TurboIMAGE/XL Database Management System Reference Manual MPE/iX V6.5 (30391-90011)
38 Chapter2
Database Structure and Protection
Data Set Types and Relationships
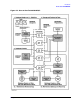
Figure 2-2. Master and Detail Data Set Relationships
Master Data Sets
Master data sets have the following characteristics:
• They are used to keep information relating to a uniquely identifiable entity. For
example, the CUSTOMER data set contains information describing customers.
• They allow for rapid retrieval of a data entry because one of the data items in the entry,
called the key item, determines the location of the data entry. A key item cannot be a
compound item. In Figure 2-3. on the next page, the CUSTOMER data set contains a
key item named ACCOUNT. The location of each entry is determined by the value of the
customer's account number.
• They can serve as indexes to the detail data set (that is, they can be related to one or
more detail data sets). The ACCOUNT key item in the CUSTOMER master data set is
related to the ACCOUNT search item in the SALES detail data set in Figure 2-3. The
entry for a customer named Abigail Brighton with account number 95430301 serves as
an index to two entries in the SALES detail data set which contain information about
purchases she made.
Although there are unused storage locations in the CUSTOMER master data set,
TurboIMAGE/XL disallows any attempt to add another data entry with account number
95430301. The key item value of each entry must remain unique. The values of other data
items in the master data set are not necessarily unique because they are not key items and
are not used to determine the location of the data entry.