User manual
Table Of Contents
- Intel® IXP2800 Network Processor
- Copyright
- Contents
- Introduction 1
- Technical Description 2
- 2.1 Overview
- 2.2 Intel XScale® Core Microarchitecture
- 2.3 Microengines
- 2.4 DRAM
- 2.5 SRAM
- 2.6 Scratchpad Memory
- 2.7 Media and Switch Fabric Interface
- 2.8 Hash Unit
- 2.9 PCI Controller
- 2.10 Control and Status Register Access Proxy
- 2.11 Intel XScale® Core Peripherals
- 2.12 I/O Latency
- 2.13 Performance Monitor
- Intel XScale® Core 3
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Features
- 3.3 Memory Management
- 3.4 Instruction Cache
- 3.5 Branch Target Buffer (BTB)
- 3.6 Data Cache
- 3.6.1 Overviews
- 3.6.2 Data Cache and Mini-Data Cache Operation
- 3.6.3 Data Cache and Mini-Data Cache Control
- 3.6.4 Reconfiguring the Data Cache as Data RAM
- 3.6.5 Write Buffer/Fill Buffer Operation and Control
- 3.7 Configuration
- 3.8 Performance Monitoring
- 3.9 Performance Considerations
- 3.9.1 Interrupt Latency
- 3.9.2 Branch Prediction
- 3.9.3 Addressing Modes
- 3.9.4 Instruction Latencies
- 3.9.4.1 Performance Terms
- 3.9.4.2 Branch Instruction Timings
- 3.9.4.3 Data Processing Instruction Timings
- 3.9.4.4 Multiply Instruction Timings
- 3.9.4.5 Saturated Arithmetic Instructions
- 3.9.4.6 Status Register Access Instructions
- 3.9.4.7 Load/Store Instructions
- 3.9.4.8 Semaphore Instructions
- 3.9.4.9 Coprocessor Instructions
- 3.9.4.10 Miscellaneous Instruction Timing
- 3.9.4.11 Thumb Instructions
- 3.10 Test Features
- 3.11 Intel XScale® Core Gasket Unit
- 3.12 Intel XScale® Core Peripheral Interface
- 3.12.1 XPI Overview
- 3.12.2 UART Overview
- 3.12.3 UART Operation
- 3.12.4 Baud Rate Generator
- 3.12.5 General Purpose I/O (GPIO)
- 3.12.6 Timers
- 3.12.7 Slowport Unit
- Microengines 4
- DRAM 5
- SRAM Interface 6
- SHaC - Unit Expansion 7
- Media and Switch Fabric Interface 8
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Receive
- 8.3 Transmit
- 8.4 RBUF and TBUF Summary
- 8.5 CSIX Flow Control Interface
- 8.6 Deskew and Training
- 8.7 CSIX Startup Sequence
- 8.8 Interface to Command and Push and Pull Buses
- 8.9 Receiver and Transmitter Interoperation with Framers and Switch Fabrics
- 8.9.1 Receiver and Transmitter Configurations
- 8.9.2 System Configurations
- 8.9.2.1 Framer, Single Network Processor Ingress and Egress, and Fabric Interface Chip
- 8.9.2.2 Framer, Dual Network Processor Ingress, Single Network Processor Egress, and Fabric Interface Chip
- 8.9.2.3 Framer, Single Network Processor Ingress and Egress, and CSIX-L1 Chips for Translation and Fabric Interface
- 8.9.2.4 CPU Complex, Network Processor, and Fabric Interface Chip
- 8.9.2.5 Framer, Single Network Processor, Co-Processor, and Fabric Interface Chip
- 8.9.3 SPI-4.2 Support
- 8.9.4 CSIX-L1 Protocol Support
