New Trends Make 10 Gigabit Ethernet the Data-Center Performance Choice
WHITE PAPER | New Trends Make 10 Gigabit Ethernet the Data-Center Performance Choice
4
CONSOLIDATION AND VIRTUALIZATION
NEED STILL MORE I/O
Data centers are migrating in greater numbers to
server consolidation and virtualization in order to
reduce server proliferation and provide greater
management efficiencies and quality of service.
Typically, the first step in the process consists of
consolidating different instances of like applications
onto a single server or fewer servers than used in
the old single-application-per-server paradigm.
More typical today, however, is the trend of
including virtualization. Virtualization allows
mixed applications and OSs to be supported on a
single sever by defining multiple virtual machines
(VMs) on the server. Each VM on a server operates
in essence like a standalone, physical machine,
but because the VMs are under the auspices of a
single server, IT gains the advantages of a reduced
server inventory, better server utilization, data-
center consolidation, and more-efficient centralized
management of resources.
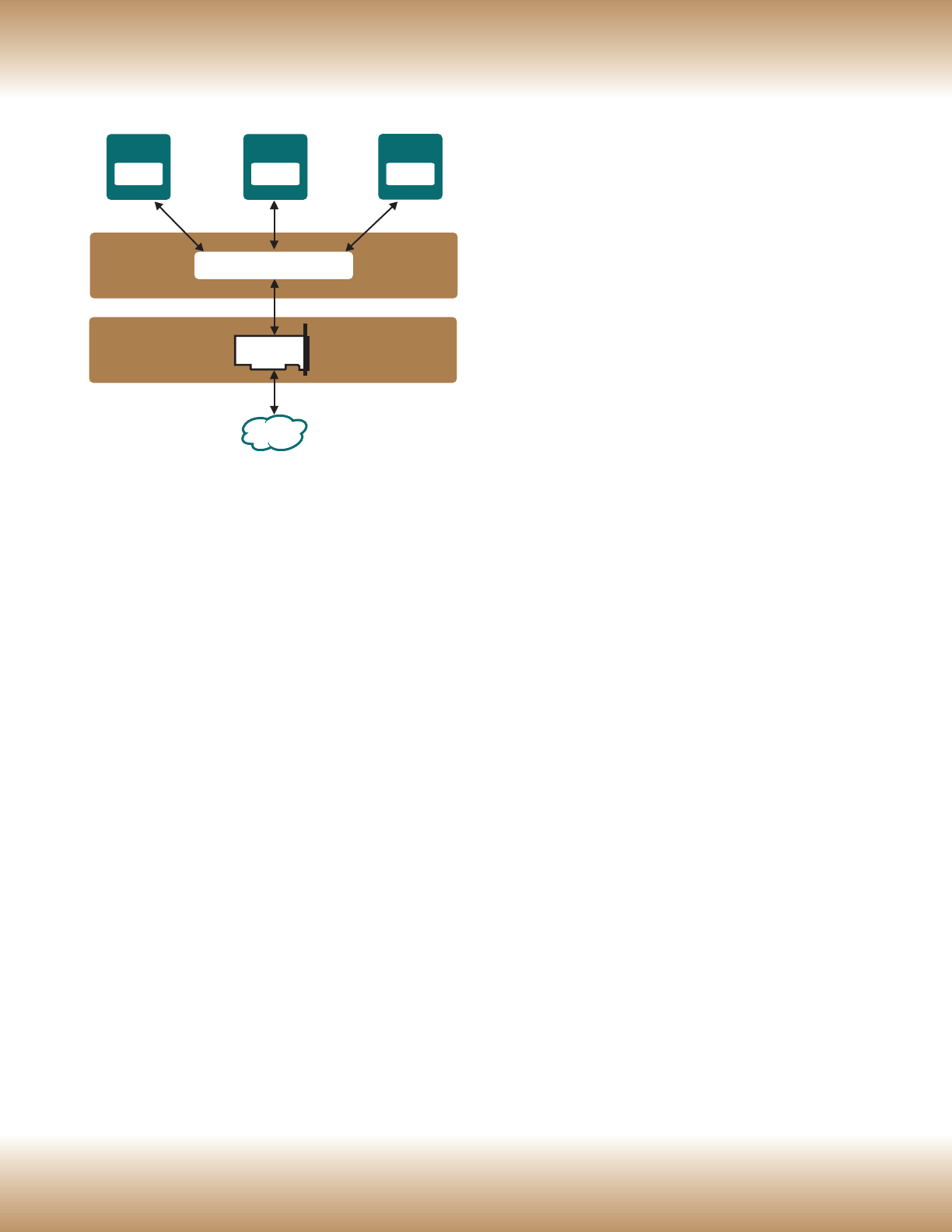
SW Switch
VMM
Software
Server
Hardware
NIC
LAN
VM1
vNIC
VM2
vNIC
VMn
vNIC
......
Figure 1. Virtualized server. Multiple VMs can be defined
on a single server, with each VM running different
applications under different operating systems.
Figure 1 illustrates the basic concept of a virtualized
server. The VMM software defines and manages
each VM and can define additional VMs as
necessary to handle application load increases. As
can be imagined, the overhead of running a VMM
and multiple VMs requires a high-performance
server and the better the performance, the more
that can be virtualized. Multi-core Intel Xeon
processor-based servers are uniquely suited to these
needs because their performance far exceeds that
of previous server generations. More than that,
however, they also include Intel
®
Virtualization
Technology (Intel
®
VT), which reduces the need for
compute-intensive software translations between
the guest and host OSs.
2
This allows consolidation
of more applications on fewer physical servers.
Multiple VMs mean multiple I/O streams, the
aggregate of which increases the I/O bandwidth
and throughput needs for each physical machine.
Use of a 10GbE network interface card (NIC)
or a dual-port 10GbE server adapter provides
maximum available connectivity bandwidth for
virtualized environments.
Additional assists from Intel I/OAT and optimization
for multi-core servers provide further performance
gains from Intel 10 Gigabit Server Adapters.
However, there is still another special assist for
virtualized environments. This assist is Virtual
Machine Data Queues, or VMDq.
VMDq is a networking hardware feature on Intel
Server Adapters that provides acceleration by
assigning packets to various virtual machines (VMs)
in a virtualized server. Received packets are sorted
into queues for the appropriate VM and are then
handed up to the virtual machine monitor (VMM)
switch, thereby reducing the number of memory
copies the system needs to make to get packets to
VMs. VMDq also handles transmission of packets
from the various VMs on the host server to ensure
timely and fair delivery to the network. This reduces
the significant I/O penalty created by overhead
associated with the added layer of VMM software








