Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 Administrator's Guide
1
The LDAP tools referenced in this guide are Mozilla LDAP, installed with Directory Server in the
/usr/lib/mozldap directory on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 i386; directories for other platforms are listed in
Section 2, “LDAP Tool Locations”. However, Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems also include LDAP tools from
OpenLDAP. It is possible to use the OpenLDAP commands as shown in the examples, but you must use the -x
argument to disable SASL and allow simple authentication.
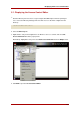
2. In the Access Control Manager window, highlight the ACI to edit, and click Edit.
3. Make the edits to the ACI in the Access Control Editor; the different screens are described
more in Section 5.2, “Creating a New ACI” and in the online help.
4. When you have finished editing the ACI, click OK.
The Access Control Editor windows closes, and the modified ACI is listed in the Access
Control Manager.
5.4. Deleting an ACI
To delete an ACI, do the following:
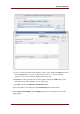
1. In the Directory tab, right-click the top entry in the subtree, and choose Set Access
Permissions from the pop-up menu.
The Access Control Manager window opens with a list of ACIs belonging to the entry.
2. In the Access Control Manager window, select the ACI to delete.
3. Click Remove.
The ACI is no longer listed in the Access Control Manager window.
6. Viewing ACIs
All the ACIs under a single suffix in the directory can be viewed from the command line by using
the following ldapsearch command:
1
ldapsearch -h host -p port -b baseDN -D rootDN -w rootPassword (aci=*) aci
See the Directory Server Configuration, Command, and File Reference for information on using
the ldapsearch utility.
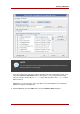
From the Directory Server Console, all of the ACIs that apply to a particular entry can be viewed
through the Access Control Manager.
1. Start the Directory Server Console. See Section 4, “Starting the Directory Server Console”.
2. In the Directory tab, right-click the entry in the navigation tree, and select Set Access
Chapter 6. Managing Access Control
210