HP XP P9000 Business Copy User Guide Abstract This guide explains how to use HP XP P9000 Business Copy Software to create nondisruptive, high-speed internal copies of information stored by open-systems hosts on HP XP P9000 disk arrays and attached heterogeneous external storage systems. Topics include how to create, split, suspend, resynchronize, and troubleshoot Business Copy pairs using the Remote Web Console web client.
© Copyright 2010, 2013 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
Contents 1 Business Copy overview..............................................................................7 How Business Copy works.........................................................................................................7 Hardware and software components...........................................................................................7 Volume pairs (primary volumes and secondary volumes)...........................................................8 Cascaded pairs.................
System options that affect performance......................................................................................38 Setting performance options................................................................................................39 5 Performing pair operations........................................................................40 Pair operations workflow.........................................................................................................40 Check pair status......
Typographic conventions.........................................................................................................71 A Interface support for BC operations and options...........................................73 Operations supported by Remote Web Console, RAID Manager...................................................73 Consistency group operations supported by Remote Web Console, RAID Manager.........................73 B Business Copy GUI reference...........................................
Status, pair operations permitted (secondary window)..........................................................125 Reviewing pair, volume details...........................................................................................126 Reviewing S-VOL path information......................................................................................127 Reviewing pair, license information ....................................................................................
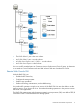
1 Business Copy overview Business Copy (BC) uses local mirroring technology to create and maintain a full copy of any volume in the storage system. With BC software you can create one or more copies of a data volume within the same storage system. You can use BC copies as backups, with secondary host applications, for data mining, for testing, and other uses — while business operations continue without stopping host application I/O to the production volume.
Volume pairs (primary volumes and secondary volumes) A pair consists of the P-VOL and secondary data volume. Each P-VOL can be paired with up to three S-VOLs. Thus, you can create three pairs using one P-VOL. During most operations, the P-VOL remains available to the host for I/O operations. Updating the P-VOL regularly copies the new data, the differential data, to the S-VOL. Because S-VOLs are updated asynchronously, the P-VOL and S-VOLs may not be identical.
• The P-VOL of the L1 pair is the root volume. • An S-VOL of the L1 pair is a node volume. • A P-VOL of an L2 pair is an L1 S-VOL — a node volume. • An S-VOL of an L2 pair is a leaf volume. You can use BC cascaded pairs as Continuous Access Synchronous (Cnt Ac-S) pairs. A distinction is not made in Cnt Ac-S between node and leaf volumes. Both are considered as S-VOLs. Remote Web Console GUI With the RWC GUI, you: • Enable the BC license key. • Configure the storage system.
RAID Manager and consistency groups With RAID Manager you use a command line interface for running most of the same operations as are performed with RWC. Pair commands are issued directly from the host. Commands can also be automated using scripts. Using RAID Manager, you can specify multiple pairs as a consistency group. With a consistency group, you perform tasks on multiple pairs at the same time. This also allows changes the pair status for all the pairs in a group.
Though the volumes are paired (PAIR status), data in the P-VOL and S-VOLs may not be the same because update copying occurs asynchronously, and therefore later data exists in the P-VOL. You can ensure that P-VOL and S-VOLs data are the same at a certain point in time, by splitting pair. Also, data in the P-VOL and the data in the S-VOL may not be the same if a copy operation is completed without host I/O. As mentioned above, the P-VOL and S-VOLs can be made the same by splitting the pair.
2 Requirements and planning This chapter describes system requirements and recommendations for planning a BC system. System requirements The following table shows minimum requirements for BC. Item Requirement BC license capacity Based on purchased capacity. For more information, see “License capacity requirements” (page 13). License key Must be installed. For more information about installation, see the HP XP P9000 Remote Web Console User Guide.
Item Requirement Maximum number of pairs decreases if LUSE volumes are used. Consistency groups • You can configure up to 256 consistency groups in a storage system, including BC, BC Z, Fast Snap (FS), and Snapshot (SS) consistency groups. Note: BC, BC Z, FS, and SS pairs cannot co-exist in the same consistency group. • You can define up to 8,192 BC pairs in a consistency group. Note: LUSE volumes that contain n LDEVs should be counted as n volumes.
Differential tables (tables managing differential bitmaps) and pair tables are required to create pairs. You must supply an adequate number of tables to handle all the pairs you plan to create. The number of differential and pair tables that are present in the system depends on additional shared memory that is installed. Therefore, you must ensure that you have sufficient additional shared memory to handle the number of pairs.
To calculate the number of differential and pair tables for emulation types other than OPEN-V Total number of differential tables per pair = (volume capacity KB ÷ 48) + (number of the control cylinders* × 15) ÷ (20,448**) * See the following table. ** Number of slots that can be managed by a differential table Round up the total number to the nearest whole number.
where: • (α): Required number of differential tables per pair (per previous calculation). • (β): Number of differential tables available in the system (Table 1 (page 14)). • (γ): The required number of pair tables per pair (per previous calculation). • (δ): The number of pair tables available in the system (Table 1 (page 14)).
Table 3 Volume Information for BC CU Port GID: LUN Pair Volume Type Associated L1 S-VOLs Associated L1 P-VOLs AssociatedL2 S-VOLs Associated L2 P-VOL 0 1A 0:00 L1 P-VOL 1B-0:00, 2A-0:00, 2B-0:00 NA NA NA 0 1A 0:01 L1 P-VOL 1B-0:01, 2A-0:01, 2B-0:01 NA NA NA etc...
• When using multiple software products simultaneously. If you are using more than one software product at the same time, ensure that your storage system is configured for optimal performance, such as sufficient cache. Contact HP Technical Support. Concurrent use affects the performance and the operation of the other software products. • When using AIX host servers. Best performance results when P-VOLs are located on one AIX host server and paired S-VOLs on another.
The following is a list of requirements and restrictions: • RAID Manager is required to run this and all operations on the pairs in the consistency group. If you have performed pair operations using the RWC after creating pairs using RAID Manager, you cannot use consistency group pair-split. • You can use consistency group pair-split when BC P-VOLs are shared with Cnt Ac-J or Cnt Ac-S S-VOLs. For more information, see “The consistency group pair-split for shared volumes” (page 19).
The following takes place when you run consistency group pair-split with shared Cnt Ac-J volumes: 1. Cnt Ac-J restore journal data created before the split time is restored to Cnt Ac-J S-VOLs (BC P-VOLs). 2. Restore journal operations are suspended when Cnt Ac-J detects restore journal data with a time stamp later than the split time. After the Cnt Ac-J suspension, the BC split operations run. 3. When BC split operations are completed, Cnt Ac-J resumes the suspended restore journal operations.
