Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- Cover
- Please Read Before Use
- Table of Contents
- Safety Guide
- Caution in Handling
- International Standards Compliances
- Names of the Parts
- 1. Specifications Check
- 2. Installation
- 3. Connecting with the Controller
- 4. Operation
- 5. Troubleshooting
- 6. Maintenance and Inspection
- 7. Life
- 8. External Dimensions
- 9. Warranty
- Change History
1. Specications Check
21
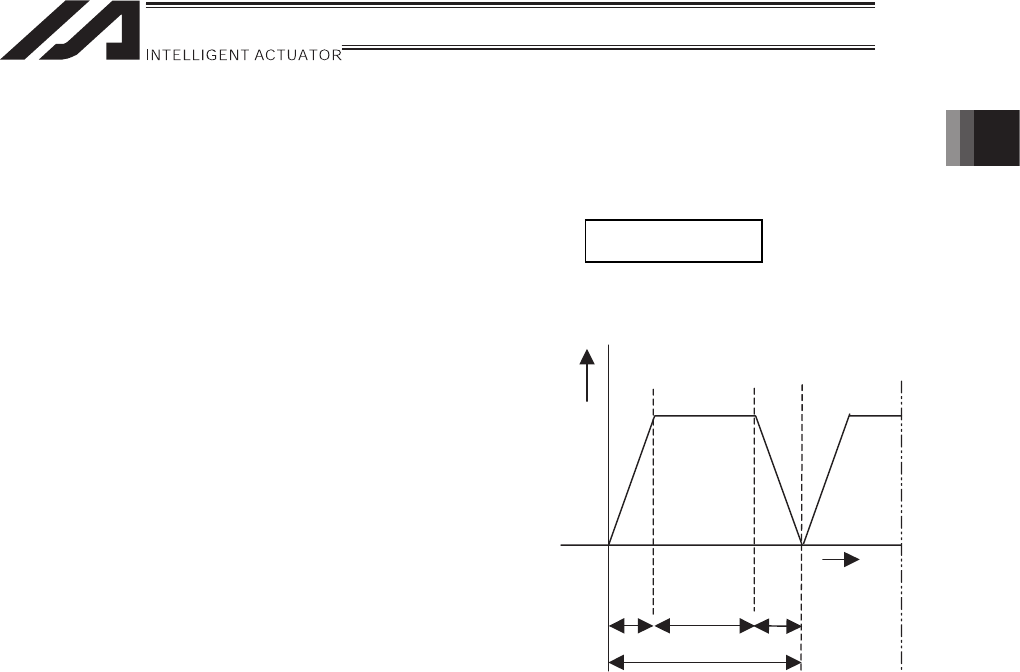
1.3.3 Example for Judging Operation Availability by Operational Conditions
[Operating conditions]
• Applicable model : H8SS/H8SM type
• Speed : 2.5m/s
• Acceleration : 19.6m/s
2
(The deceleration is
assumed to be the same.)
• Travel : 1.5m
• Slider payload : 3kg
• The actuator moves back and forth over a stroke of 1.5m.
The above operation pattern can be illustrated by
the graph shown to the right.
Now, let’s start calculation according to “Selection Method.”
1) Figure out the maximum thrust of Condition 1.
Apply the above operation pattern to the aforementioned equation of maximum thrust.
Fa = (M +m) •a + Ff
Here,
M : Slider weight (1.5kg for the H8SS/H8SM)
m : Slider load (kg) : 3kg in this example
a : Commanded acceleration (m/s
2
) : 19.6m/s
2
in this example
Ff : Traveling resistance (N) : 15N in this example
From above, Fa is calculated as follows:
Fa = (4.5 × 19.6 + 15) ĺ 103.2N
The calculated value exceeds the maximum thrust 90N of the H8SS/H8SM.
Let’s lower the specified acceleration to 14.7m/s
2
. Fa changes as follows:
Fa = (4.5 × 14.7 + 15) ĺ 81.15N.
The calculated value is smaller than the maximum thrust 90N of the H8SS/H8SM.
1G = 9.8m/s
2
Speed
Time
ta tf td
t










