Technical Product Specification
Functional Architecture Intel® Server Boards S5000PSL and S5000XSL TPS
Revision 1.7
Intel order number: D41763-008
18
3.1.3 Memory Subsystem
The MCH masters four fully buffered DIMM (FBD) memory channels. FBD memory utilizes a
narrow high-speed frame-oriented interface referred to as a channel. The four FBD channels
are organized into two branches of two channels per branch. Each branch is supported by a
separate memory controller. The two channels on each branch operate in lock-step to increase
FBD bandwidth. The four channels are routed to eight DIMM sockets and are capable of
supporting registered DDR2-533 and DDR2-667 FBDIMM memory (stacked or unstacked). The
read bandwidth of each FBDIMM channel is 4.25 GB/s for DDR2-533 FBDIMM memory, which
gives a total read bandwidth of 17 GB/s for four DIMM channels. The read bandwidth of each
FBDIMM channel is 5.35 GB/s for DDR2-667 FBDIMM memory, which gives a total read
bandwidth of 21.4 GB/s for four DIMM channels.
On the Intel
®
Server Boards S5000PSL and S5000XSL, a pair of channels becomes a branch
where Branch 0 consists of channels A and B, and Branch 1 consists of channels C and D. FBD
memory channels are organized into two branches for support of RAID 1 (mirroring).
TP02299
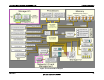
DIMM D2
DIMM D1
DIMM C2
DIMM C1
DIMM B2
DIMM B1
DIMM A2
DIMM A1
Branch 0
MCH
Channel A
Channel B
Channel D
Channel C
Branch 1
Figure 12. Memory Layout
To boot the system, the system BIOS on the server board uses a dedicated I
2
C bus to retrieve
DIMM information needed to program the MCH memory registers. The following table provides
the I
2
C addresses for each DIMM socket.
Table 3. I
2
C Addresses for Memory Module SMB
Device Address
DIMM A1 0xA0
DIMM A2 0xA2
DIMM B1 0xA0
DIMM B2 0xA2
DIMM C1 0xA0