Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 Administrator's Guide
ou=People,dc=example,dc=com. This field corresponds to the
nsSaslMapBaseDNTemplate value in the SASL mapping LDIF entry.
• Search filter. This field gives the search filter for the components to replace, such as
(objectclass=*). This field corresponds to the nsSaslMapFilterTemplate value in the
SASL mapping LDIF entry.
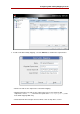
To edit a SASL identity mapping, highlight that identity in the SASL Mapping tab, and click
Modify. Change any values, and save.
To delete a SASL identity mapping, highlight it and hit Delete. A dialog box comes up to confirm
the deletion.
4. Configuring SASL Identity Mapping from the
Command-Line
To configure SASL identity mapping from the command-line, use the ldapsearch utility to
configure an identity mapping scheme, such as the following:
objectclass: top
objectclass: nsSaslMapping
cn: mymap2
nsSaslMapRegexString: \(.*\)
nsSaslMapBaseDNTemplate: ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
nsSaslMapFilterTemplate: (cn=\1)
This will match any user ID and map to the result of the the subtree search with base
ou=People,dc=example,dc=com and filter cn=userId.
For more information on the ldapsearch utility, see Appendix B, Finding Directory Entries.
5. Configuring Kerberos
Kerberos v5 must be deployed on the system to utilize the GSS-API mechanism for SASL
authentication. Table 12.1, “Supported Kerberos Systems” summarizes the Kerberos
applications supported by various platforms. GSS-API and Kerberos client libraries must be
installed on the Directory Server host to take advantage of Kerberos services.
Operating System Kerberos Version
Linux MIT Kerberos version 5
HP-UX 11i HP Kerberos version 2.1
Sun Solaris SEAM 1.0.1
Table 12.1. Supported Kerberos Systems
Chapter 12. Managing SASL
426