Desktop 4th Generation Specification Sheet
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Revision History
- 1.0 Introduction
- 2.0 Interfaces
- 3.0 Technologies
- 3.1 Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
- 3.2 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
- 3.3 Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT Technology)
- 3.4 Intel® Turbo Boost Technology 2.0
- 3.5 Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions 2.0 (Intel® AVX2)
- 3.6 Intel® Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions (Intel® AES-NI)
- 3.7 Intel® Transactional Synchronization Extensions - New Instructions (Intel® TSX-NI)
- 3.8 Intel® 64 Architecture x2APIC
- 3.9 Power Aware Interrupt Routing (PAIR)
- 3.10 Execute Disable Bit
- 3.11 Supervisor Mode Execution Protection (SMEP)
- 4.0 Power Management
- 4.1 Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) States Supported
- 4.2 Processor Core Power Management
- 4.3 Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) Power Management
- 4.4 PCI Express* Power Management
- 4.5 Direct Media Interface (DMI) Power Management
- 4.6 Graphics Power Management
- 5.0 Thermal Management
- 5.1 Desktop Processor Thermal Profiles
- 5.2 Thermal Metrology
- 5.3 Fan Speed Control Scheme with Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) 1.1
- 5.4 Fan Speed Control Scheme with Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) 2.0
- 5.5 Processor Temperature
- 5.6 Adaptive Thermal Monitor
- 5.7 THERMTRIP# Signal
- 5.8 Digital Thermal Sensor
- 5.9 Intel® Turbo Boost Technology Thermal Considerations
- 6.0 Signal Description
- 6.1 System Memory Interface Signals
- 6.2 Memory Reference and Compensation Signals
- 6.3 Reset and Miscellaneous Signals
- 6.4 PCI Express*-Based Interface Signals
- 6.5 Display Interface Signals
- 6.6 Direct Media Interface (DMI)
- 6.7 Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Signals
- 6.8 Testability Signals
- 6.9 Error and Thermal Protection Signals
- 6.10 Power Sequencing Signals
- 6.11 Processor Power Signals
- 6.12 Sense Signals
- 6.13 Ground and Non-Critical to Function (NCTF) Signals
- 6.14 Processor Internal Pull-Up / Pull-Down Terminations
- 7.0 Electrical Specifications
- 8.0 Package Mechanical Specifications
- 9.0 Processor Ball and Signal Information
8.0 Package Mechanical Specifications
The processor is packaged in a Flip-Chip Land Grid Array package that interfaces with
the motherboard using the LGA1150 socket. The package consists of a processor
mounted on a substrate land-carrier. An integrated heat spreader (IHS) is attached to
the package substrate and core and serves as the mating surface for processor
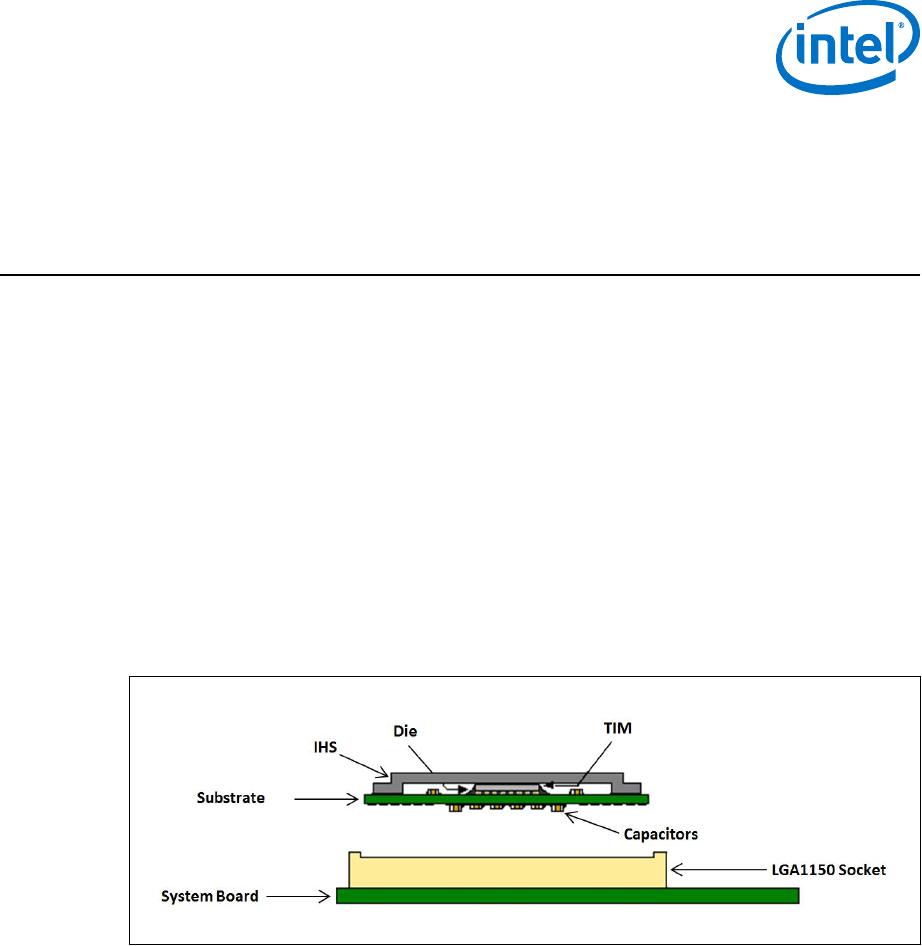
thermal solutions, such as a heatsink. The following figure shows a sketch of the
processor package components and how they are assembled together.
The package components shown in the following figure include the following:
1. Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS)
2. Thermal Interface Material (TIM)
3. Processor core (die)
4. Package substrate
5. Capacitors
Figure 24. Processor Package Assembly Sketch
Processor Component Keep-Out Zone
The processor may contain components on the substrate that define component keep-
out zone requirements. A thermal and mechanical solution design must not intrude
into the required keep-out zones. Decoupling capacitors are typically mounted to the
land-side of the package substrate. Refer to the LGA1150 Socket Application Guide for
keep-out zones. The location and quantity of package capacitors may change due to
manufacturing efficiencies but will remain within the component keep-in. This keep-in
zone includes solder paste and is a post reflow maximum height for the components.
Package Loading Specifications
The following table provides dynamic and static load specifications for the processor
package. These mechanical maximum load limits should not be exceeded during
heatsink assembly, shipping conditions, or standard use condition. Also, any
8.1
8.2
Package Mechanical Specifications—Processor
Desktop 4th Generation Intel
®
Core
™
Processor Family, Desktop Intel
®
Pentium
®
Processor Family, and Desktop Intel
®
Celeron
®
Processor Family
December 2013 Datasheet – Volume 1 of 2
Order No.: 328897-004 105










