User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- FCC and IC Statement
- Getting started
- 1.1. Document structure
- 1.2. Abbreviations
- 1.3. Document marks
- System Description
- 2.1. Introducing InfiLINK XG
- 2.2. Hardware Description
- 2.3. InfiLINK XG Specifications
- Installation
- 3.1. Installation Requirements
- 3.2. Equipment Positioning Guidelines
- 3.3. Installing the Outdoor Units
- 3.4. Installing the Indoor Unit
- Commissioning
- 4.1. Introduction
- 4.2. Step by step procedure
- Operation & Administration
- 5.1. Introduction
- 5.2. InfiLINK XG unit access
- 5.3. Status
- 5.3.1. Interface Statistics
- 5.3.2. Wireless Link Statistics
- 5.4. Antenna alignment
- 5.5. Maintenance
- 5.5.1. Firmware
- 5.5.2. Upload
- 5.5.3. Download
- 5.5.4. Bottom section of the page
- 5.6. Settings
- 5.6.1. General
- 5.6.2. Network Access
- 5.6.3. Radio
- 5.6.4. Switch
- 5.6.5. VLAN Switching
- 5.6.6. SNMP
- 5.6.7. Apply and Try buttons for the configuration
- 5.6.8. Configuring QoS
- 5.6.9. Configuring per-VLAN 802.1p priority assignment
- Troubleshooting
- 5
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. The wireless link is down (it got lost)
- 6.3. No access to the local unit
- 6.4. Expected capacity is not met
- 6.5. Errors on the wireless link, throughput fluctuations
- 6.6. No data is being transferred
- 6.7. The management of the unit is lost
- 6.7.1. ERConsole recovery procedure
- 6.7.2. Restore to factory settings using ERConsole
Chapter 3 - Configuration
Technical User Manual
InfiLINK XG
78
- “on”: allows the VLAN to pass through that port
- “off”: does not allow the VLAN to pass
- “native”: allows the VLAN to pass, but also allows the untagged traffic to
pass through that port
4. Assign an 802.1p priority. The packets received at the wired interfaces can be
marked with an 802.1p priority. “0” is the lowest priority and “7” the highest.
The following options are available for VLAN configuration:
Access mode (allows untagged traffic from certain VLAN only)
Trunk mode (allows tagged traffic only)
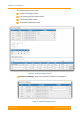
To configure the access mode or trunk mode, you need to enable or disable the
“Access” checkbox for each port. In the example below, the ge0 port is in trunk
mode and the ge1 port is in access mode.
Figure 55 - Configuring the operational mode of a port
To send and receive tagged and untagged traffic the native VLAN option should
be used. Native VLAN defines the VLAN tag number, which can receive all
incoming untagged traffic (for example, by default VLAN1 is configured as a Native
VLAN for all the ports).
In order to allow both tagged and untagged traffic to pass in trunk operational
mode, a native VLAN can be configured. The details about the native VLAN and
specific operation are described in the following section
Configuring a native VLAN.
NOTE
Changing the operational mode of a port to the access mode will disable all VLANs on
that port automatically. More specifically, the VLANs that are set to “on” or “native” for
that port will be changed automatically to “off”. Please check section 7.2.4 for more
details about the on/off/native status of a VLAN.
Priority: use this option to set the priority to the certain VLAN in compliance
with 802.1p, from 0 to 7 in increments of 1