The following table shows when you can perform consistency group pair-split based on status of the BC pairs in the consistency group that are not paired (status other than PAIR), and the resulting pair status after you perform consistency group pair-split.
case, the consistency group pair-split ends abnormally and the status of all of the pairs in the consistency group remains the same.
3 Sharing Business Copy volumes You can share BC volumes with other HP software product volumes. This chapter discusses requirements, recommendations, and restrictions for sharing volumes. Cache Residency You can use volumes with Cache Residency settings as BC P-VOLs and S-VOLs. NOTE: For important information about the operation and volumes with Cache Residency settings, see the bullet on Quick Restore in “Planning for performance” (page 17).
BC operation FS or SS pair status Delete a pair COPY1 PAIR, PFUL PSUS, PFUS COPY2 RCPY PSUE YES YES YES YES YES YES (pairsplit -S) 1. COPY status during initial copy. 2. COPY status during resynchronization. 3. After executing the pairsplit command on the FS or SS pair, you must confirm that all pairs in the FS or SS consistency group are in PSUS status before performing the BC operation.
You can also set access attributes for BC P-VOLs, S-VOLs, and reserve volumes. For BC pair operations and reserve attribute change operations after access attribute setting, see the following tables. NOTE: The Data Retention access attributes of volumes do not change as a result of BC operations. Even though the Quick Restore operation reverses the P-VOL and S-VOL, the access attributes of the P-VOL and S-VOL are not reversed. The following table shows volume access attribute and BC pair operations.
Volume specified by BC Attribute setting Pair status Volume Read/Write Read Only, Protect, or S-VOL Disable PSUS(SP)/PSUS P-VOL or S-VOL YES YES PSUS P-VOL or S-VOL YES YES SMPL(PD) P-VOL or S-VOL YES YES COPY(RS)/COPY P-VOL YES YES S-VOL YES NO COPY(RS-R)/RCPY P-VOL or S-VOL YES NO PSUE P-VOL or S-VOL YES YES Thin Provisioning and Smart Tiers You can use Thin Provisioning (THP) and Smart Tiers (Smart) volumes with BC P-VOLs and S-VOLs.
BC pair operations are limited according to the ESAM pair status. The following table shows the pair operations that are allowed.
Continuous Access Synchronous You can share Cnt Ac-S volumes with BC volumes. • You can share BC P-VOLs and S-VOLs with Cnt Ac-S P-VOLs and S-VOLs. However, you cannot share a BC S-VOL with a Cnt Ac-S S-VOL. • When you share a BC P-VOL with a Cnt Ac-S S-VOL, the write operation on the Cnt Ac-S P-VOL takes more time. This is especially true when the BC pair is in the PSUS(SP) status because of the copying time needed for the BC pair. • You can use both L1 and L2 pairs with Cnt Ac-S volumes.
For more information about these configurations, see the HP XP P9000 Continuous Access Journal User Guide. Sharing volumes in a 3-Cnt Ac-J DC multi-target configuration You can share BC volumes with Cnt Ac-J volumes in 3 DC multi-target configurations. You can share the BC P-VOL and S-VOLs with Cnt Ac-J volumes, as shown in the following figure.
The following table shows the supported BC operations when the P-VOL is shared with Cnt Ac-J S-VOL (intermediate or remote site). Cnt Ac-J* pair status BC operations Create, Split, Suspend, Delete, Resync--Normal Copy, Quick Resync Resync -- Reverse Copy, Quick Restore PAIR or COPY(PD)/COPY* YES NO PSUS/SSWS YES YES * Note: • If the BC P-VOL is shared with the intermediate site’s Cnt Ac-J S-VOL, then check Cnt Ac-J status for the local-intermediate pair.
Sharing volumes in a 3-Cnt Ac-J DC cascade configuration You can share BC volumes with Cnt Ac-J volumes in 3 DC cascade configurations. You can share BC P-VOL and S-VOLs with Cnt Ac-J volumes, as shown in the following figure. Figure 3 BC volumes in a 3-Cnt Ac-J DC cascade configuration When associated with these configurations, BC pair operations are dependent on the pair status of the Cnt Ac-J local-intermediate pair and the local-remote pair.
The following table shows the BC operations that you can perform when the P-VOL is shared with Cnt Ac-J S-VOL/P-VOL at intermediate site. Cnt Ac-J local-intermed. pair status Cnt Ac-J intermed.
The following table shows the BC operations that you can perform when the P-VOL is shared with the Cnt Ac-J P-VOL/delta resync at the local site. Cnt Ac-J local-intermed.
These sections describe the configurations and supported BC operations. For more information about these configurations, see the HP XP P9000 Continuous Access Journal User Guide. Sharing volumes in 3-Cnt Ac-J/Cnt Ac-S DC multi-target and delta resync configurations You can share BC P-VOL with Cnt Ac-S and Cnt Ac-J volumes at the intermediate and remote sites in 3DC multi-target and delta resync configurations, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 5 Cnt Ac-J, Cnt Ac-S, and BC Shared Volume Configuration 1 Figure 6 Cnt Ac-J, Cnt Ac-S, and BC Shared Volume Configuration 2 You can perform all BC operations, with the following exceptions, in the intermediate site, irrespective of Cnt Ac-S pair status. The Cnt Ac-J delta resync pair’s status must be HOLD or HLDE: • You can perform Reverse Copy only when the Cnt Ac-S and Cnt Ac-J pair status is PSUS, PSUE, or SSWS. • You cannot perform the Quick Restore.
You cannot use migration, destination, and reserved volumes of Auto LUN for BC pair operations. To perform BC operations, you must first release the Auto LUN volumes. You can assign BC volumes as Auto LUN volumes, with the following restrictions: 36 • If the BC S-VOL is paired with three T-VOLs, you must delete the pair before migrating the volumes with Auto LUN.
4 Performing configuration operations This chapter provides instructions for configuring BC. Configuration workflow Setup for BC consists of the following operations. You must have Storage Administrator (Local Copy) role to perform BC operations. • “Setting up primary and secondary volumes” (page 37). • “Reserving secondary volumes” (page 37) • “System options that affect performance” (page 38) Setting up primary and secondary volumes The P-VOL and S-VOLs must be set up prior to making copies.
Related information • “Removing reserve attribute from a volume” (page 59) System options that affect performance You can enable and disable the following options that affect performance. (To go directly to the procedure, see “Setting performance options” (page 39)). • Swap&Freeze. Alters the behavior of the quick restore operation. With Swap&Freeze, update copy operations are suppressed when the quick restore is completed and the pair is in PAIR status. Differential data is not copied to the new S-VOL.
