User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- HP Process Resource Manager User Guide
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Overview
- 2 Understanding how PRM manages resources
- 3 PRM configuration planning
- 4 Setting up PRM
- 5 Using PRM with HP System Management Homepage (SMH)
- 6 Using PRM with HP Systems Insight Manager (SIM)
- 7 Configuring and enabling PRM on the command line
- Quick start to using PRM’s command-line interface
- Configuring PRM
- The PRM configuration file
- Configuration tips and requirements
- Specifying PRM groups/controlling CPU resource use
- Controlling memory use
- Controlling applications
- Specifying PRM users
- Assigning secure compartments to PRM groups
- Assigning Unix groups to PRM groups
- Checking the configuration file
- Loading the PRM configuration
- Enabling resource managers
- Updating the configuration
- 8 Fine-tuning your PRM configuration
- 9 Administering PRM
- Moving processes between PRM groups
- Displaying application filename matches
- Displaying netgroup expansions
- Displaying accessible PRM groups
- Displaying state and configuration information
- Displaying application and configuration information
- Setting the memory manager’s polling interval
- Setting the application manager’s polling interval
- Disabling PRM
- Resetting PRM
- Monitoring PRM groups
- Logging PRM memory messages
- Logging PRM application messages
- Displaying groups’ allocated and used resources
- Displaying user information
- Displaying available memory to determine number of shares
- Displaying number of cores to determine number of shares
- Displaying past process information
- Displaying current process information
- Monitoring PRM with GlancePlus
- Monitoring PRM with OpenView Performance Agent (OVPA) / OpenView Performance Manager (OVPM)
- Automating PRM administration with scripts
- Protecting the PRM configuration from reboots
- Reconstructing a configuration file
- Special case of interest: Client/server connections
- Online cell operations
- Backing up PRM files
- A Command reference
- B HP-UX command/system call support
- C Monitoring PRM through SNMP
- D Creating Secure Resource Partitions
- E Using PRM with Serviceguard
- F Using PRM with HP Integrity Virtual Machines
- G PRM error messages
- Glossary
- Index
PRM gives higher-priority FSS PRM groups more opportunities to use CPU time. Free CPU time is
available for use by any FSS PRM group and is divided up between FSS PRM groups based on
relative number of CPU shares. As a result, tasks are given CPU time when needed, in proportion
to their stated importance, relative to others with a demand.
PRM itself has low system overhead.
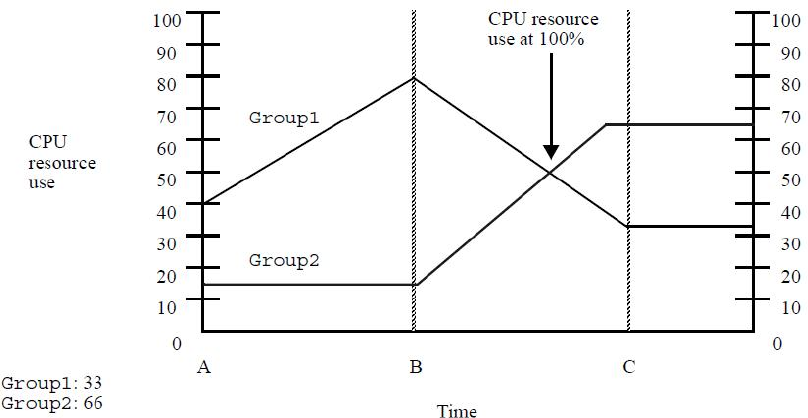
Example: PRM CPU resource management
Figure 2-2 illustrates PRM’s CPU resource management for two FSS PRM groups.
In this example, Group1 has 33 CPU shares, and Group2 has 66 CPU shares.
Note that the percentage of CPU resources referred to may not be total system CPU resources if
PSET PRM groups are configured. The percentage is of CPU resources available on the cores
assigned to the default PSET. If PSET PRM groups are not configured, then the available CPU
resources are the same as the system CPU resources.
Figure 6 PRM CPU resource management
At Time A:
• Group1 is using 40% of the available CPU resources, which is more than its share.
• Group2 is using 15% of the available CPU resources, which is less than its share.
• 45% of the available CPU resource are not used.
• PRM scheduling is not in effect.
At Time B:
• Group1’s processes are now using 80% of available CPU time, which consists of all of
Group1’s shares and an unused portion of Group2’s share.
• Group2 processes continue at a steady 15%.
• PRM scheduling is not in effect.
Between Time B and Time C:
• Group2’s demands start to increase.
• With available CPU resource use approaching 100%, PRM starts to have an effect on CPU
allocation.
• Both groups’ CPU resource use begins moving toward their assigned number of shares. In this
case, the increasing demand of Group2 causes Group1 to be pulled toward the 33% mark
despite its desire for more CPU resources.
How PRM manages CPU resources 23










