13. Global Tone Detection and Generation, and Cadenced Tone Generation
- 13.1 Global Tone Detection (GTD)
- 13.1.1 Overview of Global Tone Detection
- 13.1.2 Global Tone Detection on DM3 Boards versus Springware Boards
- 13.1.3 Defining Global Tone Detection Tones
- 13.1.4 Building Tone Templates
- 13.1.5 Working with Tone Templates
- 13.1.6 Retrieving Tone Events
- 13.1.7 Setting GTD Tones as Termination Conditions
- 13.1.8 Maximum Amount of Memory for Tone Templates
- 13.1.9 Estimating Memory
- 13.1.10 Guidelines for Creating User-Defined Tones
- 13.1.11 Global Tone Detection Application
- 13.2 Global Tone Generation (GTG)
- 13.3 Cadenced Tone Generation
- 13.3.1 Using Cadenced Tone Generation
- 13.3.2 How To Generate a Custom Cadenced Tone
- 13.3.3 How To Generate a Non-Cadenced Tone
- 13.3.4 TN_GENCAD Data Structure - Cadenced Tone Generation
- 13.3.5 How To Generate a Standard PBX Call Progress Signal
- 13.3.6 Predefined Set of Standard PBX Call Progress Signals
- 13.3.7 Important Considerations for Using Predefined Call Progress Signals
- 13.1 Global Tone Detection (GTD)
- 14. Global Dial Pulse Detection
- 14.1 Key Features
- 14.2 Global DPD Parameters
- 14.3 Enabling Global DPD
- 14.4 Global DPD Programming Considerations
- 14.5 Retrieving Digits from the Digit Buffer
- 14.6 Retrieving Digits as Events
- 14.7 Dial Pulse Detection Digit Type Reporting
- 14.8 Defines for Digit Type Reporting
- 14.9 Global DPD Programming Procedure
- 14.10 Global DPD Example Code
- 15. R2/MF Signaling
- 16. Syntellect License Automated Attendant
- 17. Building Applications
- Glossary
- Index
Voice API Programming Guide — June 2005 57
Call Progress Analysis
7.8 Modifying Default Call Progress Analysis Tone
Definitions on DM3 Boards
On DM3 boards, call progress analysis tones are maintained in the firmware on a physical board
level and are board-specific. More information on tone definitions is provided in the following
topics:
• API Functions for Manipulating Tone Definitions
• TONE_DATA Data Structure
• Rules for Modifying a Tone Definition on DM3 Boards
• Rules for Using a Single Tone Proxy for a Dual Tone
• Steps to Modify a Tone Definition on DM3 Boards
7.8.1 API Functions for Manipulating Tone Definitions
The following voice API functions are used to manipulate the default tone definitions shown in
Table 6, “Default Call Progress Analysis Tone Definitions (DM3)”, on page 57 and some, but not
all, of the default tone definitions shown in Table 5, “Special Information Tone Sequences (DM3)”,
on page 54.
Note: Default SIT definitions can be modified, except for the following SIT sequences: TID_SIT_ ANY,
TID_SIT_IO, TID_SIT_NC_INTERLATA, and TID_SIT_RO_INTERLATA.
dx_querytone( )
gets tone information for a specific call progress tone
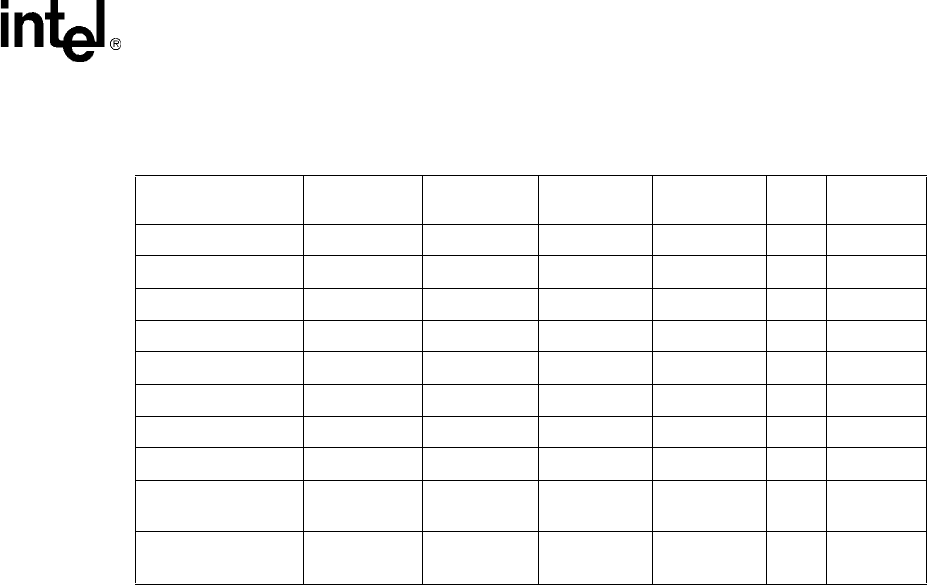
Table 6. Default Call Progress Analysis Tone Definitions (DM3)
Tone ID
Freq1
(in Hz)
Freq2
(in Hz)
On Time
(in 10 msec)
Off Time
(in 10 msec)
Reps
Twin Tone
Freq (Hz)
TID_BUSY1 450 - 510 590 - 650 30 - 100 30 - 100 2 0
TID_BUSY2 450 - 510 590 - 650 10 - 40 10 - 40 2 0
TID_DIAL_INTL 300 - 380 400 - 480 100 - 0 - 1 300 - 480
TID_DIAL_LCL 300 - 380 400 - 480 10 - 0 - 1 0
TID_DISCONNECT 360 - 410 430 - 440 30 - 60 30 - 60 1 360 - 440
TID_FAX1 1050 - 1150 - 10 - 60 - 1 -
TID_FAX2 2000 - 2300 - 10 - 0 - 1 -
TID_RNGBK1 350 - 550 350 - 550 75 - 300 0 - 800 1 350 - 550
TID_RNGBK2
(segment 0)
350 - 550 350 - 550 20 - 100 20 - 100 1 350 - 550
TID_RNGBK2
(segment 1)
350 - 550 350 - 550 20 - 100 100 - 600 1 350 - 550










