S2600GZ and S2600GL
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Product Overview
- 3. Product Architecture Overview
- 3.1 Processor Support
- 3.2 Processor Functions Overview
- 3.2.1 Processor Core Features:
- 3.2.2 Supported Technologies:
- 3.2.3 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect
- 3.2.4 Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) and Memory Subsystem
- 3.2.4.1 Supported Memory
- 3.2.4.2 Memory Slot Identification and Population Rules
- 3.2.4.3 Publishing System Memory
- 3.2.4.4 Integrated Memory Controller Operating Modes
- 3.2.4.5 Memory RAS Support
- 3.2.5 Processor Integrated I/O Module (IIO)
- 3.3 Intel® C602 Chipset Functional Overview
- 3.4 Integrated Baseboard Management Controller Overview
- 4. System Security
- 5. Technology Support
- 6. Platform Management Functional Overview
- 6.1 Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) Firmware Feature Support
- 6.2 Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
- 6.3 Power Control Sources
- 6.4 BMC Watchdog
- 6.5 Fault Resilient Booting (FRB)
- 6.6 Sensor Monitoring
- 6.7 Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) Inventory Device
- 6.8 System Event Log (SEL)
- 6.9 System Fan Management
- 6.10 Messaging Interfaces
- 6.10.1 User Model
- 6.10.2 IPMB Communication Interface
- 6.10.3 LAN Interface
- 6.10.4 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- 6.10.5 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- 6.10.6 Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
- 6.10.7 Secure Shell (SSH)
- 6.10.8 Serial-over-LAN (SOL 2.0)
- 6.10.9 Platform Event Filter (PEF)
- 6.10.10 LAN Alerting
- 6.10.11 Alert Policy Table
- 6.10.12 SM-CLP (SM-CLP Lite)
- 6.10.13 Embedded Web Server
- 6.10.14 Virtual Front Panel
- 6.10.15 Embedded Platform Debug
- 6.10.16 Data Center Management Interface (DCMI)
- 6.10.17 Lightweight Directory Authentication Protocol (LDAP)
- 7. Advanced Management Feature Support (RMM4)
- 8. On-board Connector/Header Overview
- 9. Reset and Recovery Jumpers
- 10. Light Guided Diagnostics
- 11. Power Supply Specification Guidelines
- 11.1 Power Supply DC Output Connector
- 11.2 Power Supply DC Output Specification
- 11.2.1 Output Power/Currents
- 11.2.2 Standby Output
- 11.2.3 Voltage Regulation
- 11.2.4 Dynamic Loading
- 11.2.5 Capacitive Loading
- 11.2.6 Grounding
- 11.2.7 Closed loop stability
- 11.2.8 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby mode
- 11.2.9 Common Mode Noise
- 11.2.10 Soft Starting
- 11.2.11 Zero Load Stability Requirements
- 11.2.12 Hot Swap Requirements
- 11.2.13 Forced Load Sharing
- 11.2.14 Ripple/Noise
- 11.2.15 Timing Requirements
- 12. BIOS Setup Utility
- Table 60. BIOS Setup: Keyboard Command Bar
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Main Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Advanced Screen]
- Screen Field Descriptions:
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Processor Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Figure 44. Power & Performance Screen
- Back to [Power & Performance Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Figure 45. Memory Configuration Screen
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [Memory Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Figure 46. Memory RAS and Performance Configuration Screen
- Figure 47. Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen
- Screen Field Descriptions:
- One of these strings:
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- One of these strings:
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Names of Storage Modules supported at this time are:
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Mass Storage Controller Configuration Screen]
- Figure 48. PCI Configuration Screen
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Back to [PCI Configuration Screen] — [Advanced Screen]
- Figure 49. NIC Configuration Screen
- One of these strings:
- One of these strings:
- Figure 50. Serial Port Configuration Screen
- Back to [Serial Port Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Serial Port Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Serial Port Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Serial Port Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Serial Port Configuration Screen]
- Back to [Serial Port Configuration Screen]
- Figure 51. USB Configuration Screen
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Back to [USB Configuration Screen]
