HP XP7 Replication Manager Application Agent CLI Reference Guide (TK981-96014, May 2014)
Table Of Contents
- Application Agent CLI Reference Guide
- Preface
- 1 Extended commands
- Overview of extended commands
- Before reading the extended command descriptions
- Extended command specifications (File system backups)
- Extended command specifications (Common commands)
- EX_DRM_BACKUPID_SET (Generates a backup ID file)
- EX_DRM_CG_DEF_CHECK (Checks the contents of a copy-group list file)
- EX_DRM_DB_EXPORT (Exports backup information to a file)
- EX_DRM_DB_IMPORT (Imports backup information from a file)
- EX_DRM_FTP_GET (Acquires a backup information file from the backup server)
- EX_DRM_FTP_PUT (Transfers a backup information file to the backup server)
- EX_DRM_HOST_DEF_CHECK (Checks the contents of a host environment settings file)
- EX_DRM_RESYNC (Resynchronizes a copy group)
- Extended command specifications (Tape-related commands)
- Extended command specifications (SQL Server database backups)
- EX_DRM_SQL_BACKUP (Backs up an SQL Server database)
- EX_DRM_SQL_DEF_CHECK (Checks the contents of an operation definition file and automatically creates a temporary directory)
- EX_DRM_SQL_RESTORE (Restores an SQL Server database backup to the primary volume)
- EX_DRM_SQL_TLOG_BACKUP (Backs up the transaction log of the SQL Server)
- EX_DRM_SQLFILE_EXTRACT (Deploys SQL Server metafiles to the folder to be backed up to a tape device)
- EX_DRM_SQLFILE_PACK (Saves SQL Server metafiles)
- Extended command specifications (Exchange database backups)
- EX_DRM_EXG_BACKUP (Backs up an Exchange database)
- EX_DRM_EXG_DEF_CHECK (Checks the contents of an operation definition file and automatically creates a temporary directory)
- EX_DRM_EXG_RESTORE (Restores an Exchange database backup to the primary volume)
- EX_DRM_EXG_VERIFY (Verifies the consistency of an Exchange database)
- 2 Basic commands
- List of basic commands
- Before reading the basic command descriptions
- Basic command specifications (File system backups)
- Basic command specifications (Common commands)
- drmappcat (Views catalog information on a host)
- drmcgctl (Locks or unlocks a copy group)
- drmclusinit (Registers the parameters for the cluster software)
- drmdbexport (Exports backup information to a file)
- drmdbimport (Imports backup information from a file)
- drmdevctl (Conceals and reveals a physical volume)
- drmhostinfo (Displays host information)
- drmresync (Resynchronizes copy groups)
- Basic command specifications (Tape-related commands)
- drmmediabackup (Backs up data from a secondary volume to a tape device)
- drmmediarestore (Restores data from a tape device to a secondary volume)
- drmmount (Mounts a secondary volume)
- drmtapecat (Displays or deletes backup information in a backup catalog)
- drmtapeinit (Registers parameters for a backup management product)
- drmumount (Unmounts secondary volumes)
- Basic command specifications (Utility commands)
- Basic command specifications (SQL Server database backups)
- drmsqlbackup (Backs up an SQL Server database to a secondary volume)
- drmsqlcat (Displays backup information for an SQL Server database)
- drmsqldisplay (Displays or updates information for an SQL Server database)
- drmsqlinit (Registers parameters for SQL Server)
- drmsqllogbackup (Backs up the transaction log of an SQL Server)
- drmsqlrecover (Recovers restored SQL Server databases)
- drmsqlrecovertool (Recovers restored SQL Server databases via a GUI)
- drmsqlrestore (Restores SQL Server databases from backups to a primary volume)
- Basic command specifications (Exchange database backups)
- drmexgbackup (Backs up an Exchange database)
- drmexgcat (Displays backup information for an Exchange database)
- drmexgdisplay (Displays or updates information for an Exchange database)
- drmexgrestore (Restores an Exchange database backup to the primary volume)
- drmexgverify (Verifies the consistency of an Exchange database)
- 3 Support and other resources
- Index
2. The command performs disk resynchronization to restore the backup data from a secondary
volume to the primary volume.
3. The command brings the disk resource online, and then brings the cluster resource, including
databases, online.
If ONLINE is set in CLU_MSCS_RESTORE in the Application Agent configuration definition file
(init.conf), you can perform restoration of a user database while the cluster resources are online
by specifying the -resync option. In this case, the cluster resource that manages the instance to be
restored cannot be taken offline. However, if the restoration target is a system database (master,
model, msdb, or distribution) or a database that contains a system database, restoration will be
performed offline.
In restoration, data on the primary volume is overwritten by the disk image of the secondary volume
at the time a backup is performed. Therefore, data on the primary volume that was created or updated
after the backup is invalid.
When you attempt to restore a system database (master, model, msdb, or distribution) for SQL server,
the SQL server service to be restored needs to be stopped to recover the system database. The database
to be restored cannot be accessed temporarily.
During command execution, from another computer such as an application server, you should not
connect to the database that was restored. If another server connects to the database during command
execution, the command might fail.
When you restore an SQL Server system database, to recover the system database, temporarily stop
the SQL Server service on which restore operations are to be performed. For this reason, temporarily,
you cannot access the database on which restore operations are to be performed. Do not connect to
the SQL Server during a restoration. If you connect to a database that is being restored during
command execution, the system repeats checking the processing status for the number of times specified
in the Application Agent configuration definition file init.conf (in the retry count and retry interval
used when checking the status of a processing parameter). In this case, if the user is disconnected
during repeated checks of the processing status, the command resumes.
When you execute this command to perform a restoration, if the name of the drive making up the
SQL Server database has changed since backup was performed, the command will fail. Before
performing restoration, with the drmsqlcat command or SQL Server Enterprise Manager, check the
corresponding drive name of the restoration destination.
If the physical disk partition style is changed after a backup, and then the command is executed, the
command result will vary as follows.
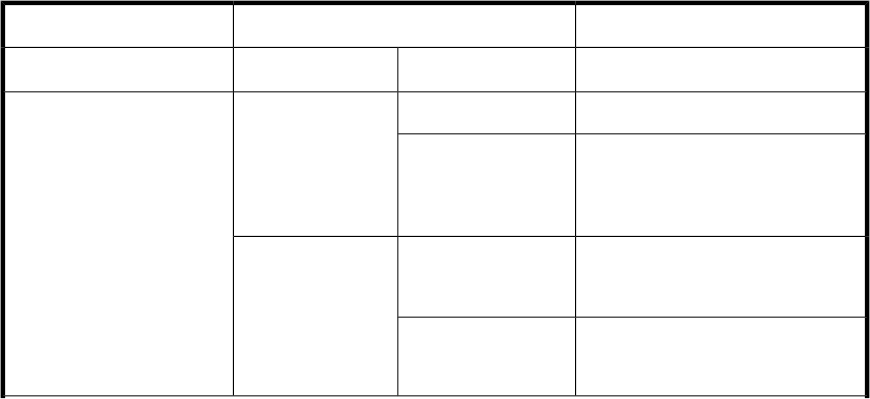
Table 44 Physical disk partition style and the command execution result
Command execution resultAfter a backupBefore a backup
Command statusSecondary volumePrimary volumePrimary volume
Normal terminationMBR disk
MBR disk
MBR disk
Error (KAVX5171-E or KAVX5137-E
message)
After resynchronizing
#1
GPT disk
Error (DRM-10337 message)
Before resynchronizing
#2
MBR disk
GPT disk
Error (DRM-10337 message)
Before resynchronizing
#2
GPT disk
Basic commands180










