User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- HP Process Resource Manager User Guide
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Overview
- 2 Understanding how PRM manages resources
- 3 PRM configuration planning
- 4 Setting up PRM
- 5 Using PRM with HP System Management Homepage (SMH)
- 6 Using PRM with HP Systems Insight Manager (SIM)
- 7 Configuring and enabling PRM on the command line
- Quick start to using PRM’s command-line interface
- Configuring PRM
- The PRM configuration file
- Configuration tips and requirements
- Specifying PRM groups/controlling CPU resource use
- Controlling memory use
- Controlling applications
- Specifying PRM users
- Assigning secure compartments to PRM groups
- Assigning Unix groups to PRM groups
- Checking the configuration file
- Loading the PRM configuration
- Enabling resource managers
- Updating the configuration
- 8 Fine-tuning your PRM configuration
- 9 Administering PRM
- Moving processes between PRM groups
- Displaying application filename matches
- Displaying netgroup expansions
- Displaying accessible PRM groups
- Displaying state and configuration information
- Displaying application and configuration information
- Setting the memory manager’s polling interval
- Setting the application manager’s polling interval
- Disabling PRM
- Resetting PRM
- Monitoring PRM groups
- Logging PRM memory messages
- Logging PRM application messages
- Displaying groups’ allocated and used resources
- Displaying user information
- Displaying available memory to determine number of shares
- Displaying number of cores to determine number of shares
- Displaying past process information
- Displaying current process information
- Monitoring PRM with GlancePlus
- Monitoring PRM with OpenView Performance Agent (OVPA) / OpenView Performance Manager (OVPM)
- Automating PRM administration with scripts
- Protecting the PRM configuration from reboots
- Reconstructing a configuration file
- Special case of interest: Client/server connections
- Online cell operations
- Backing up PRM files
- A Command reference
- B HP-UX command/system call support
- C Monitoring PRM through SNMP
- D Creating Secure Resource Partitions
- E Using PRM with Serviceguard
- F Using PRM with HP Integrity Virtual Machines
- G PRM error messages
- Glossary
- Index
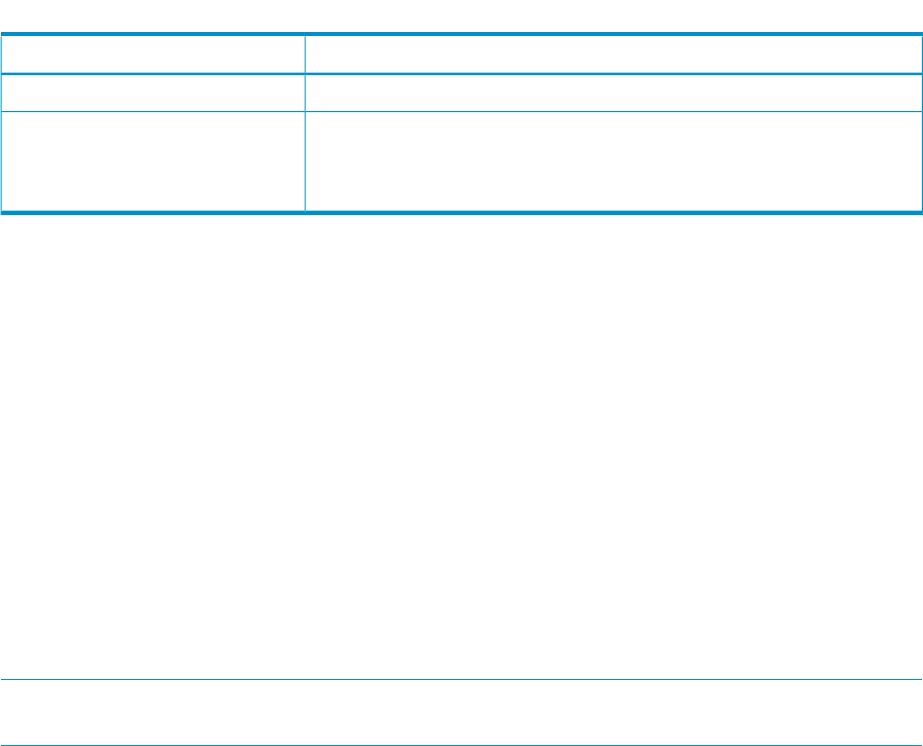
Table 17 prmagt user options/parameters. (continued)
DescriptionOption
Shuts down the currently running agent (if any).-stop
Specifies how often to sample CPU information. The seconds value must be
an integer between one and MAXINT. The default for this interval is 60
seconds.Memory information is sampled every memory manager interval, as
set by prmconfig. The default for this interval is 30 seconds.
-intervalseconds
prmanalyze
Syntax:
prmanalyze -V
prmanalyze [-s {auto | uid | gid | command | prmid}] [-f config_file]
[-r {disk | mem | cpu}] [-t {summary | conflict | hourly | daily |
weekly | monthly}] [-p] [-1] [-E]
[-d resource_density][-m minimum_duration] [-x exclude_key_value]
[filename_list]
Availability: Any user can run the prmanalyze command assuming the user has read permissions
on the files in filename_list.
You can only use prmanalyze if you have collected UNIX accounting data in a file (default
/var/adm/pacct) using accton filename.
The prmanalyze utility scans the accounting files for information on the desired resource type
(disk, memory, or CPU) and orders the accounting records by the requested sort key (user, UNIX
group, command name, or PRMID).
NOTE: The accounting files that prmanalyze uses only contain information on terminated
processes. For information on active processes, use prmanalyze with the -p option.
Use this utility when creating an initial PRM configuration (as shown in “Using prmanalyze to
quickly identify resource use” on (page 42) ) and when fine-tuning existing PRM configurations
(shown in “Using prmanalyze to analyze your configuration” on (page 83) ).
The prmanalyze report indicates the total number of accounting records processed at the beginning
of the report. There is one record for every process that has terminated since accton began routing
data to the specified accounting files.
If a process does not use a measurable amount of a given resource, it is filtered out of the data.
Consequently, different resource reports can have slightly different record totals.
If you would like to obtain information for billing based on PRM groups, use
/usr/sbin/acct/acctcom -P.
Table 18 shows the prmanalyze options and parameters.
Running prmanalyze without options or parameters is equivalent to entering the following
command line:
prmanalyze -s command -r cpu -t summary /var/adm/pacct
102 Command reference










