HP Remote Graphics Software 6.0 User Guide
●
Expect the unexpected—where possible, limit your actions to those areas you are certain of the
outcomes to minimize loss of data and productivity.
●
Always inspect error codes when reading event logs—the reliability of this RGS communication
method depends upon the Windows Event Log system. While we have yet to see a failure in this
path, we recommend using all information available to its fullest potential.
Additional features for Windows systems
The following optional procedures for the RGS Sender service can improve the reliability of your
remote agent solution.
RGS Sender Service Recovery Settings
This section discusses restart options for the RGS Sender and possible interactions of the agent with
the Sender.
●
By default, most Windows services are installed without any automatic restart/recovery settings.
This means that, when a service terminates, Windows will, by default, not restart the service
unless explicitly set. When RGS Sender software is first installed, it is installed with the Windows
default (do not restart).
●
Restarting the RGS Sender service can support RGS reconnection with a RGS Receiver client
(unless a system error prevents the RGS service from restarting).
●
In designing the agent, you should consider whether or not to check for the existence of a
running RGS Sender service as an indication of a sufficient primary user connection. If service
restarts are programmed for your environment, this test may be unnecessary.
●
To set the RGS Sender service for automatic restart, you must adjust its Recovery Property
through the Administrative Tools and Services control panel options.
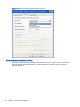
●
Actions to take for the first failure, second failure, and subsequent failures are available in the
properties menu (see
Figure 7-8 Remote computer Sender recovery options on page 98). The
Recovery options include:
◦
Take No Action
◦
Restart the Service
◦
Run a Program
◦
Restart the Computer
Remote Application Termination 97