Setting performance options 1. 2. 3. In the tree, click Replications > Local Replications. In the Local Replications window, click Edit Local Replica Options. In the Edit Local Replica Options window, for System Type, select Business Copy. 4. In the System Options list, select the option you want and click Enable. You may need to scroll down to the option you want. Copy Threshold must be enabled by your service representative. Click Finish. In the Confirm window, enter a Task Name then click Apply. 5.
5 Performing pair operations This chapter provides instructions for performing BC pair operations using RWC. Also included is an operation for splitting pairs by consistency group, using RAID Manager. Pair operations workflow A typical workflow for performing pair operations consists of the following. You must have Storage Administrator (Local Copy) role to perform BC operations. • “Check pair status” (page 40). Each operation requires a pair to have a specific status.
Prerequisite information for creating pairs • Make sure that your volumes are set up for pairing. For more information, see “Planning pair volumes” (page 13). • Volumes should be in SMPL status. However, for L1 and L2 pairs, check the status. For more information on the L1 and L2 permitted statuses, see “Status for L1, L2 pairs and operations permitted” (page 55). • When creating an L1 pair and an L2 pair at the same time, specify Non Split as the Split Type.
To change a pair’s L1 and L2 combination from the preceding topology to the one shown in the following figure, for example, you would continue through the Create Pairs wizard to the Select Secondary Volumes window. In the Select Secondary Volumes window, after pairing S-VOLs with P-VOLs, in the Selected Pairs table you would select the line with the S-VOLs whose configuration you want to modify, and then click Edit MU Number.
Creating pairs 1. 2. 3. In the tree, click Replications > Local Replications. In the Pairs tab, click Create Pairs. In the Select Pair Configuration window of the Create Pairs wizard, select the Copy Type, Business Copy. 4. 5. Select the Emulation Type. In Pair Topology Type, select the boxes that matches your configuration. For more information, see “On creating L1 and L2 pairs with different topologies” (page 41). 6. 7. 8. 9.
10. Click Next. 11. In the Select Secondary Volumes window, assign LDEVs as S-VOL to the P-VOL LDEV (or LDEVs) selected in the Select Primary Volumes window. Complete the following: • If you specified a P-VOL, select a secondary LDEV ID in the Available LDEVs table, and click Set. Repeat this step to assign additional S-VOLs. • If you specified more than one P-VOL, select an LDEV ID in the Available LDEVs table, then select a P-VOL LDEV ID in the Selected Pairs table, and click Set.
• Change Options in the middle-right allows you to change Split Type and Copy Pace (applies to all new pairs). • To change MU numbers, complete the following: a. Select the desired primary/secondary line in the Selected Pairs table. b. Click Edit Mirror Unit near the bottom-right which results in a modified pair topology after specifying S-VOL. For more information on changing a pair’s topology, see “On creating L1 and L2 pairs with different topologies” (page 41).
The P-VOL and S-VOL are synchronized when the pair status changes from PSUS(SP)/PSUS or COPY(SP)/COPY to PSUS.
The following table shows the affects of these conditions. System option mode 459 S-VOL PSUS(SP)/PSUS or COPY(SP)/COPY status OFF Internal volume Pair status changes to PSUS(SP)/PSUS after differential data is copied to the cache in the storage system External volume ON Internal volume External volume Pair status changes to PSUS after differential data is copied to the cache in the storage system and destage to the external storage system has completed.
For more information about splitting pairs, see “Splitting consistency group pairs with consistency group pair-split” (page 119). For more information about troubleshooting consistency group pair-split and the consistency group pair-split option, see “Troubleshooting the consistency group pair-split” (page 68). 1. Define a consistency group for the BC pairs that you are splitting. Complete the following: a.
• Reverse Copy. Reverse full resync from S-VOL to P-VOL. ◦ The P-VOL is inaccessible to hosts. ◦ All differential data is updated to the P-VOL. ◦ Pairs sharing the same P-VOL must be in PSUS or PSUE status. ◦ If the pair shares a volume with Cnt Ac-S or Cnt Ac-J, you must suspend the Cnt Ac-S or Cnt Ac-J pair to perform the Reverse Copy or Quick Restore operation. ◦ You cannot create a Cnt Ac-S or Cnt Ac-J pair with a volume shared by BC during the Reverse Copy or Quick Restore operation.
• For Reverse Copy or Quick Restore, the pair must be in PSUS status. • The pairresync normally takes less time when the pair is in PSUS status than when it is in PSUE. This is because the amount of differential data accumulated for a split pair is usually much less than the total amount of data in the P-VOL, which must be copied in full when the pair was suspended by the storage system.
NOTE: The following concerns possible post-resync conditions: • Make sure that pair status changes to PAIR before attempting any other operation. • If the reverse or quick restore operation ends abnormally, the pair status changes to PSUE. In this case, the P-VOL is read/write-enabled for all hosts, but the data is not guaranteed. The S-VOL remains write-disabled and data is not guaranteed. The status of other pairs sharing the same P-VOL does not change.
3. In the Delete Pairs window, enter a Task Name and click Apply. After performing the pairdelete operation, if you do not see the number of pairs and other information you expect to see in the Summary tab of the Local Replications window, the system is working and requires more time. Wait a little longer, then click File/Refresh.
6 Monitoring and maintaining the system This chapter provides information and instructions for monitoring and maintaining the BC system. Monitoring the system Monitoring helps you keep track of pairs and volumes and their current and past conditions. Monitoring should be an ongoing activity. This section provides information for the following: • “Monitoring pair activity, status ” (page 53).
(For the RAID Manager status names, see “RAID Manager pair status names” (page 54). RWC Status Description S-VOL access SMPL The volume is not assigned to a pair. The storage system accepts read/write for SMPL N/A volumes that are not reserved. Note: If the volume is in SMPL status, the status is not shown in RWC. SMPL(PD) The pair is being deleted. Pair operations are not allowed in this status. Upon deletion, Read/write the status changes to SMPL.
RWC pair status name RAID Manager pair status name COPY(RS-R)/RCPY RCPY PSUE PSUE Status, pair operations permitted A pair’s status shows whether a desired operation can be performed. Each operation requires a specific status, or is permitted for multiple possible statuses. Supported operations and statuses are shown in the following tables.
