Computer Drive User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1. HPSS 7.1 Configuration Overview
- Chapter 2. Security and System Access
- Chapter 3. Using SSM
- 3.1. The SSM System Manager
- 3.2. Quick Startup of hpssgui
- 3.3. Configuration and Startup of hpssgui and hpssadm
- 3.4. Multiple SSM Sessions
- 3.5. SSM Window Conventions
- 3.6. Common Window Elements
- 3.7. Help Menu Overview
- 3.8. Monitor, Operations and Configure Menus Overview
- 3.9. SSM Specific Windows
- 3.10. SSM List Preferences
- Chapter 4. Global & Subsystem Configuration
- 4.1. Global Configuration Window
- 4.2. Storage Subsystems
- 4.2.1. Subsystems List Window
- 4.2.2. Creating a New Storage Subsystem
- 4.2.3. Storage Subsystem Configuration Window
- 4.2.3.1. Create Storage Subsystem Metadata
- 4.2.3.2. Create Storage Subsystem Configuration
- 4.2.3.3. Create Storage Subsystem Servers
- 4.2.3.4. Assign a Gatekeeper if Required
- 4.2.3.5. Assign Storage Resources to the Storage Subsystem
- 4.2.3.6. Create Storage Subsystem Fileset and Junction
- 4.2.3.7. Migration and Purge Policy Overrides
- 4.2.3.8. Storage Class Threshold Overrides
- 4.2.4. Modifying a Storage Subsystem
- 4.2.5. Deleting a Storage Subsystem
- Chapter 5. HPSS Servers
- 5.1. Server List
- 5.1. Server Configuration
- 5.1.1. Common Server Configuration
- 5.1.1. Core Server Specific Configuration
- 5.1.2. Gatekeeper Specific Configuration
- 5.1.3. Location Server Additional Configuration
- 5.1.4. Log Client Specific Configuration
- 5.1.1. Log Daemon Specific Configuration
- 5.1.2. Migration/Purge Server (MPS) Specific Configuration
- 5.1.3. Mover Specific Configuration
- 5.1.3.1. Mover Specific Configuration Window
- 5.1.3.1. Additional Mover Configuration
- 5.1.3.1.1. /etc/services, /etc/inetd.conf, and /etc/xinetd.d
- 5.1.3.1.2. The Mover Encryption Key Files
- 5.1.3.1.3. /var/hpss/etc Files Required for Remote Mover
- 5.1.3.1.1. System Configuration Parameters on IRIX, Solaris, and Linux
- 5.1.3.1.1. Setting Up Remote Movers with mkhpss
- 5.1.3.1.2. Mover Configuration to Support Local File Transfer
- 5.1.1. Physical Volume Repository (PVR) Specific Configuration
- 5.1.1. Deleting a Server Configuration
- 5.1. Monitoring Server Information
- 5.1.1. Basic Server Information
- 5.1.1. Specific Server Information
- 5.1.1.1. Core Server Information Window
- 5.1.1.1. Gatekeeper Information Window
- 5.1.1.1. Location Server Information Window
- 5.1.1.2. Migration/Purge Server Information Window
- 5.1.1.3. Mover Information Window
- 5.1.1.1. Physical Volume Library (PVL) Information Window
- 5.1.1.2. Physical Volume Repository (PVR) Information Windows
- 5.1. Real-Time Monitoring (RTM)
- 5.2. Starting HPSS
- 5.1. Stopping HPSS
- 5.2. Server Repair and Reinitialization
- 5.1. Forcing an SSM Connection
