LDAP-UX Client Services B.04.15 with Microsoft Windows Active Directory Server Administrator's Guide (edition 8)
Table Of Contents
- LDAP-UX Client Services B.04.15 with Microsoft Windows Active Directory Administrator's Guide
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Installing LDAP-UX Client Services
- Before You Begin
- Summary of Installing and Configuring LDAP-UX Client Services
- Planning Your Installation
- Installing LDAP-UX Client Services on a Client
- Configuring Active Directory for HP-UX Integration
- Step 1: Install Active Directory
- Step 2: Install SFU 2.0, 3.0 or 3.5 including Server for NIS
- Step 3: Create a Proxy User
- Step 4: Add an HP-UX Client Machine Account to Active Directory
- Step 5: Use ktpass to Create the Keytab File for the HP-UX client machine
- Step 6: Add POSIX Attributes into the Global Catalog
- Importing Name Service Data into Your Directory
- Configuring LDAP-UX Client Services
- Step 1: Run the Setup Program
- Step 2: Install the PAM Kerberos Product
- Step 3: Configure Your HP-UX Machine to Authenticate Using PAM Kerberos
- Step 4: Configure the Name Service Switch (NSS)
- Step 5: Configure the PAM Authorization Service Module (pam_authz)
- Step 6: Configure the Disable Login Flag
- Step 7: Verify LDAP-UX Client Services for Single Domain
- Step 8: Configure Subsequent Client Systems
- Configuring the LDAP-UX Client Services with SSL or TLS Support
- Downloading the Profile Periodically
- 3 Active Directory Multiple Domains
- 4 LDAP-UX Client Services with AutoFS Support
- 5 LDAP Printer Configurator Support
- 6 Dynamic Group Support
- 7 Administering LDAP-UX Client Services
- Using the LDAP-UX Client Daemon
- Integrating with Trusted Mode
- SASL GSSAPI Support
- PAM_AUTHZ Login Authorization
- Policy And Access Rules
- How Login Authorization Works
- PAM_AUTHZ Supports Security Policy Enforcement
- Policy File
- Policy Validator
- Dynamic Variable Support
- Constructing an Access Rule in pam_authz.policy
- Static List Access Rule
- Dynamic Variable Access Rule
- Security Policy Enforcement with Secure Shell (SSH) or r-commands
- Adding Additional Domain Controllers
- Adding Users, Groups, and Hosts
- User and Group Management
- Displaying the Proxy User's Distinguished Name
- Verifying the Proxy User
- Creating a New Proxy User
- Displaying the Current Profile
- Creating a New Profile
- Modifying a Profile
- Changing Which Profile a Client is Using
- Creating an /etc/krb5.keytab File
- Considering Performance Impacts
- Client Daemon Performance
- Troubleshooting
- 8 Modifying User Information
- 9 Mozilla LDAP C SDK
- A Configuration Worksheet
- B LDAP-UX Client Services Object Classes
- C Command, Tool, Schema Extension Utility, and Migration Script Reference
- LDAP-UX Client Services Components
- Client Management Tools
- LDAP User and Group Management Tools
- Environment Variables
- Return Value Formats
- Common Return Codes
- The ldapuglist Tool
- The ldapugadd Tool
- The ldapugmod Tool
- The ldapugdel Tool
- The ldapcfinfo Tool
- LDAP Directory Tools
- Schema Extension Utility
- Name Service Migration Scripts
- Unsupported Contributed Tools and Scripts
- D Sample PAM Configuration File
- E Sample /etc/krb5.conf File
- F Sample /etc/pam.conf File for HP-UX 11i v1 Trusted Mode
- G Sample /etc/pam.conf File for HP-UX 11i v2 Trusted Mode
- H Sample PAM Configuration File for Security Policy Enforcement
- Glossary
- Index
Unsupported Contributed Tools and Scripts
This section describes contributed tools and scripts which are not officially supported by HP at
the present time.
beq Search Tool
The new beq tool expands the search capability beyond that currently offered by nsquery,
which is limited to hosts, passwd, and group. This search utility bypasses the name service
switch and queries the backend directly based on the specified library. The search will include
the following services: pwd, grp, shd, srv, prt, rpc, hst, net, ngp, and grm.
NOTE: HP does not support the beq tool at the present time.
The syntax for this tool, along with example output, is shown below.