Table 6 Supported L1 pair operations for related L2 Status (continued) L2 Pair Status L1 pair operation Create pairs Split pairs Resync pairs Suspend pairs Delete pairs COPY(RS)/COPY YES YES YES YES YES COPY(RS-R)/RCPY NO NO NO YES YES PSUE YES YES YES YES YES Table 7 Supported L2 pair operations for related L1 Status L1 Pair Status L2 pair operation Split pairs Resync pairs1 Suspend pairs Delete pairs COPY(PD)/COPY YES NO YES YES YES PAIR YES NO YES YES YES COPY(SP)/CO
Status of unaffected S-VOLs, operations permitted The pair operations you can perform depend on the pair’s status, but also on the status of unaffected S-VOLs. The following table shows which operations can be performed, given the status of S-VOLs related to the P-VOL in other pairs.
Related information • “Local Replications window” (page 76) Monitoring reserve volumes You can see the number of reserve volumes and a list of the individual reserve volumes and their details. • View the number of reserve volumes in the Summary section of the Local Replications window. • View a list of reserve volumes and their details on the Reserve Volumes tab in the Local Replications window.
Code Description Explanation 4790 PSUE SUSPEND The pair was suspended and pair status has changed to PSUE. 47D0 COPY ABNORMAL END The copy has terminated abnormally for reasons other than above. 47E9 INITIALIZE START Initialization processing has begun. 47EA INITIALIZE END Initialization processing has terminated normally. 47EB INITIALIZE ENDED ABNORMAL Initialization processing has terminated abnormally.
7 Troubleshooting This topic provides BC troubleshooting information. Business Copy Troubleshooting This section provides instructions for troubleshooting in BC. Operation and display troubleshooting The following table provides operation and display troubleshooting information for BC pairs. Error Corrective action RWC hangs, or BC operations do not function properly. • Make sure all BC requirements and restrictions are met. • Make sure the storage system is powered on and fully functional.
Cause Response The S-VOL’s HDD or external storage has an error. Check the error and make the necessary correction. The P-VOL’s HDD or external storage has an error. Check the error and make the necessary correction. Troubleshooting with RAID Manager This section provides troubleshooting information for operations performed using RAID Manager. The following describes RAID Manager error codes and instructions for using them. Also, see “Troubleshooting the consistency group pair-split” (page 68).
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description 201B The consistency group pair-split was rejected because the Cnt Ac-J pair was not in PAIR status, split (PSUS status), or suspended (PSUE status). The Cnt Ac-J S-VOL was the BC P-VOL included in the consistency group on which the consistency group pair-split was performed. 2026 The quick restore operation was rejected because the cache mode of the P-VOL you specified was different from the cache mode of the external S-VOL.
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description 2078 Because the P-VOL you specified was also a Cnt Ac-J P-VOL for delta resync, one of the following errors occurred: • The reverse copy operation was rejected because the Cnt Ac-J pair was not split (PSUS status). • The quick restore operation was rejected. 2079 The pair operation was rejected because the P-VOL you specified was also a Cnt Ac-J P-VOL for delta resync.
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description 20B7 The pair operation was rejected because you did not define an LU path to the volume you specified as the P-VOL. 20B8 The pair operation was rejected because you did not define an LU path to the volume you specified as S-VOL. 20D0 The P-VOL rejected the paircreate operation because the THP pool is initializing in the Thin Provisioning or Smart Tiers V-VOL.
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description • The consistency group pair-split was rejected because some of the pairs in the consistency group were being resynchronized, split, or were already suspended. • The pair operation was rejected because the pair status of the P-VOL, the S-VOL, or both showed that the pair could not receive the issued command. 2312 The pair operation was rejected because the volume you specified as the S-VOL was online to the host.
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description 2337 The pair operation was rejected because of one of the following reasons: • The volume you specified as the P-VOL is an intermediate volume. • The number of volumes you specified for P-VOLs combined as a LUSE volume differs from that for S-VOLs. • You specified only P-VOLs for the LUSE volume. • You specified only S-VOLs for the LUSE volume.
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description 235B The volume you specified as a P-VOL was a Cnt Ac-S P-VOL. The reverse copy or the quick restore operation was rejected because the Cnt Ac-S pair was not suspended (PSUE status) or split (PSUS status). 235C The volume you specified as a P-VOL was a Cnt Ac-S S-VOL. Because the Cnt Ac-S pair was not suspended (PSUE status) or split (PSUS status), the reverse copy or the Quick Restore operation was rejected.
Table 10 RAID Manager Error Codes (continued) SSB2 code Description 239E The Paircreate operation was rejected because the Protect attribute was set for the volume you specified as the S-VOL. 23A8 The quick restore or reverse copy operation was rejected because the volume you specified as the volume was specified as the P-VOL for XRC. 23A9 The quick restore or reverse copy operation was rejected because the volume you specified as the volume was specified as the P-VOL for CC.
◦ The BC pair is a part of cascaded pairs. The other pairs in the cascaded pairs are in a status that does not allow the pairsplit operation. For more information, see “Status for L1, L2 pairs and operations permitted” (page 55). ◦ A BC pair volume is also used in a Cnt Ac-S (Cnt Ac-S) or Cnt Ac-J pair. The Cnt Ac-S or Cnt Ac-J pair is in a status that does not allow the pairsplit operation. After these factors are removed, perform the pairresync operation, and run the pairsplit command.
8 Support and other resources Contacting HP For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website: http://www.hp.
HP websites For additional information, see the following HP websites: • http://www.hp.com • http://www.hp.com/go/storage • http://www.hp.com/service_locator • http://www.hp.com/support/manuals • http://www.hp.com/support/downloads • http://www.hp.
Table 11 Document conventions (continued) Convention Element Monospace text • File and directory names • System output • Code • Commands, their arguments, and argument values Monospace, italic text • Code variables • Command variables Monospace, bold text WARNING! CAUTION: IMPORTANT: NOTE: TIP: 72 Emphasized monospace text Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death. Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
A Interface support for BC operations and options This appendix lists BC operations and options, and consistency group operations and options, and the interfaces that support them. Operations supported by Remote Web Console, RAID Manager The following table lists BC operations and options supported by RWC and RAID Manager.
Table 13 Consistency group operations by user interface Operation Option RWC RAID Manager Command Option Reserve CG No options YES Not necessary Not necessary Remove CG reserve No options YES Not necessary Not necessary Add pairs to a CG No options NO paircreate -m grp [CTGID] MU number NO paircreate Uses MU# in HORCM.