- Figure 52. System Acoustic and Performance Configuration
- Back to [System Acoustic and Performance Configuration]
- Back to [System Acoustic and Performance Configuration]
- Back to [System Acoustic and Performance Configuration]
- Back to [System Acoustic and Performance Configuration]
- Back to [System Acoustic and Performance Configuration]
- Figure 53. Security Screen
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Back to [Security Screen]
- Figure 54. Server Management Screen
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Server Management Screen]
- Figure 55. Console Redirection Screen
- Back to [Console Redirection Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Console Redirection Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Console Redirection Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Console Redirection Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Console Redirection Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [Console Redirection Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Figure 56. System Information Screen
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [System Information Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Figure 57. BMC LAN Configuration Screen
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Option Values: [Entry Field 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0 is default]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Option Values: [Entry Field 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0 is default]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Option Values: [Entry Field 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0 is default]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Option Values: [Entry Field 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0 is default]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Option Values: [Entry Field 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0 is default]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Option Values: [Entry Field 0.0.0.0, 0.0.0.0 is default]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Back to [BMC LAN Configuration Screen] — [Server Management Screen]
- Figure 58. Boot Options Screen
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Back to [Boot Options Screen]
- Figure 59. CDROM Order Screen
- Back to [CDROM Order Screen] — [Boot Options Screen]
- Figure 60. Hard Disk Order Screen
- Back to [Hard Disk Order Screen] — [Boot Options Screen]
- Figure 61. Floppy Order Screen
- Back to [Floppy Order Screen] — [Boot Options Screen]
- Figure 62. Network Device Order Screen
- Back to [Network Device Order Screen] — [Boot Options Screen]
- Figure 63. BEV Device Order Screen
- Back to [BEV Device Order Screen] — [Boot Options Screen]
- Figure 64. Add EFI Boot Option Screen
- Figure 65. Delete EFI Boot Option Screen
- Figure 66. Boot Manager Screen
- Back to [Boot Manager Screen]
- Back to [Boot Manager Screen]
- Figure 67. Error Manager Screen
- Back to [Error Manager Screen]
- Back to [Error Manager Screen]
- Back to [Error Manager Screen]
- Back to [Error Manager Screen]
- Figure 68. Save & Exit Screen
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Back to [Save & Exit Screen]
- Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips
- Appendix B: Integrated BMC Sensor Tables
- Appendix C: Management Engine Generated SEL Event Messages
- Appendix D: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
- Appendix E: POST Code Errors
- Appendix F: Supported Intel® Server Systems
Product Architecture Overview Intel® Server Board S2600GZ/GL TPS
Each memory slot on the server board is identified by channel and slot number within that channel. For
example, DIMM_A1 is the first slot on Channel A on processor 1; DIMM_E1 is the first DIMM socket on
Channel E on processor 2.
The memory slots associated with a given processor are unavailable if the corresponding processor
socket is not populated.
A processor may be installed without populating the associated memory slots provided a second
processor is installed with associated memory.
In this case, the memory is shared by the processors.
However, the platform suffers performance degradation and latency due to the remote memory.
Processor sockets are self-contained and autonomous. However, all memory subsystem support (such
as Memory RAS, Error Management,) in the BIOS setup are applied commonly across processor
sockets.
