Mobile Intel Pentium 4 Processor Supporting Hyper-Threading Technology on 90-nm Process Technology
12 Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 Processor Supporting Hyper-Threading Technology on 90-nm Process Technology Datasheet
Electrical Specifications
NOTE: Individual processors operate only at or below the rated frequency.
2.3 Voltage Identification
The voltage set by the VID signals is the reference VR output voltage to be delivered to the
processor Vcc pins. A minimum voltage is provided in Table 2-8 and changes with frequency. This
allows processors running at a higher frequency to have a relaxed minimum voltage specification.
The specifications have been set such that one voltage regulator can work with all supported
frequencies.
Individual processor VID values may be calibrated during manufacturing such that two devices at
the same speed may have different VID settings.
The processor uses six voltage identification pins, VID[5:0], to support automatic selection of
power supply voltages. Table 2-2 specifies the voltage level corresponding to the state of VID[5:0].
A 1 in this table refers to a high voltage level and a 0 refers to low voltage level. If the processor
socket is empty (VID[5:0] = x11111), or the voltage regulation circuit cannot supply the voltage
that is requested, it must disable itself.
Power source characteristics must be guaranteed to be stable whenever the supply to the voltage
regulator is stable.
The processor’s Voltage Identification circuit requires an independent 1.2-V supply and some other
power sequencing considerations.
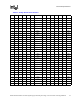
Table 2-1. Core Frequency to Front Side Bus Multiplier Configuration
Multiplication of System
Core Frequency to Front
Side Bus Frequency
Core Frequency
(133 MHz BCLK/533
MHz FSB)
1/14 1.86 GHz
1/15 2.00 GHz
1/16 2.13 GHz
1/17 2.26 GHz
1/18 2.40 GHz
1/19 2.53 GHz
1/20 2.66 GHz
1/21 2.80 GHz
1/22 2.93 GHz
1/23 3.06 GHz
1/24 3.20 GHz
1/25 3.33 GHz
1/26 3.46 GHz
1/27 3.60 GHz