User's Manual
Virtual Connect networks 87
Identifying an associated network as the native VLAN causes all untagged incoming Ethernet packets to be
placed onto this network. Only one associated network can be designated as the native VLAN. All outgoing
Ethernet packets are VLAN-tagged.
To enable native VLAN when defining a shared uplink set, select the box under Native. To enable or disable
native VLAN on an existing network, go to the Edit Shared Uplink Set screen (on page 140). Click on the Edit
icon, and then select or deselect the box under Native.
Smart Link
Smart Link actively manages downlink states when uplinks lose link state. Each VC downlink port connects to
a server NIC. If an uplink port loses link to the external switch, Virtual Connect drops all of the Ethernet
downlinks in that network connected to each server NIC. This allows servers to see the downed link and to
failover, if needed. This feature is useful when using certain server network teaming (bonding) configurations.
An uplink port is required to support Smart Link.
HP recommends using Smart Link in the following domain configurations:
• When the domain is configured with active/active uplinks
• When the domain stacking mode is configured with Primary Slice or Horizontal stacking
If the server NIC is a Flex-10, the NIC can create up to 4 logical ports. VC treats each logical port as a
separate NIC and allows them to be assigned to different networks.
When Smart Link is triggered for Flex-NICs, observe the following information:
• If DCC exchanges are successful, the logical port is disabled.
• If DCC exchanges fail, the logical port is not disabled.
Private Networks
The Private Networks option provides extra networking security. When selected, the network is configured so
that all server ports connected to it cannot communicate with each other within the Virtual Connect domain.
All packets from servers are sent through the VC domain and out the uplink ports only. Servers on the network
can only communicate with each other through an external Layer 3 router that redirects the traffic back to the
VC domain.
VC limits the number of Private Networks to 128.
VLAN Tunneling Support
With VC 3.30 and higher, you can have both mapped and tunneled networks within the same domain.
VLAN tunneling support is now controlled on a per network basis. You can enable or disable VLAN tunneling
when adding or modifying a network with a dedicated uplink. Dedicated VLANs that are not part of a shared
uplink set can be tunneled. Networks that are associated with a shared uplink set cannot be tunneled
because they are already being mapped.
When the 'Enable VLAN Tunneling' check box is selected, packets on that network with VLAN tags are
passed through the VC domain without modification. When the 'Enable VLAN Tunneling' check box is not
selected, the uplink ports in the network do not pass any packets that have VLAN tags.
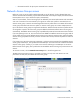
The following figure shows tunneled VLAN tags. On the dedicated green network, both uplink and server
VLAN tags are tunneled through Virtual Connect unchanged. On the shared red and blue networks, uplink