HP XP P9000 Business Copy User Guide (AV400-96573, July 2013)
Table Of Contents
- HP XP P9000 Business Copy User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Business Copy overview
- 2 Requirements and planning
- 3 Sharing Business Copy volumes
- Cache Residency
- Fast Snap and Snapshot
- Data Retention
- Thin Provisioning and Smart Tiers
- External Storage Access Manager
- LUN Manager
- Open Volume Management
- Resource Partition
- Continuous Access Synchronous
- Continuous Access Journal
- External Storage
- Auto LUN
- 4 Performing configuration operations
- 5 Performing pair operations
- 6 Monitoring and maintaining the system
- 7 Troubleshooting
- 8 Support and other resources
- A Interface support for BC operations and options
- B Business Copy GUI reference
- Replications window
- Local Replications window
- View Pair Properties window
- View Pair Synchronous Rate window
- View Histories window
- Consistency Group Properties window
- Create Pairs wizard
- Split Pairs wizard
- Resync Pairs wizard
- Suspend Pairs window
- Delete Pairs window
- Edit Mirror Units dialog box
- Change Options dialog box
- Add Reserve Volumes Wizard
- Remove Reserve Volumes window
- Edit Local Replica Option wizard
- C Configuration operations (secondary window)
- D Pair operations (secondary window)
- E Monitoring and maintaining the system (secondary window)
- F Business Copy GUI reference (secondary window)
- Glossary
- Index
RAID Manager and consistency groups
With RAID Manager you use a command line interface for running most of the same operations
as are performed with RWC. Pair commands are issued directly from the host. Commands can
also be automated using scripts.
Using RAID Manager, you can specify multiple pairs as a consistency group. With a consistency
group, you perform tasks on multiple pairs at the same time. This also allows changes the pair
status for all the pairs in a group.
Initial and update copy operations
Creating a pair causes the storage system to create an initial copy. The storage system
asynchronously copies updates received by the P-VOL to the S-VOL. Before the pair is created, the
pair’s status is SMPL. While the initial copy is in progress, the status is COPY(PD)/COPY. When
the initial copy is complete, the volumes are paired (PAIR status).
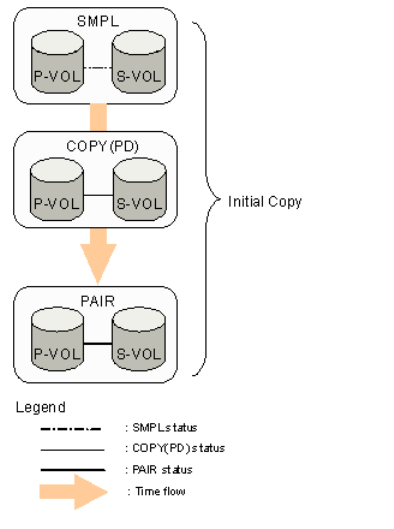
Initial copy
Creating a pair causes the storage system to start the initial copy and copies all the data in the
P-VOL to the S-VOL.
• Before the pair is created, the pair’s status is SMPL.
• While the initial copy is in progress, the status is COPY(PD)/COPY.
• The status changes to PAIR when the initial copy is complete.
A P-VOL continues receiving updates from the host during the initial copy. When the initial copy
is completed, update copy operations start.
Update copy
I/O sent to the P-VOL that is paired (PAIR status) is marked as differential data and stored in bitmaps
for transfer to the S-VOL. Update copy operations are performed periodically by the storage system.
The timing of the update copy operation is based on the amount of differential data that accumulates
and the elapsed time since the previous update.
10 Business Copy overview