- Chapter 6. Storage Configuration
- 6.1. Storage Classes
- 6.2. Storage Hierarchies
- 6.3. Classes of Service
- 6.4. Migration Policies
- 6.5. Purge Policies
- 6.6. File Families
- Chapter 7. Device and Drive Management
- Chapter 8. Volume and Storage Management
- 8.1. Adding Storage Space
- 8.2. Removing Storage Space
- 8.3. Monitoring Storage Space
- 8.4. Dealing with a Space Shortage
- 8.5. Volume Management
- 8.6. Monitoring and Managing Volume Mounts
- 8.7. New Storage Technology Insertion
- Chapter 9. Logging and Status
- Chapter 10. Filesets and Junctions
- Chapter 11. Files, Directories and Objects by SOID
- Chapter 12. Tape Aggregation
- Chapter 13. User Accounts and Accounting
- Chapter 14. User Interfaces
- Chapter 15. Backup and Recovery
- Chapter 16. Management Tools
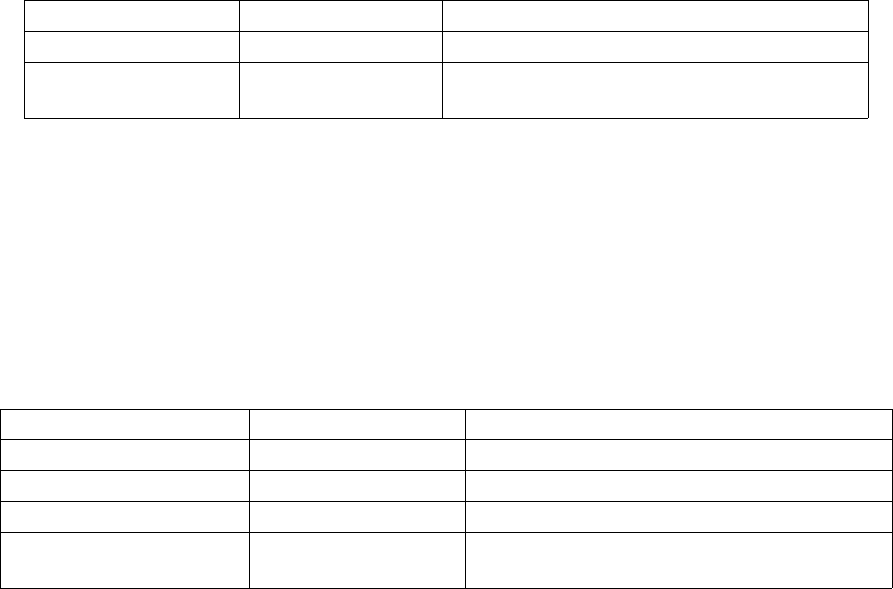
Table 1. IRIX System Parameters
Parameter Name Minimum Value Parameter Description
semmsl 512 Maximum number of semaphores per set
maxdmasz 513 Maximum DMA size (required for Ampex
DST support)
Solaris
Solaris system parameters which affect the remote Mover can be modified by editing the /etc/system
configuration file and rebooting the system. The following table defines the parameter names and
minimum required values.
Note that the semmns and semmnu values should be increased if running more than one Mover on the
Solaris machine (multiply the minimum value by the number of Movers to be run on that machine).
Table 2. Solaris System Parameters
Parameter Name Minimum Value Parameter Description
semsys:seminfo_semmns 1024 Maximum number of semaphores in system
semsys:seminfo_semmnu 512 Maximum number of undo structures in system
semsys:seminfo_semmsl 512 Maximum number of semaphores per set
shmsys:shminfo_shmmax 8388608 Maximum shared memory segment size (will
allow up to a 2MB Mover buffer size)
Linux
Linux system parameters which affect the remote Mover are detailed in the following table and can be
modified as follows.
To temporarily change SEMMSL and SHMMAX, use the sysctl(8) commands as shown in the example
below (the values take effect immediately, but will not be preserved across reboots).
% /sbin/sysctl -w kernel.sem="512 32000 32 128"
% /sbin/sysctl -w kernel.shmmax="33554432"
Where "512 32000 32 128" are the values for SEMMSL, SEMMNS, SEMOPM, and SEMNI
respectively (only change SEMMSL).
To make the changes permanent (across reboots), edit sysctl.conf(5) and add the following lines
(preserving spaces).
# Increase SEMMSL and SHMMAX for HPSS Mover
kernel.sem = 512 32000 32 128
kernel.shmmax = 33554432
Note that the minimum SEMMSL value in the following table should be multiplied by the number of
Movers running on the Linux machine.
HPSS Management Guide November 2009
Release 7.3 (Revision 1.0) 107










