Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 Administrator's Guide
This will match any user ID and map to the result of the the subtree search with base
ou=People,dc=example,dc=com and filter cn=userId.
The Directory Server has pre-defined SASL mapping rules to handle some of the most common
cases:
• Kerberos UID Mapping. This mapping matches a Kerberos principal using a two part realm,
such as user@example.com. The realm is then used to define the search base, and the
authid defines the filter. In this example, the search base would be dc=example,dc=com and
the filter of (uid=user).
• RFC 2829 DN Syntax. This mapping matches an authid that is a valid DN (defined in RFC
2829) prefixed by dn:. The authid maps directly to the specified DN.
• RFC 2829 U Syntax. This mapping matches an authid that is a UID prefixed by u:. The
value specified after the prefix defines a filter of (uid=value). The search base is hard-coded
to be the suffix of the default userRoot database.
• uid Mapping. This mapping matches an authid that is any plain string that does not match
the other default mapping rules. It use this value to define a filter of (uid=value). The search
base is hard-coded to be the suffix of the default userRoot database.
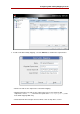
3. Configuring SASL Identity Mapping from the Console
To create a new SASL identity mapping, do the following:
1. In the Directory Server Console, open the Configuration tab.
2. Select the SASL Mapping tab.
Chapter 12. Managing SASL
424