HP StorageWorks XP Command View Advanced Edition Software 6.4 Server Administrator Guide for Device Manager and Provisioning Manager (web) (T1780-96341, July 2010)
Table Of Contents
- Overview
- 1-1 System configuration
- 1-2 Network configuration
- 1-2-1 Common security risks
- 1-2-2 Most secure configuration: separate management LAN plus firewall
- 1-2-3 Second-most secure configuration: separate management LAN plus firewalled devices under management
- 1-2-4 Third-most secure configuration: dual-homed management servers plus separate management LAN
- 1-2-5 Least secure configuration: flat network
- 1-3 Management server requirements
- 1-4 System requirements for storage subsystems
- 1-5 Host requirements
- 1-6 Products related to Device Manager
- 1-7 System requirement for managing copy pairs
- Settings for various network configurations
- 2-1 Port settings
- 2-2 Settings required to use a management server that has multiple NICs
- 2-3 Settings required to operate in an IPv6 environment
- 2-4 Changing the IP address or host name of the management server
- 2-5 Changing the URLs for accessing XP Command View AE Suite products
- 2-6 Settings required when disconnecting the management server network
- Settings required for managing user accounts
- Security settings for Device Manager
- Settings required for linking with related products
- Setting up logs and alerts
- Settings for CIM/WBEM (SMI-S CIMOM)
- 7-1 Device Manager and CIM/WBEM
- 7-2 CIM/WBEM features of Device Manager
- 7-3 Basic settings required to use the CIM/WBEM features
- 7-4 Settings for ports used by CIM/WBEM features
- 7-5 Properties file settings for executing CIM
- 7-6 Settings for the service discovery feature
- 7-7 The performance information acquisition feature
- 7-8 User permissions for using CIM/WBEM features
- Starting and stopping the Device Manager server
- 8-1 Before controlling the Device Manager server
- 8-2 Starting the Device Manager server
- 8-3 Stopping the Device Manager server
- 8-4 Checking the operating status of the Device Manager server
- 8-5 Starting the Device Manager server and Common Component
- 8-6 Stopping the Device Manager server and Common Component
- 8-7 Checking the operating status of Device Manager server and Common Component
- Managing the database
- Troubleshooting
- Support and other resources
- Appendix A Specifying properties
- A-1 Properties overview
- A-2 Device Manager server configuration properties
- A-2-1 server.http.host
- A-2-2 server.http.port
- A-2-3 server.https.port
- A-2-4 server.http.default
- A-2-5 server.http.request.timeout
- A-2-6 server.http.connection.priority
- A-2-7 server.http.connection.bufSize
- A-2-8 server.http.socket.backlog
- A-2-9 server.http.socket.maxThreads
- A-2-10 server.http.socket.linger
