HP Remote Graphics Software 6.0 User Guide
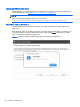
Figure 4-6 Network Interface binding order numerical sequence
Again, refer to Network Interface binding properties on page 140 for a description of these properties.
Using RGS through a firewall
The Receiver can use the public IP address of the Sender so that RGS can be used through a simple
firewall. To take advantage of this feature, the Sender and Receiver firewalls must both support NAT
(Network Address Translation). In addition, the Sender firewall must support port forwarding.
For more information on how to set up port forwarding on your firewall, refer to the documentation for
your firewall.
NOTE: The port used by the RGS Receiver is assigned by the local computer OS and can vary. The
RGS Sender listens on TCP/IP port 42966 by default, but the port number can be changed using the
Rgsender.Network.Port property as described in
Network Interface binding properties on page 140. If
this property is used to change the Sender port number from its default value of 42966, the Sender
port number must then be specified in establishing an RGS connection from the Receiver to the
Sender.
Remote computer power saving states
In order for a local computer to establish connection to a remote computer, the remote computer
cannot be in a power saving state, such as Windows hibernate or standby. Furthermore, the remote
computer cannot utilize wake-on-LAN in an attempt to power-up in order to respond to a connection
request from the local computer—the remote computer must be powered-up, and able to respond to
an RGS connection request at all times.
Using RGS through a firewall 31