HP-UX System Administrator's Guide: Overview HP-UX 11i v3 (B3921-90011, September 2010)
Partitioning (Multiple Operating Systems, One Multi-processor Server)
When you have multiple cores available, more virtualization possibilities become available as
well. This area of virtualization technology is known as partitioning. There are several types of
partitioning available on HP systems, but they fall into two major categories—hardware partitioning
and software partitioning.
Hardware Partitioning
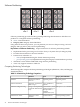
nPartition 1 nPartition 2
Hardware partitioning is accomplished at the cell board or Superdome 2 blade level, using an
HP technology called nPartitions.
Implemented on servers that support multiple cell boards and on Superdome 2 blade-based
systems, nPartitions isolate (both logically and electrically) multiple operating system instances.
That is, cell boards/Superdome 2 blades, cores, I/O components, and memory assigned to one
nPartition are available only to operating systems running in that partition.
Should problems occur with an operating system, software, or even hardware in one partition,
operating systems and software running in other partitions are unaffected.
Key Features of Hardware Partitioning Important features of hardware partitioning include:
• Implemented at the cell board / Superdome 2 blade level.
• Provides both functional and electrical isolation.
• Partitions are referred to as nPartitions.
• nPartitions can be further sub-divided using Software Partitioning.
• On servers that support them, nPartitions can run HP-UX, Linux, Microsoft Windows, or
all of these operating systems (in separate partitions).
Partitioning (Multiple Operating Systems, One Multi-processor Server) 35