B Business Copy GUI reference This appendix describes BC windows and dialog boxes in RWC. Replications window Use this window to view pair information for local replication. Summary tab Item Description Licensed Capacity The used and licensed capacity of each product. Number of Replica LDEVs The number of LDEVs used for all local replication pairs. Number of FC Z/FCSE Relationships The number of relationships that Compatible FlashCopy and Compatible FlashCopy SE use.
Replica LDEVs tab Item Description LDEV ID The selected LDEV’s identifier LDEV Name The selected LDEV’s name Emulation Type The selected LDEV’s emulation type Capacity The selected LDEV’s capacity Copy Type Shows the following copy types: • BC-L1: BC L1 P-VOL or S-VOL • BC-L2: BC L2 P-VOL or S-VOL • FS: FS P-VOL or S-VOL • SS: SS P-VOL or S-VOL • BC Z: BC Z P-VOL or S-VOL • FC Z: Compatible FlashCopy relationship • FCSE: Compatible FlashCopy SE relationship Export button Click to open the dialo
Summary tab Item Description Number of Pairs The number of pairs for each local replication software type Number of Consistency Groups The number of consistency groups whose status is other than Free Number of Reserve Volumes The number of reserved volumes.
Item Description Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank. For BC, BC Z, and SS, a hyphen (-) is shown. Status Shows the following icons and pair status names: (SIMPLEX and SMPL are not statuses that are shown in RWC.) • The pair is being deleted. Status names are: BC, FS: SMPL(PD) BC Z: Deleting/TRANS • This icon is used for the following: The pair is being copied.
Item Description Status, continued • This icon is used for the following: The pair is split. Status names are: BC: PSUS BC Z: Split/SUSPOP The pair is being split in Quick Split mode. Status names are: BC: PSUS(SP)PSUS BC Z: V-Split/SUSPVS The pool is full. Status name is: FS, SS: PFUS • The pair is suspended. Status names are: BC: PSUE BC Z: Supend/SUSPER For more information, see “Pair status definitions” (page 53). Secondary Volume • LDEV ID: The S-VOL’s LDEV identifier.
Item Description Split Pairs button Click to open the Split Pairs window. Resync Pairs button Click to open the Resync Pairs window. View Pair Synchronous Rate* Opens the View Pair Synchronous Rate window. View Pair Properties* Opens the View Pair Properties window. Suspend Pairs* Opens the Suspend Pairs window. Delete Pairs* Opens the Delete Pairs window. Export* Opens the dialog box for downloading table information to a file. *An option you can choose from the More Actions menu.
Item Description CTG ID The consistency group identifier. Click to open the Consistency Group Properties window. Status Possible values include: • BC Used: Consistency group used by BC. • BC Z Used (RAID Manager): Consistency group used for BC Z pairs and managed with RAID Manager. • BC Z Used (PPRC/BCM): Consistency group used for BC Z pairs and managed using PPRC or BCM. • FS Used: Consistency group used by FS pairs. • SS Used: Consistency group used for SS pairs.
Pair Properties tab Item Description Copy Type The type of pair: • Business Copy • Business Copy for Mainframe • Fast Snap • Snapshot Pool Name (ID) (FS and SS only.) The pool name and ID. If you have not set a pool name for FS pairs, this item is blank. For BC and BC Z, a hyphen (-) is shown. Most Recent Snapshot Date (FS and SS only.) The date and time that the most recent snapshot was acquired. If you have not set a most recent snapshot date for FS pairs, this item is blank.
Item Description The snapshot group name. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank. For BC, BC Z and SS, a hyphen (-) is shown. Status The pair status. For more information, see “Pair status definitions” (page 53). Secondary Volume • LDEV ID: The S-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV name: The S-VOL’s LDEV name. • Emulation Type: The S-VOL’s emulation type. • Capacity: The S-VOL’s volume capacity. • CLPR: The S-VOL’s CLPR number.
Pairs table Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name. • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number. Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC L1 • BC-L2: BC L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank. For BC, BC Z and SS pairs, a hyphen (-) is shown. Status The pair status.
Item Description Mirror Unit The mirror unit number Refresh When clicked, updates the information in the Pairs table. View Histories window Use this window to review the operations that have been performed on pairs. You can view a maximum of 16,384 operation histories. For full information, see “Monitoring a pair’s operation history ” (page 58).
Histories table Item Description Date The operation date and time Primary Volume (Source Volume for FC Z/FCSE) • LDEV ID: The P-VOL/source volume’s LDEV identifier • Provisioning Type: The provisioning type. Values: - Basic: Internal volume - THP: THP V-VOL - External: External volume - External MF: Migration volume Secondary Volume (Target Volume for FC Z/FCSE) • LDEV ID: The secondary/target volume’s LDEV identifier. • Provisioning Type: The provisioning type.
Consistency Group Properties table Item Description CTG ID The consistency group identifier Status The consistency group status • BC Used: The consistency group is in use by BC. • BC Z Used (RAID Manager): The consistency group is used by BC Z and managed with RAID Manager. • BC Z Used (PPRC/BCM): The consistency group is used by BC Z and managed with PPRC/BCM. • FS Used: The consistency group is used by FS. • SS Used: The consistency group is used by SS.
Pairs table This table shows pairs for P-VOL and/or S-VOL to which you are allocated. Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name. • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type. • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity. • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number. Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC L1 • BC-L2: BC L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name.
This wizard includes the following windows: • Select Pair Configuration window • Select Primary Volumes window • Select Secondary Volumes window • Confirm window For full information, see “Creating pairs” (page 43). Select Pair Configuration window Use this window to configure the pairs you will create. Item Description Copy Type The copy type. Values: Business Copy, Business Copy for Mainframe, FS, or Snapshot Emulation Type The emulation type. For FS or SS, you can only specify OPEN-V.
Select Primary Volumes window Use this window to select LDEVs that are P-VOLs. Item Description Use Primary Volumes of BC/SS Pairs (FS and SS only.) Indicates whether the P-VOLs are used. • Yes: Only FS and SS P-VOL LDEVs are shown in the Available LDEVs table. • No: Only unpaired LDEVs are shown in the Available LDEVs table. Port ID (BC/SS, FS, SS only.) Filters LDEVs in the Available LDEVs table according to the port ID. Host Group Name (BC/SS, FS, SS only.
Item Description Capacity Capacity of the LDEV CLPR CLPR number of the LDEV Number of Secondary Volumes The number of S-VOLs. (BC only) The number for an L1 pair does not include the number of L2 S-VOL. Primary Volumes (FS and SS only.) Information about the P-VOL when the LDEV is used as a S-VOL for an existing pair. Values: • LDEV ID: The LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The LDEV name. • Port ID: The port name of the LDEV’s LUN path. • Host Group Name: The host group name of the LDEV’s LUN path.