- 8.9.5 Dual Protocol (SPI and CSIX-L1) Support
- 8.9.6 Transmit State Machine
- 8.9.7 Dynamic De-Skew
- 8.9.8 Summary of Receiver and Transmitter Signals
- PCI Unit 9
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 PCI Pin Protocol Interface Block
- 9.2.1 PCI Commands
- 9.2.2 IXP2800 Network Processor Initialization
- 9.2.3 PCI Type 0 Configuration Cycles
- 9.2.4 PCI 64-Bit Bus Extension
- 9.2.5 PCI Target Cycles
- 9.2.6 PCI Initiator Transactions
- 9.2.7 PCI Fast Back-to-Back Cycles
- 9.2.8 PCI Retry
- 9.2.9 PCI Disconnect
- 9.2.10 PCI Built-In System Test
- 9.2.11 PCI Central Functions
- 9.3 Slave Interface Block
- 9.4 Master Interface Block
- 9.5 PCI Unit Error Behavior
- 9.5.1 PCI Target Error Behavior
- 9.5.1.1 Target Access Has an Address Parity Error
- 9.5.1.2 Initiator Asserts PCI_PERR_L in Response to One of Our Data Phases
- 9.5.1.3 Discard Timer Expires on a Target Read
- 9.5.1.4 Target Access to the PCI_CSR_BAR Space Has Illegal Byte Enables
- 9.5.1.5 Target Write Access Receives Bad Parity PCI_PAR with the Data
- 9.5.1.6 SRAM Responds with a Memory Error on One or More Data Phases on a Target Read
- 9.5.1.7 DRAM Responds with a Memory Error on One or More Data Phases on a Target Read
- 9.5.2 As a PCI Initiator During a DMA Transfer
- 9.5.2.1 DMA Read from DRAM (Memory-to-PCI Transaction) Gets a Memory Error
- 9.5.2.2 DMA Read from SRAM (Descriptor Read) Gets a Memory Error
- 9.5.2.3 DMA from DRAM Transfer (Write to PCI) Receives PCI_PERR_L on PCI Bus
- 9.5.2.4 DMA To DRAM (Read from PCI) Has Bad Data Parity
- 9.5.2.5 DMA Transfer Experiences a Master Abort (Time-Out) on PCI
- 9.5.2.6 DMA Transfer Receives a Target Abort Response During a Data Phase
- 9.5.2.7 DMA Descriptor Has a 0x0 Word Count (Not an Error)
- 9.5.3 As a PCI Initiator During a Direct Access from the Intel XScale® Core or Microengine
- 9.5.3.1 Master Transfer Experiences a Master Abort (Time-Out) on PCI
- 9.5.3.2 Master Transfer Receives a Target Abort Response During a Data Phase
- 9.5.3.3 Master from the Intel XScale® Core or Microengine Transfer (Write to PCI) Receives PCI_PERR_L on PCI Bus
- 9.5.3.4 Master Read from PCI (Read from PCI) Has Bad Data Parity
- 9.5.3.5 Master Transfer Receives PCI_SERR_L from the PCI Bus
- 9.5.3.6 Intel XScale® Core Microengine Requests Direct Transfer when the PCI Bus is in Reset
- 9.5.1 PCI Target Error Behavior
- 9.6 PCI Data Byte Lane Alignment
- Clocks and Reset 10
- 10.1 Clocks
- 10.2 Synchronization Between Frequency Domains
- 10.3 Reset
- 10.4 Boot Mode
- 10.5 Initialization
- Performance Monitor Unit 11
- 11.1 Introduction
- 11.2 Interface and CSR Description
- 11.3 Performance Measurements
- 11.4 Events Monitored in Hardware
- 11.4.1 Queue Statistics Events
- 11.4.2 Count Events
- 11.4.3 Design Block Select Definitions
- 11.4.4 Null Event