- A-2-11 server.http.socket.noDelay
- A-2-12 server.http.headers.maxNumber
- A-2-13 server.http.headers.maxLength
- A-2-14 server.http.entity.maxLength
- A-2-15 server.http.log.reverseDNS
- A-2-16 server.http.cache.size
- A-2-17 server.http.cache.maxFileSize
- A-2-18 server.http.fileTypes.noLog
- A-2-19 server.http.mode
- A-2-20 server.installTime
- A-2-21 server.base.home
- A-2-22 server.horcmconfigfile.hostname
- A-2-23 server.base.initialsynchro
- A-2-24 server.cim.agent
- A-2-25 server.cim.support
- A-2-26 server.cim.support.job
- A-2-27 server.cim.support.protocol
- A-2-28 server.cim.http.port
- A-2-29 server.cim.https.port
- A-2-30 server.configchange.enabled
- A-2-31 server.configchange.autorefresh.lastrefreshed
- A-2-32 server.mail.enabled
- A-2-33 server.mail.from
- A-2-34 server.mail.smtp.host
- A-2-35 server.mail.smtp.port
- A-2-36 server.mail.smtp.auth
- A-2-37 server.mail.alert.type
- A-2-38 server.mail.alert.status
- A-2-39 server.subsystem.ssid.availableValues
- A-2-40 server.smisclient.indication.port
- A-3 Device Manager database properties
- A-4 Device Manager logger properties
- A-5 Device Manager dispatcher properties
- A-5-1 server.dispatcher.agent.priority
- A-5-2 server.dispatcher.message.timeout
- A-5-3 server.dispatcher.message.timeout.in.processing
- A-5-4 server.dispatcher.daemon.pollingPeriod
- A-5-5 server.dispatcher.traps.purgePeriod
- A-5-6 server.dispatcher.startTimeOfIgnoringConnectionAlert
- A-5-7 server.dispatcher.endTimeOfIgnoringConnectionAlert
- A-5-8 server.dispatcher.daemon.receiveTrap
- A-5-9 server.dispatcher.daemon.configUpdate.detection.interval
- A-5-10 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.doRefresh
- A-5-11 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.type
- A-5-12 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.dayOfWeek
- A-5-13 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.startTime
- A-5-14 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.interval
- A-5-15 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.refresh.interval
- A-5-16 server.dispatcher.daemon.autoSynchro.refresh.timeout
- A-6 Device Manager MIME properties
- A-7 Device Manager client properties
- A-8 Device Manager security properties
- A-9 Device Manager SNMP trap log output function properties
- A-10 Device Manager mainframe host agent properties
- A-11 Device Manager report function properties
- A-12 XP Provisioning Manager server configuration properties
- A-13 XP Provisioning Manager server log properties
- A-14 XP Provisioning Manager client properties
- Glossary
- Index
Overview
48
The following table describes the storage subsystem requirements for managing copy pairs by using
Device Manager.
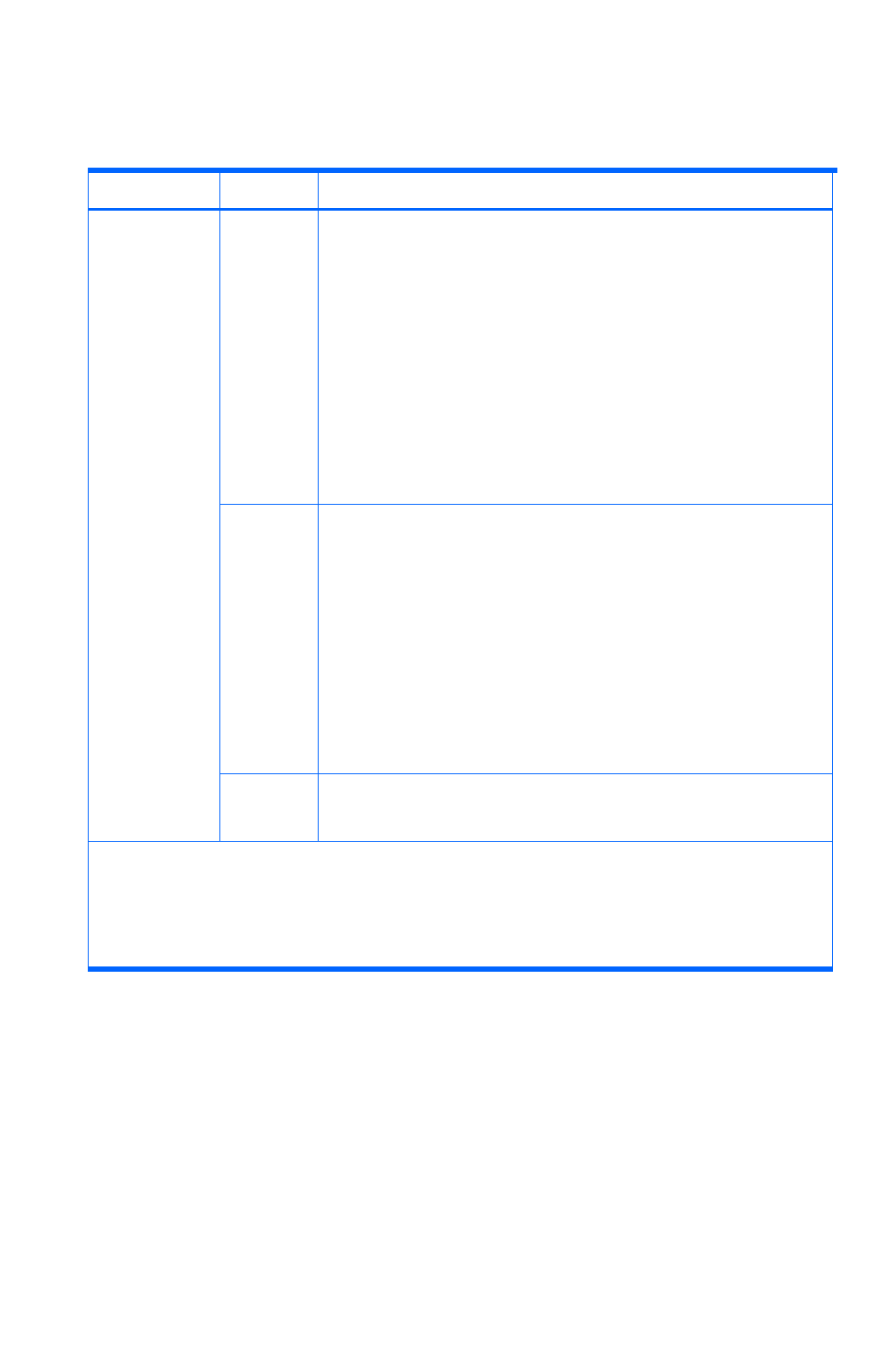
Table 1-26 Storage subsystem requirements for managing copy pairs
