64-bit Intel Xeon Processorwith 1MB L2 Cache Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
Table Of Contents
R
Thermal/Mechanical Reference Design
64-bit Intel
®
Xeon™ Processor MP with 1 MB L2 Cache 11
Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines
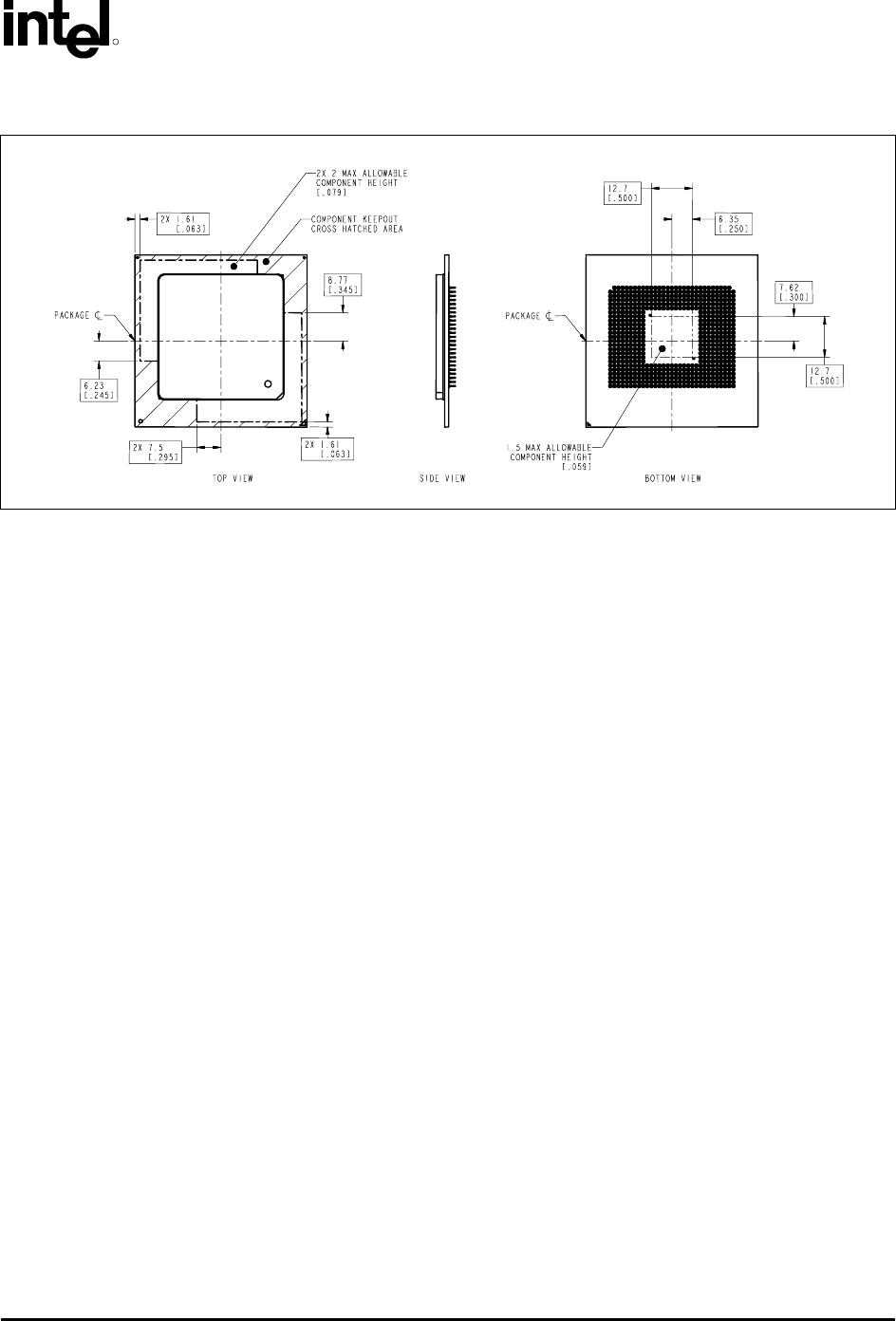
Figure 2-2. Critical Interface Dimensions (Sheet 2 of 2)
2.2 Thermal Requirements
In order to remain within a certain case temperature (T
CASE
) specification to achieve optimal
operation and long-term reliability, the thermal specification methodology, referred to as the thermal
profile, is used. The intent of the thermal profile specification is to support acoustic noise reduction
through fan speed control and ensure the long-term reliability of the processor. For information on
thermal testing, please see Appendix B.
To ease the burden on thermal solutions, the Thermal Monitor feature and associated logic have
been integrated into the silicon of the processor. By taking advantage of the Thermal Monitor
feature, system designers may reduce thermal solution cost by designing to Thermal Design Power
(TDP) instead of maximum power. The TDP is defined as the power level at which the processor
thermal solutions be designed to dissipate. TDP is not the maximum power that the processor can
dissipate. TDP is based on measurements of processor power consumption while running various
high power applications. This data set is used to determine those applications that are interesting
from a power perspective. These applications are then evaluated in a controlled thermal environment
to determine their sensitivity to activation of the thermal control circuit. This data set is then used to
derive the TDP targets published in the processor datasheet. Thermal Monitor can protect the
processor in rare workload excursions above TDP. Therefore, thermal solutions should be designed
to dissipate the target TDP level.
The relationship between TDP to the thermal profile, and thermal management logic and thermal
monitor features, is discussed in the sections to follow. The thermal management logic and thermal
monitor features are discussed in extensive detail in Appendix F.
2.2.1 Thermal Profile
The thermal profile is a linear line that defines the relationship between a processor’s case
temperature and its power consumption as shown in Figure 2-3. The equation of the thermal profile
is defined as:
y = ax + b Equation 1