Item Description Emulation Type The emulation type of LDEV Capacity The capacity of LDEV. CLPR The cLPR number Number of Secondary Volumes The number of S-VOL. (BC only) The number for an L1 pair does not include the number of L2 S-VOL. Primary Volume (FS and SS only.) Information about the P-VOL. Values: • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier: • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name. • Port ID: The port name of the P-VOL LDEV’s LUN path.
Item Description Capacity list Allows you to filter the available LDEVs according to the capacity you select. The remaining number you have to select Refers to the selected P-VOLs in the Selected Pairs table that do not have an assigned S-VOL. Exclude Paired Volumes (BC/SS only.) Select to hide the volumes that are already in a pair from the list. Default: Selected Port ID (BC/SS, FS, and SS only.) Filters LDEVs in the Available LDEVs table according to the port ID.
Item Description Choose to create a new snapshot group or use an existing snapshot group. • Create new snapshot group: The new snapshot group name is entered. • Use defined snapshot group: An existing snapshot group is selected. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank. Change Options button (BC/SS and BC Z only.) Click to open the Change Options dialog box, from which you can change the Split Type and Copy Pace. Remove button Click to remove the pair from the table.
Item Description • Port ID: The port name of the P-VOL LDEV’s LUN path. For BC Z, this item is blank. • Host Group Name: The host group name of the P-VOL LDEV’s LUN path. For BC Z, this item is blank. • LUN ID: The LUN ID of the P-VOL LDEV's LUN path. For BC Z, this item is blank. • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type. • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity. Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank.
Item Description For FS and SS pairs, a hyphen (-) is shown. Pool Name (ID) (FS and SS only.) The pool name and ID number. For BC/SS and BC Z pairs, a hyphen (-) is shown. Confirm window Selected Pairs table Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name. • Port ID: The port name of the P-VOL LDEV’s LUN path. For BC Z, this item is blank. • Host Group Name: The host group name of the P-VOL LDEV’s LUN path. For BC Z, this item is blank.
Item Description New Snapshot Group (FS only.) • Yes: New snapshot group is used. • No: Existing snapshot group is used. Secondary Volume • LDEV ID: The S-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The S-VOL’s LDEV name. • Port ID: (FS and BC/SS only.) The port name of the S-VOL LDEV’s LUN path. • Host Group Name: (FS and BC/SS only.) The Host group name of the S-VOL LDEV’s LUN path. • LUN ID: (FS and BC/SS only.) The LUN ID of the S-VOL LDEV's LUN path. • Emulation Type: The S-VOL’s emulation type.
Selected Pairs table The same Selected Pairs table appears on the Confirm window and the Split Pairs window. Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: P-VOL’s LDEV identifier • LDEV Name: P-VOL’s LDEV name • Emulation Type: P-VOL’s emulation type • Capacity: P-VOL’s volume capacity • CLPR: P-VOL’s CLPR number Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC/SS L1 • BC-L2: BC/SS L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name.
Item Description Secondary Volume • LDEV ID: S-VOL’s LDEV identifier • LDEV Name: S-VOL’s LDEV name • Emulation Type: S-VOL’s emulation type • Capacity: S-VOL’s volume capacity • CLPR: S-VOL’s CLPR number Pool Name (ID) (FS and SS only.) The pool name and ID number. For BC/SS and BC Z pairs, hyphen (-) is shown. Mirror Unit Mirror unit number Split Type list The split type. Values: • Quick Split: Splits the pair immediately • Steady Split: After all differential data is copied, the pair is split.
Selected Pairs table Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC/SS L1 • BC-L2: BC/SS L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank.
For full information, see “Resynchronizing pairs” (page 50). Selected Pairs table Item Primary Volume Description • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC/SS L1 • BC-L2: BC/SS L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name.
Item Description Secondary Volume • LDEV ID: The S-VOL’s LDEV identifier • LDEV Name: The S-VOL’s LDEV name • Emulation Type: The S-VOL’s emulation type • Capacity: The S-VOL’s volume capacity • CLPR: The S-VOL’s CLPR number Snapshot Date (FS and SS only.) The date and time that a snapshot was acquired. For BC/SS and BC Z pairs, a hyphen (-) is shown. Pool Name (ID) (FS and SS only.) The pool name and identification number. For BC/SS and BC Z pairs, a hyphen (-) is shown.
Selected Pairs table Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC L1 • BC-L2: BC L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.) The snapshot group name. If you have not set a snapshot group for FS pairs, this item is blank.
Item Description For BC/SS and BC Z pairs, a hyphen (-) is shown. Mirror Unit The mirror unit number. Suspend Pairs window Use this window to suspend pair creation. For full information, see “Suspending pair creation” (page 45). Selected Pairs table Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name. • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type. • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity. • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number.
Delete Pairs window Use this window to delete pairs. For full information, see “Deleting pairs” (page 51). Selected Pairs table Item Description Primary Volume • LDEV ID: The P-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The P-VOL’s LDEV name. • Emulation Type: The P-VOL’s emulation type. • Capacity: The P-VOL’s volume capacity. • CLPR: The P-VOL’s CLPR number. Copy Type Shows the following types of pairs: • BC-L1: BC L1 • BC-L2: BC L2 • FS: FS • SS: SS • BC Z: BC Z Snapshot Group (FS only.
Item Description Secondary Volume • LDEV ID: The S-VOL’s LDEV identifier. • LDEV Name: The S-VOL’s LDEV name. • Emulation Type: The S-VOL’s emulation type. • Capacity: The S-VOL’s volume capacity. • CLPR: The S-VOL’s CLPR number. Snapshot Date (FS and SS only.) The date and time that a snapshot was acquired. For BC/SS and BC Z, a hyphen (-) is shown. Pool Name (ID) (FS and SS only.) The pool name and identification number. For BC/SS and BC Z, a hyphen (-) is shown.
Item Description Split Type • Non Split: Does not split the pair • Quick Split: Splits the pair immediately. Specify this if you want to have the S-VOL available for read and write I/O immediately after the pair split operation is issued. Any remaining differential data is copied to the S-VOL in the background. • Steady Split: After all differential data is copied, the pair is split. Default: Non Split Copy Pace (BC/SS and BC Z only.) The speed at which the split operation is performed.
Available LDEVs table Item Description LDEV ID The LDEV identification number. LDEV Name The LDEV name Emulation Type The emulation Type of each LDEV Capacity The capacity of each LDEV Number of Paths The number of paths to each LDEV Selected LDEVs table Item Description LDEV ID The selected reserved volume’s LDEV identifier.
