HP XP P9000 Continuous Access Synchronous for Mainframe Systems User Guide
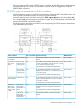
The following table lists the internal macro commands for scripting.
DescriptionMacroType
Set (define) a list of items.SetListFor lists
Add items to a list.AddList
Declares the beginning of a script.StartFor non-lists
Declares the end of a script.End
Suspends script execution for the specified length of time.Delay
Executes a script conditionally.If
Terminates a script conditionally.EndIf
Makes strings; converts numeric value to character string.MakeString
The Message command is not yet supported.Message
Scripting syntax
Before you create a script, make sure you understand the statement and syntax requirements.
Syntax overview
A script file can be written using any text editor (for example, WordPad, NotePad). A script file
consists of an unlimited number of statements that consist of macros (commands), work variables,
and comments. The first executable statement in a script file must be the Start macro, and the last
statement must be the End macro. Each line in a script file cannot exceed 320 bytes. A leading
blank is ignored, and a leading tab character (0x09) is converted to a space (0x20). A tab
character (0x09) within a string is not converted to a space.
Each script file should contain the five script statements:
• A comment statement, including a short preface for the script: purpose, author, usage,
description, operation, creation date, update date, and any reminder notes to the author. The
comment statement is a non-execution statement. A comment statement begins with “//”and
contains text (any character string) without any commands. Do not use the “//” symbol
anywhere else in a script file, only at the beginning of a comment statement.
• A macro statement, which is an execution statement. Only one macro instruction can be set
per line; however, a single macro can span more than one line.
• A work variable statement, which is also an execution statement. Only one work variable
statement can be set per line; also, a work variable statement cannot span more than one
line.
• A blank statement, which is a non-execution statement. An empty statement is a non-execution
statement.
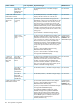
The following table describes scripting syntax.
DescriptionStatement name
Space or Tab with a returnBlank statement
One line beginning with //Comment statement
Return onlyEmpty statement
Work variable statement (non-list type work variable = constant)Execution statement
Macro name [parameter list]Macro statement
Scripting syntax 127