64-bit Intel Xeon Processorwith 1MB L2 Cache Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
Table Of Contents
Processor Thermal Management Logic and Thermal Monitor Features
R
58 64-bit Intel
®
Xeon™ Processor MP with 1 MB L2 Cache
Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
hysteresis period has expired, the operating frequency and voltage transition back to the normal
system operating point. Transition of the VID code will occur first, in order to insure proper
operation once the processor reaches its normal operating frequency. Refer to Figure F-3 for an
illustration of this ordering.
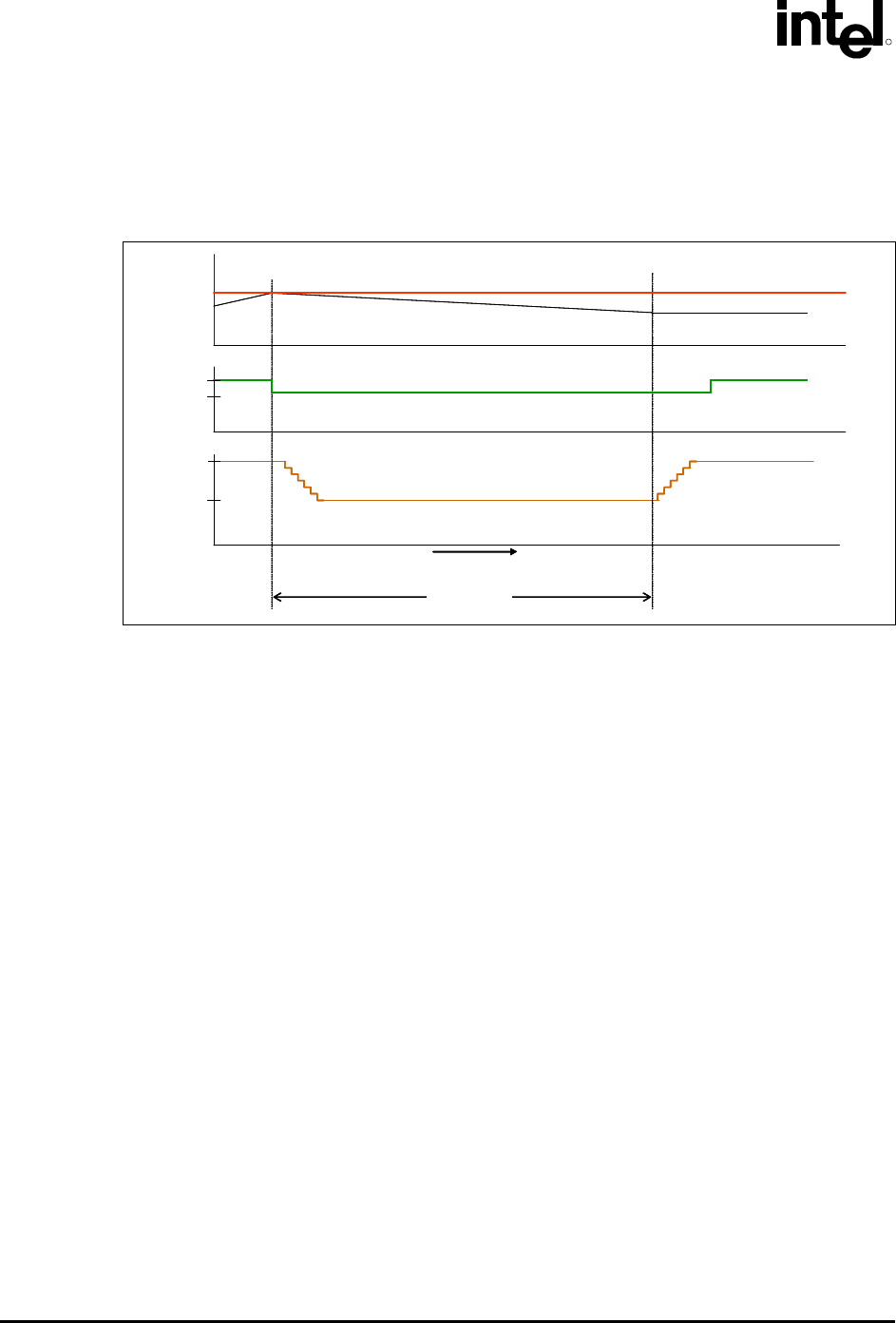
Figure F-3. Thermal Monitor 2 Frequency and Voltage Ordering
Vcc
Temperature
V
NOM
Frequency
Time
f
TM2
f
MAX
T
TM2
V
TM2
T(hysterisis)
Vcc
Temperature
V
NOM
Frequency
Time
f
TM2
f
MAX
T
TM2
V
TM2
T(hysterisis)
F.1.5 System Considerations
The Thermal Monitor feature may be used in a variety of ways, depending upon the system design
requirements and capabilities.
Note: Intel requires the TCC to be enabled for all 64-bit Intel Xeon processor MP with 1 MB L2
cache -based systems. At a minimum, the TCC provides an added level of protection against
processor thermal solution failure.
A system designed to meet the TDP and T
CASE
targets published in the processor datasheet greatly
reduces the probability of real applications causing the TCC to activate under normal operating
conditions. Systems that do not meet these specifications could be subject to more frequent
activation of the TCC depending upon ambient air temperature and application power profile.
Moreover, if a system is significantly under designed, there is a risk that the Thermal Monitor
feature will not be capable of maintaining a safe operating temperature and the processor could
shutdown and signal THERMTRIP#.
For information regarding THERMTRIP#, refer to Appendix F.1.7.2 and to the processor datasheet
F.1.6 Operating System and Application Software Considerations
The Thermal Monitor feature and its TCC work seamlessly with ACPI compliant operating systems
and those utilizing hardware based timing routines. The Thermal Monitor feature is transparent to
application software since the processor bus snooping, ACPI timer, and interrupts are active at all
times.
Activation of the TCC during a non-ACPI aware operating system boot process may result in
incorrect calibration of operating system software timing loops. This is also the case with operating










