Intel RAID Controllers Alert Code Decoding White Paper
Intel® RAID Controllers: SAS Software Stack Appendix A
Revision 1.0
11
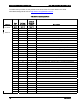
Table 4: CDB Commands Usage Matrix – Write (EXTENDED): (2AH)
bit→
↓byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0
2A
1
LUN Reserved
2
Logical Block Address (MSB)
3
Logical Block Address
4
Logical Block Address
5
Logical Block Address (LSB)
6
Reserved
7
Transfer Length (MSB)
8
Transfer Length (LSB)
9
Control
The WRITE command writes the consecutive data blocks transferred from the RAID controller,
as specified in the Transfer Length field, to the medium starting with the block address in the
Logical Block Address field.
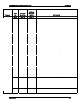
Table 5: CDB Commands Usage Matrix - Write and Verify (EXTENDED): (2EH)
bit→
↓byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0
2E
1
LUN Reserved BytChk 0
2
Logical Block Address (MSB)
3
Logical Block Address
4
Logical Block Address
5
Logical Block Address (LSB)
6
Reserved
7
Transfer Length (MSB)
8
Transfer Length (LSB)
9
Control
The WRITE AND VERIFY command writes the number of consecutive data blocks from the
RAID Controller specified in the Transfer Length field to the medium, starting with the block
address in the Logical Block Address field and verifies that the data is written correctly.
When the Byte Check (BytChk) bit is set to 0, the target device verifies the written data in the
medium using ECC. When the BytChk bit is set to 1, the target device performs a byte-by-byte