- 11.4.5 Threshold Events
- 11.4.6 External Input Events
- 11.4.6.1 XPI Events Target ID(000001) / Design Block #(0100)
- 11.4.6.2 SHaC Events Target ID(000010) / Design Block #(0101)
- 11.4.6.3 IXP2800 Network Processor MSF Events Target ID(000011) / Design Block #(0110)
- 11.4.6.4 Intel XScale® Core Events Target ID(000100) / Design Block #(0111)
- 11.4.6.5 PCI Events Target ID(000101) / Design Block #(1000)
- 11.4.6.6 ME00 Events Target ID(100000) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.7 ME01 Events Target ID(100001) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.8 ME02 Events Target ID(100010) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.9 ME03 Events Target ID(100011) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.10 ME04 Events Target ID(100100) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.11 ME05 Events Target ID(100101) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.12 ME06 Events Target ID(100110) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.13 ME07 Events Target ID(100111) / Design Block #(1001)
- 11.4.6.14 ME10 Events Target ID(110000) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.15 ME11 Events Target ID(110001) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.16 ME12 Events Target ID(110010) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.17 ME13 Events Target ID(110011) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.18 ME14 Events Target ID(110100) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.19 ME15 Events Target ID(110101) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.20 ME16 Events Target ID(100110) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.21 ME17 Events Target ID(110111) / Design Block #(1010)
- 11.4.6.22 SRAM DP1 Events Target ID(001001) / Design Block #(0010)
- 11.4.6.23 SRAM DP0 Events Target ID(001010) / Design Block #(0010)
- 11.4.6.24 SRAM CH3 Events Target ID(001011) / Design Block #(0010)
- 11.4.6.25 SRAM CH2 Events Target ID(001100) / Design Block #(0010)
- 11.4.6.26 SRAM CH1 Events Target ID(001101) / Design Block #(0010)
- 11.4.6.27 SRAM CH0 Events Target ID(001110) / Design Block #(0010)
- 11.4.6.28 DRAM DPLA Events Target ID(010010) / Design Block #(0011)
- 11.4.6.29 DRAM DPSA Events Target ID(010011) / Design Block #(0011)
- 11.4.6.30 IXP2800 Network Processor DRAM CH2 Events Target ID(010100) / Design Block #(0011)
- 11.4.6.31 IXP2800 Network Processor DRAM CH1 Events Target ID(010101) / Design Block #(0011)
- 11.4.6.32 IXP2800 Network Processor DRAM CH0 Events Target ID(010110) / Design Block #(0011)
Hardware Reference Manual 383
Intel
®
IXP2800 Network Processor
Performance Monitor Unit
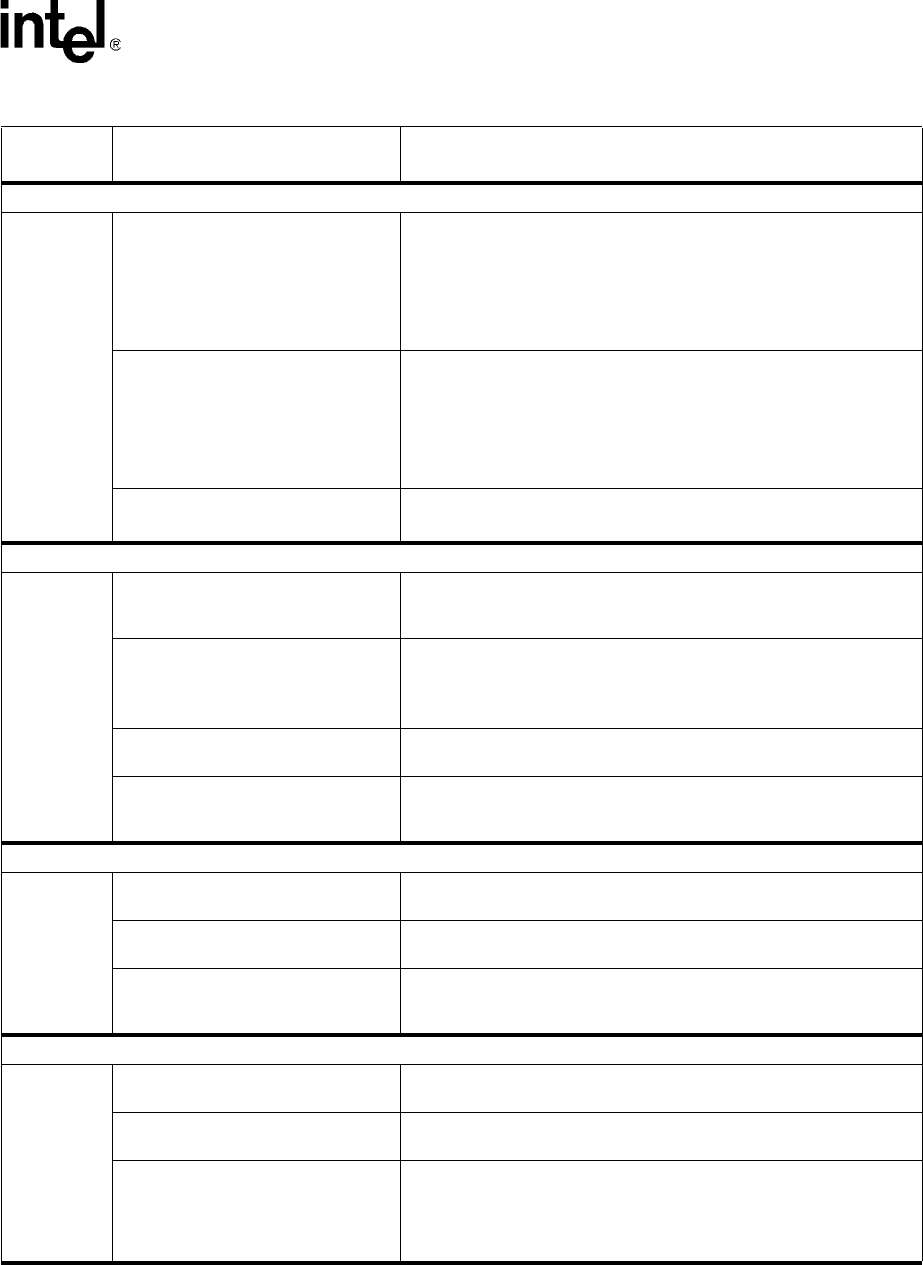
Table 152. Hardware Blocks and Their Performance Measurement Events (Sheet 1 of 2)