For full information, see “Removing reserve attribute from a volume” (page 59). Selected Reserve Volumes table Item Description LDEV ID The selected reserved volume’s LDEV identifier LDEV Name The selected reserved volume’s LDEV name Emulation Type The selected reserved volume’s emulation type Capacity The selected reserved volume’s capacity Number of Paths The number of paths to each LDEV Edit Local Replica Option wizard Use this wizard to enable and disable options that affect performance.
BC/FS/SS System Options table Item Description System Option The options that you can change. Values: • Swap & Freeze • Host I/O Performance • Copy Pace Ext. Slower1 • Copy Pace Ext. Slower2 • Copy Pace Ext. None For more information, see “Setting performance options” (page 39). 110 Status Shows whether the option is currently enabled or disabled. Enable button Click to enable the selected option. Disable button Click to disable the selected option.
Confirm window BC/FS/SS System Options table Item Description System Option The options that can be changed. Status Shows whether the option is currently enabled or disabled.
C Configuration operations (secondary window) This appendix provides instructions for configuring BC using the previous RWC GUI, which opens in a secondary window. Configuration workflow Setup for BC consists of the following: 1. Ensuring that primary and secondary volumes are set up correctly. 2. (Optional) Reserving volumes for use as S-VOLs. 3. Setting the HOST I/O Performance option, which boosts I/O performance, though copy time slows as a result. (Optional.
7. In the Set Reserve Attribute dialog box, confirm that the volumes you want to reserve are shown and selected, then click OK. The selected volumes are shown in the Preview list. 8. In the Pair Operations window, click Apply. Reserving a consistency group A consistency group number is required when assigning pairs to a consistency group. Once you have assigned pairs to a consistency group, you can perform pair operations on the pairs in the group, including consistency group pair-split. 1.
Setting performance options You can enable and disable the following options that affect performance. For descriptions of these options, see “System options that affect performance” (page 38). If you have both BC Z and BC pairs, HP recommends that you enable this option on both; otherwise host I/O response may not improve. 1. In RWC, click Actions > Local Replications > BC/SS > Option. 2. 3. 114 Change to Modify mode by clicking the icon.
D Pair operations (secondary window) This appendix provides instructions for performing pair operations using the previous RWC GUI, which opens in a secondary window. Pair operations workflow A typical pair-operations workflow follows: • Check pair status. Each operation requires a pair to have a specific status. You also check pair status to ensure that an operation completed successfully. • Create the pair, in which the S-VOL becomes a duplicate of the P-VOL.
• When a pair is created, the S-VOL’s LDEV is allocated to the same processor blade to which the P-VOL’s LDEV is allocated. • You must first create the BC pair if you are using one of its volumes as a FS P-VOL. If an MU number is not available, complete the following: 1. Delete a FS pair whose MU number is 0-to-2. 2. Create a BC pair. 3. Create the FS pair. WARNING! The BC paircreate operation overwrites all existing data on the S-VOL.
9. Select an MU number for the pair. • An MU number can be assigned to only one pair. • Use 0, 1, or 2 for an L1 pair. • Use 1 or 2 for an L2 pair. 10. Show the volumes available for S-VOLs by selecting the following filters from the Select S-VOL box: • Select a Port to show associated volumes. • Select a Volume Type to show internal or external volumes. You can select both if desired. • Select an Attribute to show volumes previously reserved as S-VOLs, or volumes that are not reserved.
Prerequisite information • Pair status must be one of the following: ◦ If you are splitting an existing pair, PAIR ◦ If you are creating and immediately splitting an L1 pair, SMPL status ◦ If you are creating and immediately splitting an L2 pair, the L1 pair must be split (PSUS status) • For a split operation on an existing pair to complete faster, stop host access to the P-VOL.
1. 2. 7. 8. Ensure the pairs that you want to split are shown. Select the volume that is not assigned to a pair (SMPL status) that you want to be the P-VOL in an L1 pair-create-and-split operation. 3. Select the L1 pair whose S-VOL are the P-VOL in an L2 pair create and split operation. From Copy Pace, select the pace at which the pairs are to be split, Slower, Medium, or Faster. Copy Pace affects the host I/O performance: a slower pace minimizes impact, a faster pace has the greatest impact.
Prerequisite information • On registering split time: ◦ When you register the Split time, you can only perform Suspend or Delete pair operations. Split time is rejected if you perform Paircreate, Split, or Resync operation. If you want to perform one of these operations, reset the registration of the Split time. ◦ The Split time you specified is reset when power is switched off. ◦ The operation is performed when the read/write request—with a time stamp past the specified Split time—is received.
5. 6. 7. On the Pairsplit-E dialog box, select the pairs you want to suspend, and click OK to reflect the settings to the Preview List on the Pair Operation window. To remove pairs from the list, complete the following: 1. Select the unneeded pairs. 2. Right-click while selecting the pairs. 3. From the menu, select the Delete command. Repeat steps 4 and 5 to suspend additional pairs in the Pair Operation window. In the Pair Operation window, click Apply to suspend the specified pairs.
Prerequisite information • To Reverse Copy or Quick Restore, the pair must be split (PSUS status).
5. In the Pairresync dialog box, select the Resync Type as follows: • Normal Copy(P->S) to resynchronize the pairs normally. All differential data is updated to the S-VOL. • Quick Resync(P->S) to immediately change pair status to PAIR. Resynchronization of data does not occur immediately. Differential data is copied during update copying. • Reverse Copy(S->P) to copy the S-VOL data to the P-VOL. All differential data is updated to the P-VOL. Not available for L2 pairs.
• • 1. 2. ◦ If the result of the pairdisplay command is SMPL, and the result of the Inqraid command is PVOL or SVOL, then BC is still using the pair and status is SMPL(PD). ◦ If the result of the pairdisplay command is SMPL, and the result of the Inqraid command is not PVOL or SVOL, BC is not using the volumes. Therefore, status is confirmed as SMPL.
E Monitoring and maintaining the system (secondary window) This appendix provides information and instructions for monitoring and maintaining the BC system using the previous RWC GUI, which opens in a secondary window. Monitoring the system (secondary window) Monitoring helps you keep track of pairs and volumes and their current and past conditions. Monitoring should be an ongoing activity. This section provides information for monitoring the following: • Pair status. • Pair and pair volume details.
Supported operations and statuses are shown in the following tables.
