Configuring and Managing Host-Based X.25 Links - Edition 6 (36939-90057)
Preparing to Configure X.25 iX System Access
Identify Neighbor Gateways
Chapter 5
128
Identify Neighbor Gateways
This section only applies if one of the nodes on your network is a gateway. A neighbor
gateway is a gateway that is on the same network as a given node. A non-gateway node
on a network may need to go through a neighbor gateway in order to send messages to
an entirely different network. Two nodes are on the same network if the network portion
of their IP addresses are the same. All X.25 nodes on the same network need to know the
identities of any accessible neighbor gateways. Therefore, when using NMMGR to
configure any node, you will be entering the identities of all the neighbor gateways into
the configuration of the node. Following is an example:
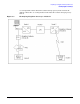
Example: Identifying Neighbor Gateways of Node B
In Figure 5-3, Net 1 is a LAN, Net 2 is an X.25 network, and Net 3 is a point-to- point
network. Node A is on both Net 1 and Net 2 and is a full gateway between them. Node A
is the Neighbor Gateway for all nodes on Net 1 to reach Net 2. Node C is on Net 1 and
Net 3 and is a gateway half. Node C is the Neighbor Gateway for all nodes on Net 1 to
reach Net 3.
If you were configuring a node such as Node B in Figure 5-3, you would enter the
identities of Nodes A and C as neighbor gateways of Node B (at the Neighbor Gateways
screen and the Neighbor Gateway Reachable Networks screen). On the Neighbor
Gateway Reachable Networks screen, you would also enter the IP address of Network 2