Patch Management User Guide for HP-UX 11.x Systems (5900-3011, April 2013)
Table Of Contents
- Patch Management User Guide for HP-UX 11.x Systems
- Contents
- 1 HP-UX patches and patch management
- 2 Quick start guide for patching HP-UX systems
- 3 HP-UX patch overview
- 4 Patch management overview
- Patch management life cycle
- HP service contracts
- Patch management and software change management strategies
- Establishing a software change management strategy
- Recommendations for software change management
- Consideration of HP patch rating
- Patch management and software depots
- Proactive patching strategy
- Reactive patching strategy
- Advanced topic: security patching strategy
- Advanced topic: scanning for security patches
- Testing the patches to be installed
- 5 What are standard HP-UX patch bundles?
- 6 Using the HP Support Center
- Obtaining an HPSC user account
- Useful pages on the HPSC
- Find individual patches
- Advanced topic: checking for special installation instructions
- Advanced topic: checking for all patch dependencies
- Standard patch bundles
- Custom patch bundles - run a patch assessment
- Support information digests
- Ask your peers in the forums
- Search knowledge base
- 7 Using software depots for patch management
- Common software distributor commands for patching
- Depot types
- Using depots
- Viewing depots
- Creating and adding to a directory depot
- Registering and unregistering directory depots
- Verifying directory depots
- Removing software from a directory depot
- Removing a directory depot
- Installing patches from a depot
- Custom patch bundles
- 8 Using HP-UX Software Assistant for patch management
- 9 Using Dynamic Root Disk for patch management
- 10 The Patch Assessment Tool
- 11 Support and other resources
- A Patch usage models
- Glossary
- Index
PHSS_26619.AGRM,fa=HP-UX_B.11.11_32/64
PHSS_26622.AGRM,fa=HP-UX_B.11.11_32/64
PHSS_26638.AGRM,fa=HP-UX_B.11.11_32/64
PHSS_29169.AGRM,fa=HP-UX_B.11.11_32/64
PHSS_29183.AGRM,fa=HP-UX_B.11.11_32/64
For more information see the Software Distributor Administration Guide on the HP Business Support
Center website at http://www.hp.com/go/sd-docs.
Supersession
Supersession is the process of replacing an earlier patch with a new patch. A new patch supersedes
all previous patches for its particular patch chain. Upon installation of the new (superseding) patch,
its files replace files of the patches being superseded. Patches for HP-UX products are always
cumulative. Each new patch contains all aspects of all its preceding patches.
A series of patches form a supersession chain. A supersession chain includes the following:
• The nonpatch software product being patched.
• Each patch that fixes the nonpatch software product.
• Each patch that fixes the patches.
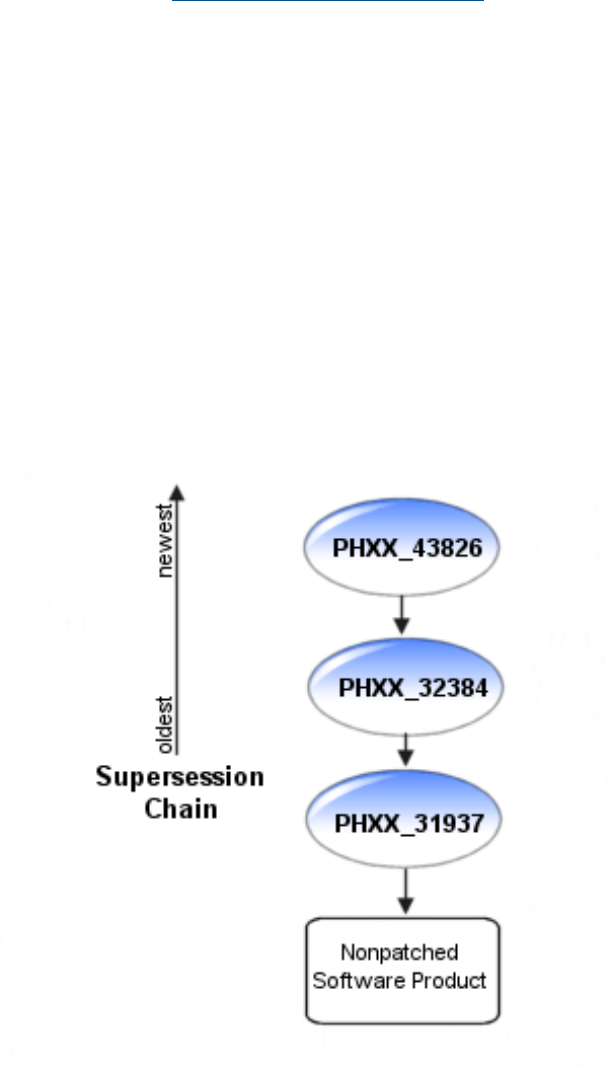
Figure 1 shows a simple, hypothetical supersession chain in which a product has been superseded
by PHXX_31937, which in turn has been superseded by PHXX_32384, which has been superseded
by PHXX_43826. In general, patch numbers increase along a patch supersession chain.
Figure 1 Patch Supersession Chain in a Patch Family
The cumulative nature of a patch allows it to satisfy all dependencies on all patches it supersedes.
The converse is not true, however. A superseded patch will not satisfy a dependency on a
superseding patch. For more information about dependencies, see “Patch dependencies” (page 32).
You can determine which patches a given patch supersedes by viewing either the patch's patch
details page or the patch's patch text file. See the Supersedes field for more information.
Ancestors and supersession 27










