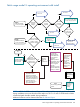
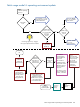
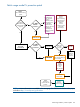
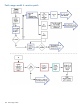
Patch Management User Guide for HP-UX 11.x Systems (5900-3011, April 2013)
Table Of Contents
- Patch Management User Guide for HP-UX 11.x Systems
- Contents
- 1 HP-UX patches and patch management
- 2 Quick start guide for patching HP-UX systems
- 3 HP-UX patch overview
- 4 Patch management overview
- Patch management life cycle
- HP service contracts
- Patch management and software change management strategies
- Establishing a software change management strategy
- Recommendations for software change management
- Consideration of HP patch rating
- Patch management and software depots
- Proactive patching strategy
- Reactive patching strategy
- Advanced topic: security patching strategy
- Advanced topic: scanning for security patches
- Testing the patches to be installed
- 5 What are standard HP-UX patch bundles?
- 6 Using the HP Support Center
- Obtaining an HPSC user account
- Useful pages on the HPSC
- Find individual patches
- Advanced topic: checking for special installation instructions
- Advanced topic: checking for all patch dependencies
- Standard patch bundles
- Custom patch bundles - run a patch assessment
- Support information digests
- Ask your peers in the forums
- Search knowledge base
- 7 Using software depots for patch management
- Common software distributor commands for patching
- Depot types
- Using depots
- Viewing depots
- Creating and adding to a directory depot
- Registering and unregistering directory depots
- Verifying directory depots
- Removing software from a directory depot
- Removing a directory depot
- Installing patches from a depot
- Custom patch bundles
- 8 Using HP-UX Software Assistant for patch management
- 9 Using Dynamic Root Disk for patch management
- 10 The Patch Assessment Tool
- 11 Support and other resources
- A Patch usage models
- Glossary
- Index

Glossary
This glossary defines key terms related to patching that are used in this book. HP
recommends the Software Distributor Administration Guide on the HP Business Support
Center website at http://www.hp.com/go/sd-docs for additional terms.
ancestor An ancestor of a patch is the preexisting software that is being modified or replaced by the patch.
applied One of four possible states in which a patch is first installed. When a patch is installed, by default
it has the patch_state of applied. Other patch states include committed,
committed/superseded, and superseded.
base software The software that will be modified by a patch.
bundle An encapsulation of products, subproducts, and filesets into a single software object. Bundles
are a convenient way to group software objects for easy selection. When a bundle is specified
in a Software Distributor operation, all products or filesets contained in that bundle are included
in the operation. If the filesets within the bundle are patches, this is known as a patch bundle.
See also patch bundle.
catalog, catalog
directory
An area within a depot that contains all the information needed by SD-UX to define the
organization and contents of the products stored in the depot. The catalog (or catalog directory)
includes a global index file and a directory of information for each product version in the depot.
category tags See patch category.
committed The patch state in which the patch is applied and rollback files have been deleted.
committed/
superseded
The patch state in which the patch is both committed and superseded.
See also superseded.
control script An optional script that is run during software installation, software removal, or software
configuration.
corequisite A dependency in which a fileset requires that another fileset be installed or configured at the
same time. For example, if fileset A requires that fileset B is installed at the same time, fileset B
is a corequisite.
See also dependency, prerequisite.
cumulative patch Each new patch contains all aspects of all its preceding patches. Patches for HP-UX products are
always cumulative.
dependency A relationship between filesets in which one requires another in a specific manner. For example,
before fileset A can be installed, it might require fileset B to be installed. SD-UX supports corequisite
and prerequisite dependencies.
See also dependent.
dependent A fileset that has a dependency on another fileset. For example, if fileset A depends on fileset B,
then B is dependent or has a dependency on A.
depot A repository of software products and a catalog, organized so that SD-UX commands use it as
a software source. The contents of a depot reside in a directory structure with a single, common
root.
depot source See depot.
directory depot The directory on a target host in which a depot is located. The default is /var/spool/sw.
DRD See Dynamic Root Disk.
Dynamic Root Disk Patches HP-UX systems, reduces system downtime for software maintenance, provides the ability
to install and manage patches on an inactive system image while the system is up and running,
allows most software maintenance tasks to be done during normal business hours, limits the
downtime required to the time it takes to reboot the system, and enables use of both proactive
and reactive patching.
fileset A grouping of one or more files contained in a product or subproduct. A fileset groups a subset
of a product's files into a manageable unit. Most Software Distributor operations are performed
on filesets.
109