User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- FCC and IC Statement
- Getting started
- 1.1. Document structure
- 1.2. Abbreviations
- 1.3. Document marks
- System Description
- 2.1. Introducing InfiLINK XG
- 2.2. Hardware Description
- 2.3. InfiLINK XG Specifications
- Installation
- 3.1. Installation Requirements
- 3.2. Equipment Positioning Guidelines
- 3.3. Installing the Outdoor Units
- 3.4. Installing the Indoor Unit
- Commissioning
- 4.1. Introduction
- 4.2. Step by step procedure
- Operation & Administration
- 5.1. Introduction
- 5.2. InfiLINK XG unit access
- 5.3. Status
- 5.3.1. Interface Statistics
- 5.3.2. Wireless Link Statistics
- 5.4. Antenna alignment
- 5.5. Maintenance
- 5.5.1. Firmware
- 5.5.2. Upload
- 5.5.3. Download
- 5.5.4. Bottom section of the page
- 5.6. Settings
- 5.6.1. General
- 5.6.2. Network Access
- 5.6.3. Radio
- 5.6.4. Switch
- 5.6.5. VLAN Switching
- 5.6.6. SNMP
- 5.6.7. Apply and Try buttons for the configuration
- 5.6.8. Configuring QoS
- 5.6.9. Configuring per-VLAN 802.1p priority assignment
- Troubleshooting
- 5
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. The wireless link is down (it got lost)
- 6.3. No access to the local unit
- 6.4. Expected capacity is not met
- 6.5. Errors on the wireless link, throughput fluctuations
- 6.6. No data is being transferred
- 6.7. The management of the unit is lost
- 6.7.1. ERConsole recovery procedure
- 6.7.2. Restore to factory settings using ERConsole
Chapter 3 - Configuration
Technical User Manual
InfiLINK XG
90
The packet scheduling algorithms available for determining how the packets shall
exit the priority queues are the following:
- Strict priority queuing: packets from lower priority queues are delayed
in case higher priority queues has traffic
- Weighted round robin: weights are used for every queue of an interface,
which allows different queues to have different service shares depending
on the weight value
Per-port egress rate limiting
Traffic shaping can be configured by limiting the egress rate on a selected wired
port.
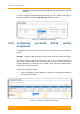
In order to configure per-port egress rate limiting go to the “Switch” menu page in
the Web interface and set the “Rate” parameter for a specific wired interface. In
the example below, the traffic outgoing at the ge0 interface is limited to 100 Mbps.
It can be also noticed that the radio interface does not have available the option of
configuring a rate limit. Radio throughput depends only on current modulation:
Figure 68 - Configuring per-port egress rate limiting
5.6.8.2. QoS radio interface capabilities
The radio interface QoS capabilities of the InfiLINK XG unit are the following:
Traffic selection and prioritization based on 802.1p
The packets received at the radio interface that are marked with an 802.1p priority
will be recognized and sent to a specific priority queue.
Four priority queues
The same considerations mentioned for the wired interface capabilities are valid:
each received packet is sent to one of the 4 priority queues based on the PCP field
that contains the 802.1p priority.