User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- FCC and IC Statement
- Getting started
- 1.1. Document structure
- 1.2. Abbreviations
- 1.3. Document marks
- System Description
- 2.1. Introducing InfiLINK XG
- 2.2. Hardware Description
- 2.3. InfiLINK XG Specifications
- Installation
- 3.1. Installation Requirements
- 3.2. Equipment Positioning Guidelines
- 3.3. Installing the Outdoor Units
- 3.4. Installing the Indoor Unit
- Commissioning
- 4.1. Introduction
- 4.2. Step by step procedure
- Operation & Administration
- 5.1. Introduction
- 5.2. InfiLINK XG unit access
- 5.3. Status
- 5.3.1. Interface Statistics
- 5.3.2. Wireless Link Statistics
- 5.4. Antenna alignment
- 5.5. Maintenance
- 5.5.1. Firmware
- 5.5.2. Upload
- 5.5.3. Download
- 5.5.4. Bottom section of the page
- 5.6. Settings
- 5.6.1. General
- 5.6.2. Network Access
- 5.6.3. Radio
- 5.6.4. Switch
- 5.6.5. VLAN Switching
- 5.6.6. SNMP
- 5.6.7. Apply and Try buttons for the configuration
- 5.6.8. Configuring QoS
- 5.6.9. Configuring per-VLAN 802.1p priority assignment
- Troubleshooting
- 5
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.2. The wireless link is down (it got lost)
- 6.3. No access to the local unit
- 6.4. Expected capacity is not met
- 6.5. Errors on the wireless link, throughput fluctuations
- 6.6. No data is being transferred
- 6.7. The management of the unit is lost
- 6.7.1. ERConsole recovery procedure
- 6.7.2. Restore to factory settings using ERConsole
Chapter 3 - Configuration
Technical User Manual
InfiLINK XG
89
QoS strategies were introduced for the InfiLINK XG units in order to be able to
customize the balance between the maximum achievable capacity and the allowed
packet loss for the priority packets. The QoS capabilities of the unit fall in two
categories:
QoS wired interface capabilities
QoS radio interface capabilities
5.6.8.1. QoS wired interface capabilities
The wired interface capabilities of InfiLINK XG unit are the following:
Traffic selection and prioritization based on 802.1p
The IEEE 802.1p standard provides the means to implement QoS techniques at
Layer 2 (MAC layer). QoS is implemented using a 3 bit field called Priority Code
Point (PCP) part of the Ethernet header when 802.1Q VLAN tagging is in use.
There are eight 802.1p priorities, “0” being the lowest and “7” - the highest. The
InfiLINK XG unit is capable to recognize and prioritize packets received on the
wired interfaces. Each packt will be further sent to a specific priority queue.
Four hardware priority queues on InfiLINK XG
Each received packet is sent to one of the 4 priority queues based on the PCP field
that contains the 802.1p priority.
When the actual traffic load reaches the egress rate, the switch will favor the
transmission of the highest priority packets in the detriment of the lower priority
ones.
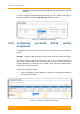
The mapping between the 802.1p priorities and the 4 queues can be found below:
802.1p priority Traffic type InfiLINK XG priority queue
0
Background
1
1
Best Effort
2
Excellent Effort
2
3
Critical Applications
4
Video
3
5
Voice
6
Internetwork control
4
7
Network control
Table 37 - Priority queues mapping
Strict or weighted round robin packet scheduling algorithms