Implementing disaster recovery for HP Integrity Virtual Machines with Metrocluster and Continentalclusters on HP-UX 11i
Table Of Contents
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Audience
- Configuring Integrity Virtual Machines as packages in HP Metrocluster
- Verifying failover of Metrocluster packages across data centers
- Troubleshooting Metrocluster VM problems
- Application startup and monitoring
- Configuring Integrity Virtual Machines as packages in HP Continentalclusters
- Overview
- Software requirements for HP VMs in Continentalclusters
- Configuring HP VM packages in Continentalclusters
- Creating VM switches in all nodes of the primary cluster
- Configuring replicated storage for VM in Continentalclusters
- Installing the operating system on the virtual machine
- Testing the virtual guest OS in all nodes of the primary cluster
- Creating VM switches in all nodes of the recovery cluster
- Preparing the replicated storage for use in the recovery cluster
- Creating the virtual machine in all nodes of the recovery cluster
- Testing the virtual guest OS in all nodes of the recovery cluster
- Resynchronizing the replicated storage
- Packaging the HP VM in the primary cluster and the recovery cluster
- Creating a Continentalclusters package
- Creating a Continentalclusters configuration with the VM packages
- Running the Continentalclusters monitoring daemon in the recovery cluster
- Recovering to the recovery cluster
- Related documentation
- Appendix I
- Appendix II
- For more information
- Call to action
4
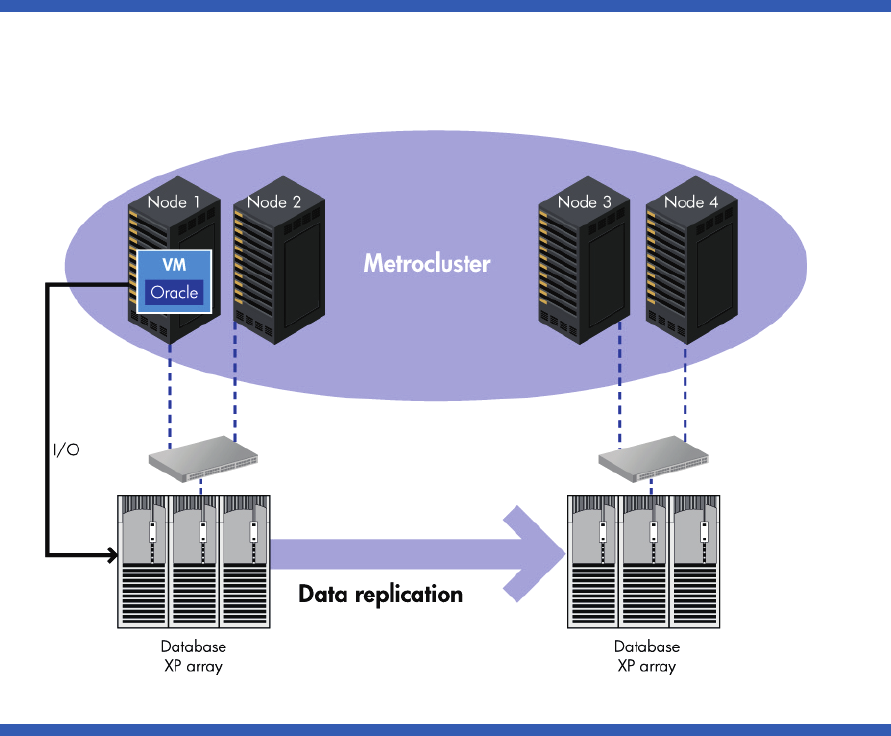
Figure 1. Metrocluster configuration for setting up virtual machines
Configuring Metrocluster packages
Let’s configure a Metrocluster package called vmmetropkg using this setup. To configure a virtual
machine into a Metrocluster package, the VM must first be configured individually on all the cluster
nodes and must have the same name on all cluster nodes. For our example, we’ll use vmmetro as the
VM name.
Setting up virtual machines
Complete the following procedure to set up a virtual machine:
1. Create VM switches.
2. Configure VM storage.
3. Create the virtual machine.
Creating VM switches
As per Serviceguard guidelines, you need at least two virtual switches for availability. For this
example, two VM switches are created to be used by the virtual machine. Run the “
hpvmnet”
command on each node to create the switches.
# hpvmnet –c –S vs1 –n 0
# hpvmnet –c –S vs2 –n 1










