HP XP P9000 Business Continuity Manager User Guide (T5253-96086, November 2013)
Table 110 Operation Examples in a 2DC Configuration with HyperSwap and Continuous Access
Journal Z (continued)
SeeContentsTargetMaintenance or FailureNumber
“Operating procedure
during a primary host
failure” (page 480)
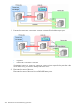
An operation example
when the primary site
stops due to a primary
During a primary host
failure
11
host failure. This
procedure reverses the
copy direction of copy
pairs between the
primary storage
system and the remote
storage system, in
order to continue
operations at the
secondary site.
“Operating procedure
during a path failure
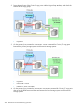
An operation example
when a path failure
During a path failure
between the primary
12
between the primaryoccurs between thestorage system and
storage system and theprimary storagethe local storage
system local storage system”
(page 484)
system and the local
storage system. This
procedure suspends
Cnt Ac-S Z copy pairs
with the HyperSwap
attribute, and then
recovers the failure.
TIP: The term "storage system failure, with information lost from memory," indicates a failure that
causes the loss of information in memory. In such a failure, the copy pair information and the data
are completely lost, so the hardware information must be reconfigured.
This section describes maintenance and troubleshooting procedures in a 2DC configuration with
HyperSwap and Cnt Ac-J Z.
The figures in the procedures contained in this section use the following legend:
The itemized lists under the figures in the procedures describe the commands that are executed in
the procedures.
Operation startup procedure
Business Continuity Manager provides commands for detecting HyperSwaps, such as YKCONMSG
and YKEWAIT. Table 111 (page 459) describes the differences in functionality between the
YKCONMSG command and the YKEWAIT command.
458 Maintenance and troubleshooting operations