3. From the volume list, complete the following: 1. Select and right-click the volume or pair whose information you want to see. 2. From the menu, select Detail. The Detail dialog box opens. Field descriptions are provided in the following table. Field Description P-VOL Information Volume ID: Shows LUN information using LDKC number:CU number:LDEV number format. CLPR: Shows CLPR number:CLPR name. Volume Information Shows the volume’s emulation type, capacity, and number of blocks.
2. 3. In the tree, select the appropriate port or host group for the desired pairs. Related volumes are shown. Complete the following: 1. Select a pair. 2. Right-click and select S-VOL Path from the menu. The S-VOL Path dialog box opens. Field descriptions are provided in the following table. Field Description Pair Information P-VOL and S-VOL columns shows the following path information (examples below from P-VOL column): • Port ID (cluster name and channel number.
2. Complete the following: 1. Right-click the volume list, in any location. 2. From the menu, select Information. The Information dialog box opens. Field descriptions are provided in the following table. Field Description BC pair(s) Shows the number of BC pairs/and the total number of pair tables for BC and BC Z. For example: 12/12. Notes: • The maximum number of pairs allowed in one storage system is 16,384, including migration plans and relationships.
Field Description • SS • Auto LUN Used Capacity (TB) Shows license information used by BC, and the total license capacity reserved for BC. Unlimited is shown when there is no limit on license capacity for BC. XP Snapshot Used Capacity (TB) Shows license information used by SS, and the total license capacity reserved for SS. Unlimited is shown when there is no limit on license capacity for SS.
4. If the information on the list is not updated, click File and then Refresh. The list is updated to the latest information. For operations involving the copying process, the History window does not show information about the operations until the copying process starts. If you perform an operation on a pair before the copying process starts, the History window does not show information about the operation. 5. If there are many records of operations, click the scroll button.
5. Select the pairs from which you want to remove the attribute, then click OK. The selected volumes display in the Preview list. 6. 7. To change a selection, right-click, select Modify, and make your changes. When ready, on the Pair Operations window click Apply.
F Business Copy GUI reference (secondary window) This appendix describes the BC windows and dialog boxes in the previous version of the RWC GUI, which opens in a secondary window. Pair Operation window Use this window to view BC pairs.
Field Description Note: P-VOLs and S-VOLs listed in RWC may end in special symbols. An LDEV number that ends with a pound or gate symbol (#) indicates an external volume (for example, 00:00:01#). An LDEV number that ends with a letter X indicates that a virtual volume used by Thin Provisioning (for example, 00:00:01X). Icons Indicate the following information: L1 pair L2 pair S-VOL Reserved volume. In Preview list, this is a preview item. Error. Is shown in Preview list. Port. Is shown in Tree.
Field Description MU The MU number of the BC pair formed with the P-VOL. MU#s are mirror unit numbers. The storage system assumes the same numbers of P-VOLs as S-VOLs. For example, when a P-VOL is paired with three S-VOLs, though just one P-VOL exists, the storage system assumes that there are three P-VOLs. These virtual P-VOLs are mirror units, MUs. Status The pair status. For more information, see “Pair status definitions” (page 53). S-VOL The S-VOL information in AAA-BB-CCC(XX:YY:ZZ) format.
Preview list The Preview list is shown below the Volume list. It shows the pair operations and changes you have made. You can review your changes, make modifications, and apply them to the storage system. Field Description P-VOL The P-VOL information in AAA-BB-CCC(XX:YY:ZZ) format. • AAA is the port ID (cluster and channel number) • BB is the group number of host group • CCC is the LU number • XX:YY:ZZ is the LDKC number:CU number:LDEV number MU The MU number of the BC pair formed with the P-VOL.
Display Filter dialog box Use this dialog box to filter the volumes on the Pair Operations window. To open this dialog box, click Display Filter in the Pair Operation window. The filter settings you select are effective in the current session only. They reset when you select another software product. Field Description CLPR The cache logical partition (CLPR) Volume Type The internal or external volumes are specified. Both boxes are selected by default. Clear the box you do not want.
Field Description Date The date and time of the operation. P-VOL The LDKC:CU:LDEV of the P-VOL used in the operation. S-VOL The LDKC:CU:LDEV of the S-VOL used in the operation. Code The BC reference codes. The codes refer to the messages shown in the following table. Message The description of the operation or part of an operation. Table 14 Reference Codes Code Message Description 4710 PAIR START The initial copy started.
Table 14 Reference Codes (continued) Code Message Description 47E9 INITIALIZE START Initialization started. 47EA INITIALIZE END Initialization ended normally. 47EB INITIALIZE ENDED ABNORMAL Initialization ended abnormally. Option window Use this window to set the Swap&Freeze, the HOST I/O Performance, Copy Threshold, and Copy Pace options. For more information, see “System options that affect performance” (page 38).
Glossary allocation The ratio of allocated storage capacity versus total capacity as a percentage. Allocated storage refers to those logical devices (LDEVs) that have paths assigned to them. Allocated storage capacity is the sum of the storage of these LDEVs. Total capacity is the sum of the capacity of all LDEVs on the disk array. BC P9000 or XP Business Copy. An HP application that provides volume-level, point-in-time copies in the disk array.
MU Mirror unit. OPEN-x A general term describing any of the supported OPEN emulation modes (for example, OPEN-E). There are two types of OPEN-x devices: legacy OPEN-x devices with a fixed size (such as OPEN-3, OPEN-8, OPEN-9, and OPEN-E), and OPEN-V, which has a variable size and is a CVS-based volume. P-VOL Primary volume. parity group A set of hard disk drives that have the same capacity and that are treated as one group.
Index Symbols L 3 Cnt Ac-J data center, sharing volumes with, 28 3 data center, sharing volumes with, 34 L1, L2 pairs, 8 license capacity exceeded , 13 capacity requirements, 13 expired, 13 viewing information about, 53 load sharing and performance, 17 LUN Manager, 27 A adjusting pair topology, 41 AIX and Business Copy performance, 18 At-Time Split with Cnt Ac-J Z volumes, 19 B BC, BC Z - role required to perform operations, 37 M C maximum number of pairs, 14 monitoring and pair statuses, 53 MU numb
quick split, 46 types, 12 R W RAID level, 12 RAID Manager error codes, 61 pair statuses, 54 requirements for, 12 related documentation, 70 Remote Web Console, 9 reserve attribute, 113 reserve volumes adding, 37, 112 information about, 58 removing, 59, 131 Resource Partition, 27 resynchronizing pairs, 48 resynchronizing pairs (subwindow), 121 reverse copy, 49 role required for BC, BC Z operations, 37, 40 websites HP , 71 HP Subscriber's Choice for Business, 70 product manuals, 70 S S-VOL path informati