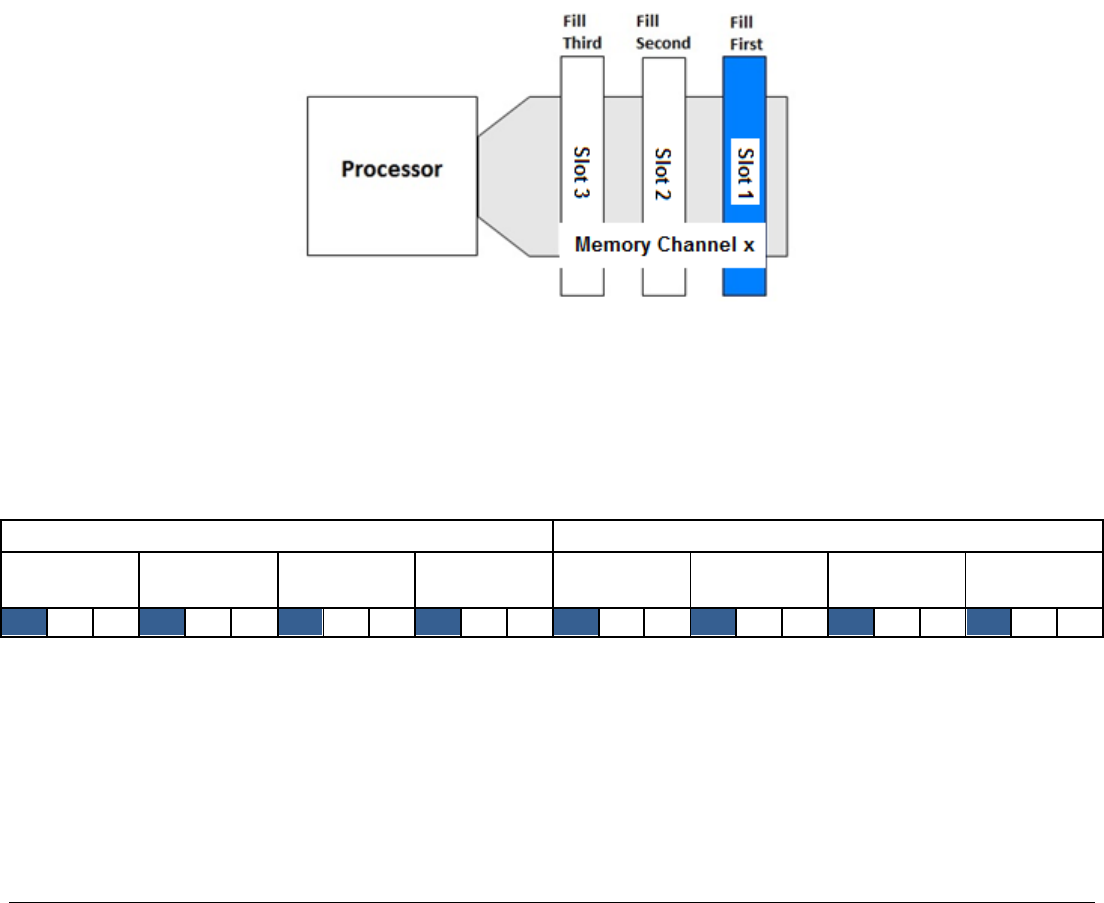
The BLUE memory slots on the server board identify the first memory slot for a given memory channel.
DIMM population rules require that DIMMs within a channel be populated starting with the BLUE DIMM slot or
DIMM farthest from the processor in a “fill-farthest” approach. In addition, when populating a Quad-rank DIMM
with a Single- or Dual-rank DIMM in the same channel, the Quad-rank DIMM must be populated farthest from
the processor. Note that Quad-rank DIMMs and UDIMMs are not allowed in three slots populated
configurations. Intel MRC will check for correct DIMM placement.
Figure 13. Memory Slots Definition
On the Intel
®
Server Board S2600GZ, a total of 24 DIMM slots is provided (2 CPUs – 4 Channels/CPU, 3
DIMMs/Channel). The nomenclature for memory slots is detailed in the following table:
Table 10. Intel
®
Server Board S2600GZ Memory Slot Identification
Processor Socket 1
Processor Socket 2
(0)
Channel A
(1)
Channel B
(2)
Channel C
(3)
Channel D
(0)
Channel E
(1)
Channel F
(2)
Channel G
(3)
Channel H
A1
A2
A3
B1
B2
B3
C1
C2
C3
D1
D2
D3
E1
E2
E3
F1
F2
F3
G1
G2
G3
H1
H2
H3
Revision 2.4
22