Disk array Function Requirement
XP
Continuous
Access
Journal
1
• Prerequisite software for XP Continuous Access Journal must be
installed and the license must be enabled.
• There must be a fibre-channel connection between the two ports
used for an MCU-RCU path
2
• The MCU port for an MCU-RCU path must be an Initiator port, and
the RCU port must be an RCU Target port
2
• The RCU and the MCU-RCU path must be registered in the MCU
2
• The storage subsystem cache or nonvolatile memory must be
sufficient.
• Journal volumes must be registered in the journal group.
NOTE: After configuring the ports, you need to refresh the storage
subsystem. If you need to increase the cache, contact maintenance
personnel.
XP
Continuous
Access
Software
1
• Prerequisite software for XP Continuous Access Software must be
installed and the license must be enabled
• There must be a fibre-channel connection between the two ports
used for an MCU-RCU path.
• The MCU port for a MCU-RCU path must be an Initiator port, and
the RCU port must be an RCU Target port.
• The RCU and the MCU-RCU path must be registered in the MCU.
• The storage subsystem cache or nonvolatile memory must be
sufficient.
NOTE: After configuring the ports, you need to refresh the storage
subsystem. If you need to increase the cache, contact maintenance
personnel.
XP24000/XP200
00
XP12000/XP100
00/SVS200
XP1024/XP128
XP512/XP48
XP Business
Copy
Software
1
Prerequisite software for XP Business Copy Software must be installed
and the license must be enabled.
1
For mainframe volume copy pairs, the only operation you can perform with Device Manager is to check
the configuration. To check the copy pair configuration by using Device Manager, there are no storage
subsystem requirements.
2
The settings specified in XP Continuous Access Software can be shared with XP Continuous Access
Journal. However, in XP Continuous Access Journal, the settings must be specified for both storage
subsystems used for the P-VOL and the S-VOL.
1-7-4 Notes on using Device Manager when XP RAID
Manager is already managing copy pairs
If a copy pair is already managed by XP RAID Manager, the copy pair can be managed by Device
Manager once Device Manager is installed.
Note the following if you are using XP RAID Manager to manage existing copy pairs:
• If you want to use Device Manager to control copy pairs managed by XP RAID Manager, the
configuration definition file on the host that manages the P-VOL of the copy pair and the
configuration definition file on the host that manages the S-VOL of the copy pair must have the
same group name and the same pair name. If different names are specified, Device Manager
cannot control that copy pair. In addition, if you want to use a single host to manage multiple