Hardware
Block
Performance Measurement Event Description
Intel XScale
®
Core
DRAM Read Head of Queue Latency
Histogram
The Intel XScale
®
core generates a read or write command to the
DRAM primarily to either push or pull data of the DDRAM. These
commands are scheduled to the DRAM through the push-pull arbiter
through a command FIFO in the gasket. The DRAM-read head of queue
enables the PMU to monitor when the read and write commands posted
by the Intel XScale
®
core in the gasket gets fetched and delivered to
DDRAM.
SRAM Read Head of Queue Latency
Histogram
The Intel XScale
®
core generates a read or write command to the
SRAM primarily to either push or pull data of the SRAM. These
commands are scheduled to the SRAM through the push-pull arbiter
through a command FIFO in the gasket. The SRAM-read head of queue
enables the PMU to monitor when the read and write commands posted
by the Intel XScale
®
core in the gasket gets fetched and delivered to
SRAM.
Interrupts
Number of interrupts seen.
Histogram of time between interrupts.
Microengines
Command FIFO Number of
Commands
These statistics give the number of the commands issued by the
Microengine in a particular period of time. It also can count each
different thread.
Control Store Measures
Count time between two microstore locations (locations can be set by
instrumentation software).
Histogram time between two microstore locations (locations can be set
by instrumentation software)
Execution Unit Status
Histogram of stall time. Histogram of aborted time. Histogram of
swapped out time. Histogram of idle time.
Command FIFO Head of Queue Wait
Time Histogram (Latency)
This is to measure the latency of a command, which is at the head of
the queue and is waiting to be sent out to the destination over the
chassis.
SRAM
SRAM Commands
A count of SRAM commands received. These are maskable by
command type such as Put and Get.
SRAM Bytes, Cycles Busy
This measurement describes the number of bytes transferred and the
SRAM busy time.
Queue Depth Histogram
This measurement analyzes the different queues such as ordered,
priority, push queue, pull queue, read lock fail, and HW queues, and
provides information about utilization.
DRAM
DRAM Commands
This measurement lists the total commands issued to the DRAM, and
they can be counted based on command type and error type.
DRAM Bytes, Cycles Busy
This measurement indicates the DRAM busy time and bytes
transferred.
Maskable by Read/Write,
Microengine, PCI, or the Intel XScale
®
Core
This measurement indicates the different accesses that are initiated to
the DRAM. These measurements could be for all the accesses to the
memory or can be masked using a specific source such as PCI, the
Intel XScale
®
core, or Microengine. This can further be measured
based on read or write cycles.