HP Pascal/iX Programmer's Guide (31502-90023)
5-: 18
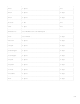
Table 5-6. Allocation and Alignment of Crunched Sets in Arrays and Records
(HP Pascal Packing Algorithm)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
||||
| Structure Containing Set | Allocation | Alignment |
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
||||
| Unpacked array | * Minimum # | Byte |
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
||||
| Unpacked record | * Minimum # | Byte |
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
||||
| Packed array | * Minimum # | Byte |
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
||||
| Packed record | * Minimum # | Bit |
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Minimum number of bits required to represent every member of the set.
Enumerations and Subranges
HP Pascal allocates and aligns variables of enumeration and subrange
types the same way. An enumeration of
n
elements and the subrange 0..
n
-1
are equivalent. The allocation and alignment are based on the values of
the subrange or the ordinal value of the enumeration.
Example
TYPE
enum_type = (red,blue,yellow); {enumeration of 3 elements}
subr_type = 0..2; {subrange 0..(3-1)}
VAR
enum_var : enum_type;
subr_var : subr_type;
The compiler allocates and aligns the variables enum_var and subr_var the
same way.
The allocation and alignment of an enumeration or subrange variable
depends on whether it is:
* Unpacked.
* An element of a packed array.
* A field of a packed record.
* In a crunched structure.
Unpacked Enumeration or Unsigned Subranges
Table 5-7 shows how the HP Pascal packing algorithm allocates and
aligns unpacked enumeration or unsigned subrange variables.