Syntax
beq -k [n|d] -s <service> (-l <library>) (-h | -H <#>) <idl> (id1>
(<id2> (...))
where:
k [n|d] Required. The search key may be either n for name string or d for digit (a numeral
search).
-s <service>
Required. Indicates what backends are to be searched for information.
-l <library>
Query the backend directly. Bypass the APIs and skip the name service
switch.
-h
Provides Help on this command.
-H <#>
Specifies Help level (0-5). Larger numbers provide more information. If you
specify -h or -H, no other parameters are needed.
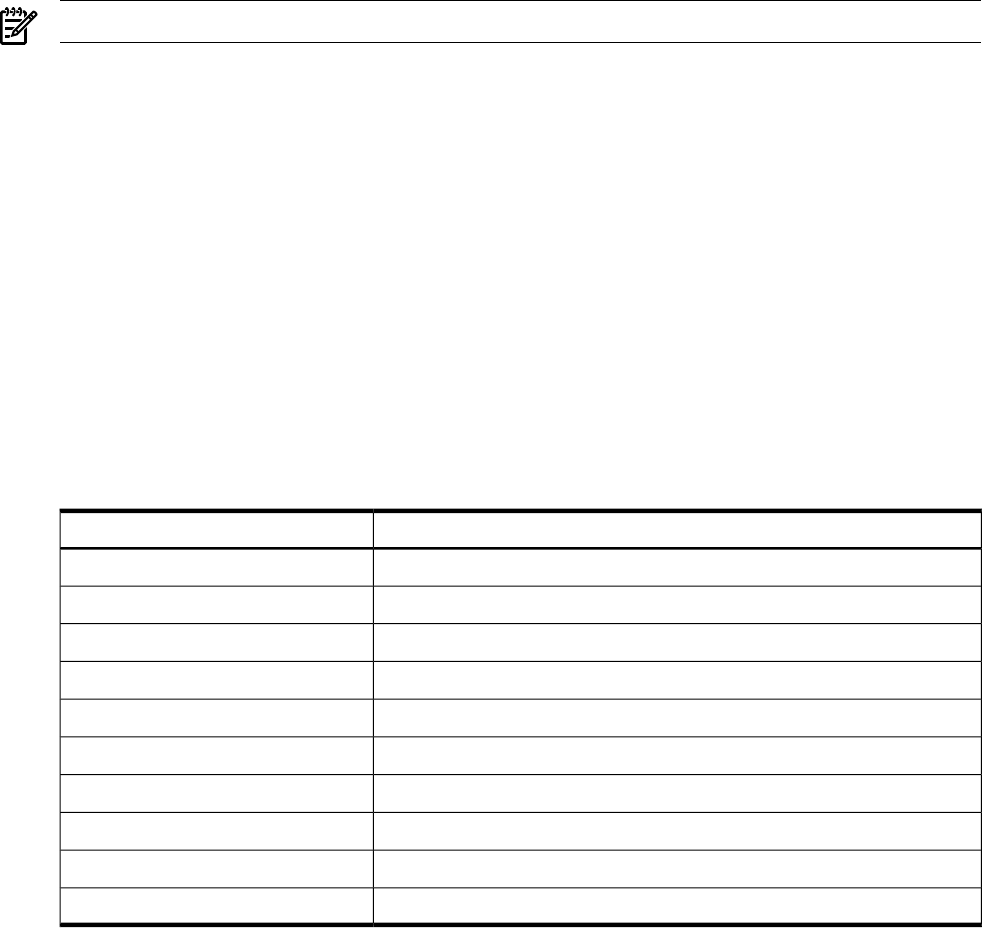
Table C-16 Service Description
DescriptionService
Password
pwd
Group
grp
Shadow Password
shd
Service
srv
Protocol
prt
RPC
rpc
Host
hst
Network
net
Netgroup
ngp
Group Membership
grm
Examples:
• An example beq command using iuser1 (user name) as the search key, pwd (password)
as the service, and ldap as the library on the 32 bit of an HP-UX 11i v1, v2 or v3 PA machine
is shown below:
./beq -k n -s pwd -l /usr/lib/libnss_ldap.1 iuser1
nss_status.............. NSS_SUCCESS
pw_name...........(iuser1)
260 Command, Tool, Schema Extension Utility, and Migration Script Reference










