Java Troubleshooting Guide for HP-UX Systems
1. Start the application with the -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote option. This option
sets the com.sun.management.jmxremote system property, which enables the JMX
agent.
2. Start jconsole with the jconsole command.
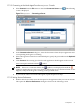
3. When jconsole starts, it shows a screen listing the managed Java VMs on the machine.
The process id (pid) and command line arguments for each Java VM are displayed. Select
one of the Java VMs, and jconsole attaches to it.
The following example shows invocation of jconsole. First the Java application must be started
with the JMX agent enabled:
$ java -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -jar Java2Demo.jar &
[1] 13028
Now the jconsole tool can be started on the managed Java VM:
$ /opt/java1.5/bin/jconsole 13028
The following figure shows a jconsole screen:
Figure 1-15 jconsole Screen
jconsole can also be run remotely. To learn more about jconsole, including remote invocation,
refer to the following webpage:
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/guide/management/jconsole.html
1.14 jdb
The SDK includes a command-line debugger, jdb, to help you find and fix bugs in Java programs
running on a local or remote Java machine. Refer to the following webpage for more information:
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/docs/tooldocs/solaris/jdb.html
A jdb tutorial can be found at:
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/javaqa/2000-06/04-qa-0623-jdb.html
1.15 jhat
Beginning with JDK 6.0, jhat is included with the standard JDK distribution. This tool can be
used for heap analysis; it is an improved version of hat. It starts a Web server on a binary-format
1.14 jdb 39