Patch Management User Guide for HP-UX 11.x Systems (5900-3011, April 2013)
Table Of Contents
- Patch Management User Guide for HP-UX 11.x Systems
- Contents
- 1 HP-UX patches and patch management
- 2 Quick start guide for patching HP-UX systems
- 3 HP-UX patch overview
- 4 Patch management overview
- Patch management life cycle
- HP service contracts
- Patch management and software change management strategies
- Establishing a software change management strategy
- Recommendations for software change management
- Consideration of HP patch rating
- Patch management and software depots
- Proactive patching strategy
- Reactive patching strategy
- Advanced topic: security patching strategy
- Advanced topic: scanning for security patches
- Testing the patches to be installed
- 5 What are standard HP-UX patch bundles?
- 6 Using the HP Support Center
- Obtaining an HPSC user account
- Useful pages on the HPSC
- Find individual patches
- Advanced topic: checking for special installation instructions
- Advanced topic: checking for all patch dependencies
- Standard patch bundles
- Custom patch bundles - run a patch assessment
- Support information digests
- Ask your peers in the forums
- Search knowledge base
- 7 Using software depots for patch management
- Common software distributor commands for patching
- Depot types
- Using depots
- Viewing depots
- Creating and adding to a directory depot
- Registering and unregistering directory depots
- Verifying directory depots
- Removing software from a directory depot
- Removing a directory depot
- Installing patches from a depot
- Custom patch bundles
- 8 Using HP-UX Software Assistant for patch management
- 9 Using Dynamic Root Disk for patch management
- 10 The Patch Assessment Tool
- 11 Support and other resources
- A Patch usage models
- Glossary
- Index
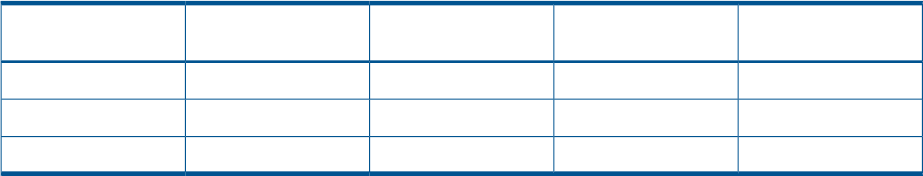
The following are three strategies for software change management. These strategies are described
in Table 5: “Operational factor and patch management strategy matrix” (page 48):
• Restrictive
• Conservative
• Innovative
Table 5 Operational factor and patch management strategy matrix
Self-MaintenanceImpact on Core
Business
Unplanned Down TimeNew FeaturesPatch Management
Strategy
NoHighUnacceptableNoRestrictive
NoMediumUnacceptableNoConservative
YesLowAcceptableYesInnovative
The process of selecting an appropriate software change management strategy seeks to align
behavior with the key business objectives of the systems involved. The goals of evaluating an
operation and choosing an appropriate strategy include:
• Reduced risk
• Increased system and application availability
• Reduced maintenance time
There are four operational factors that should determine your appropriate strategy:
• New features
Do you need to introduce new operating system or application features into the operating
environment?
• Unplanned down time
What is your tolerance for the operation being unavailable outside the scheduled maintenance
windows?
• Impact on core business
How are business functions affected by down time?
• Self-maintenance
This is an indication of whether or not all system planning and maintenance activities are
performed inhouse without vendor or third-party involvement.
Recommendations for software change management
The following are recommendations for software change management that correspond to each
software change strategy. They cover the following five areas:
• Operating System and Applications
Includes versions of the operating system as well as the applications running in the environment.
• Proactive Patching
Includes all patching activities for which no symptoms or problems are currently evident.
• Reactive Patching
Performed in response to a visible system problem.
48 Patch management overview










