System Startup, Configuration, and Shutdown Reference Manual (32650-90892)
Chapter 3 55
System Startup Functions
Activating and Deactivating Autoboot and Autosearch Functions
Modifying Boot Paths in Stable Storage
The ISL commands PRIMPATH, ALTPATH, and CONSPATH are available for placing new
primary boot path, alternate boot path, or console boot path information in stable storage.
The changes need to be in stable storage to execute the autoboot sequence properly in the
event of a power outage or other serious failure.
CAUTION The commands described in the above paragraph may disrupt normal system
functions if used inappropriately. For this reason, do not attempt to use these
commands without assistance from Hewlett-Packard service personnel.
To execute any of these three commands, enter the command with its appropriate
parameter or enter
Return after the command and wait to be prompted for further input:
ISL> altpath 0/0/1/0.6
or
ISL> ALTPATH
Enter alternate boot path: 0/0/1/0.6
To withdraw a command (without changing the path), enter
Return after entering the
command without any parameter. For example,
ISL> ALTPATH
Enter alternate boot path:
Return
Invalid Input.
Trailing zeros are not required when a boot path is entered:
ISL> PRIMPATH primpath 0/0/2/0.6.0.0
ISL> CONSPATH 0/0/4/0
If an improper path format is entered, or you have withdrawn a command as shown above,
the system issues an Invalid Input message. Then ISL prompts for a new command:
ISL> PRIMPATH 240
Invalid Input.
ISL>
Displaying Current Boot Path, Autoboot, and Autosearch Settings
Since an improper path keeps the system from booting, use the DISPLAY command to check
the paths entered. Double check these entries against a recent I/O map from the ISL IOMAP
utility or a configuration listing from the SYSGEN utility. For more information on
SYSGEN, refer to Chapter 4 , “Using the System Generator (SYSGEN).”
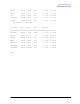
The DISPLAY or DI command lists the autoboot and autosearch settings, the primary boot
path, the alternate boot path, and the system console path held in stable storage. Use the
DISPLAY command to verify that correct information resides in stable storage. Example 3-3
demonstrates using the ISL DISPLAY command. This is an example from a N-class system.
The boot paths may vary, depending on the system.